About Axis of the Symmetry
The axis of symmetry is the hypothetical straight line which divides a shape into two identical portions, one of which is the mirror image of the other. The two sections are overlaid when folded along the symmetry axis. The symmetry line, also known as the mirror line, is a straight line. This line might be straight, slanted, or vertical.
What is the Axis of Symmetry?
A symmetry axis is a straight line that makes an object's shape symmetrical. On each of its sides, the axis of symmetry creates identical reflections. It might be horizontal, vertical, or lateral in nature. The 2 sides of an object are identical when folded and unfolded along the axis of symmetry. Different forms have many symmetry lines. A square has 4 symmetry lines, a rectangle has 2 symmetry lines, a circle has infinite symmetry lines, & a parallelogram has none. Regular polygon which has n sides has n symmetry axes.
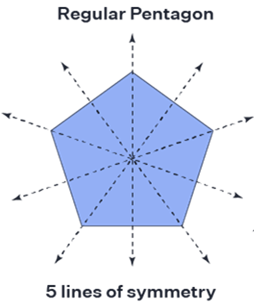
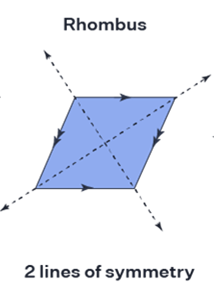
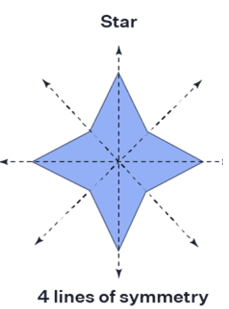
Axis of Symmetry Definition
The axis of symmetry is a hypothetical line that divides a figure into two identical sections, each of which is a mirror image of the other. The two identical parts of the figure superimpose when folded along the axis of symmetry.
Axis of Symmetry of a Parabola
A parabola has only one symmetry line. The straight line which divides a parabola into two symmetrical pieces is the axis of symmetry. The parabola can take four different shapes. It might be horizontal or vertical, & it can face left or right. The parabola's shape is determined by its symmetry axis.
Parabola is vertical (opens up/down) if the axis of symmetry is vertical.
The parabola is horizontal (opens left/right) if it is horizontal.
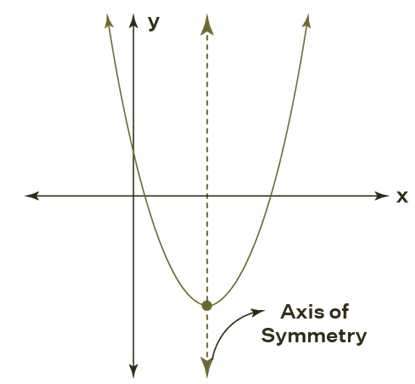
The axis of symmetry that is horizontal has zero slopes, and the axis of symmetry which is vertical has an undefined slope.
Axis of Symmetry Equation
The vertex is the point on the parabola where the axis of symmetry crosses. This is the most important factor in determining the equation. The axis of symmetry of a parabola that expands up or down is vertical, and its equation is the vertical line which passes through its vertex in this case. The axis of symmetry is horizontal if the parabola opens right or left, and the equation is the horizontal line which passes through its vertex. i.e.,
A parabola whose vertex is (h, k) and opens up/down has an axis of symmetry equation of
x = h.
A parabola vertex is (h, k) and opens left/right has an axis of symmetry equation of
y = k.
Axis of Symmetry Formula
When using the conventional form of the equation and the line of symmetry, the axis of symmetry formula is applied to quadratic equations. Axis of symmetry is the line that divides or bifurcates any object into two equal halves, both of which are mirror images of each other. This axis that divides the objects could be one of three types: horizontal (x-axis), vertical (y-axis), or inclined line.
When a parabola is in two forms, the equation for the axis of symmetry can be represented:
- Standard form & 2. Vertex form
Standard form
The quadratic equation is in standard form, y = ax2+ b x+c
where a, b, & c are real numbers.
Here, axis of symmetry formula : x = - b/2a.
Vertex Form
The quadratic equation vertex form, y = a (x-h)2 + k
where (h, k) vertex of the parabola.
Here, the Axis of symmetry formula is x = h.
To get all the Maths formulas check out the main page.



