About Work Formula
The work is calculated using the work formula. Let us first define work before learning the formula. When we apply a force to an item and the thing moves, we are said to have completed work. The work done becomes 0 if the displacement in the direction of force is zero. The work formula is used to calculate the amount of effort required to move an object. The work formula is used to compute the amount of work required to move any object. The product of the applied force and the displacement in the direction of the applied force is work. The dot product of 2 vectors, force and displacement, is work. Work is thus a scalar quantity. The Joule is the SI unit of work.
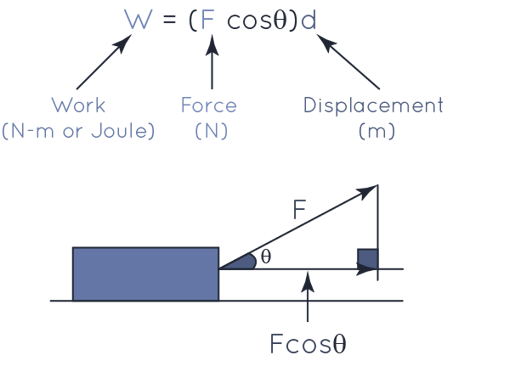
Work Formula
The formula for Work can be expressed as,
W = F.d
W = (Fcos θ)d
Where,
- W = Work done
- F = Magnitude of force applied
- d = Magnitude of displacement in the direction of the force.
- θ = Angle between vectors: force and displacement
SI unit of work - Joule (J).
1 joule of work is done - formula for work 1 J = 1 N.m
Derivation of Work Formula
Consider a block that is put on a frictionless horizontal floor and is operated upon by a constant force F, which causes it to travel a distance d in a straight line in the force's direction.
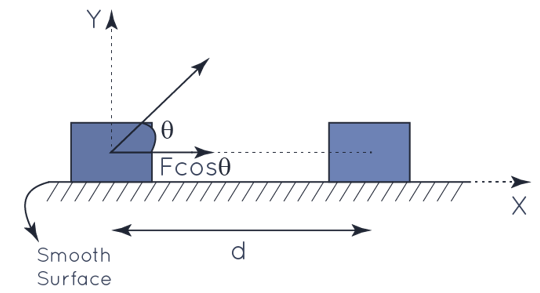
Work done by force F = to the change in kinetic energy
W = (1/2)mv2 - (1/2) mu2 = 1/2m(v2-u2)
Applying v2-u2 = 2as
W = (1/2) x m x (2as)
W = mas
Since F = ma (Newton's 2nd law), thus W = Fs. (s=d=displacement)
Now, if the effective component of force along the displacement direction is Fcos, then the work done by the force F in displacing the body through displacement d is
W=(|F|cosθ)|d|
Maths Formulas List.

