About Simple Interest
Simple interest (SI) is a method for calculating the amount of interest charged on a sum over a set period of time at a set rate. Simple interest has a constant principal, unlike compound interest, which adds the interest from previous years' principal to determine the next year's interest.
This course will introduce you to the notion of borrowing money and the simple interest that can be earned as a result of borrowing. You'll also learn about terminologies like principal, quantity, interest rate, and time period.
Simple interest is a quick and simple technique of calculating interest (I) on money. Interest is always applied to the initial principal amount under the simple interest method, with the same rate of interest for each time cycle. When we deposit money in a bank, the bank pays us interest on our investment. Banks charge various sorts of interest, one of which is simple interest. Before delving more into the concept of simple interest, it's important to grasp what a loan is.
A loan is a sum of money borrowed from a bank or other financial institution to meet one's requirements. Home loans, vehicle loans, student loans, and personal loans are all instances of loans. A loan amount must be returned to the authorities on time, along with an additional amount, which is usually the interest paid on the loan.
Simple Interest Formula
Simple interest is computed using the formula S.I. = P R T, where P is the principal, R is the annual rate of interest in per cent, and T is the time, commonly expressed in years. The interest rate is expressed in percentages and is written as r/100.
Principal: The amount that was initially borrowed from the bank or invested. P stands for the principal.
- Rate: The rate of interest at which the principal amount is delivered to someone for a specific period of time is known as the rate of interest. The rate of interest can be 15%, 20%, or 13%, for example. R stands for the rate of interest.
- Time: The principal amount is handed to someone for a specific amount of time. T stands for time.
- Amount: When a person takes out a loan from a bank, he or she is required to repay the principal plus interest, which is referred to as the Amount.
Amount = Principal + Simple Interest
- A = P + S.I.
- A = P + PRT
- A = P(1 + RT)
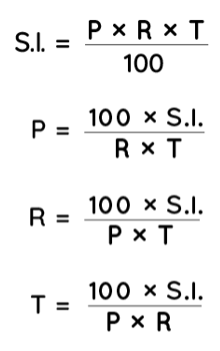
Amount(A) = Principal(P) + Simple Interest(S.I)
Simple Interest (SI) vs Compound Interest (CI)
The two methods for calculating interest on a loan amount are simple interest and compound interest. Compound interest is thought to be more difficult to compute than the simple interest due to some fundamental distinctions between the two.
| Simple Interest | Compound Interest |
| Every time, simple interest is calculated on the original principal amount. | The accumulated amount of principal and interest is used to compute compound interest. |
| S.I.= P × R × T | C.I.= P × (1+r)t - P |
| It is the same for each year on a fixed principal. | It is different for each time period because it is based on the amount rather than the principal. |
Check out the list of Maths formulas prepared by the experts of Home tution.com