Distance Formula
As the name implies, any distance formula calculates the distance (the length of the line segment). The length of the line segment connecting two places, for example, is the distance between them. The Pythagoras theorem is used to obtain the distance formula between two points in a two-dimensional plane, which may also be extended to find the distance between two points in a three-dimensional plane. In coordinate geometry, there exist various distance formulas:
- In 2-D plane, the distance between two points.
- The distance between two points in a 3-D plane.
What is the distance formula?
In coordinate geometry, we have a list of distance formulas that may be used to find the distance between two points, the distance between two parallel lines, the distance between two parallel planes, and so on. The distance formulas are listed below, and we'll go through each one separately in the following sections.
Calculate of the distance between two points using the distance formula
The distance between two points in a 2-D plane and 3-D space will be demonstrated. The Pythagoras theorem is used to derive both distance formulas.
Distance between Two Points in 2D
The Euclidean distance formula is a distance formula that is used to find the distance between two locations in a two-dimensional plane. Consider two locations in the 2D plane A (x1,y1) and B (x1,y2) to obtain the formula (x2,y2). Assume the distance between A and B is d.
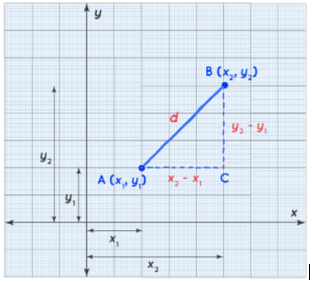
Derivation of distance formula
By the Pythagoras theorem,
AB2 = AC2 + BC2
d2 = (x2 – x1)2 + (y2 – y1)2
Taking square root on both the sides,
d = √ [(x2 – x1)2 + (y2 – y1)2]
This is distance between two points.
Distance between two points in 3D
Distance formula for 2 points in the 3-D plane, let us consider two points in a three-dimensional plane A (x1,y1,z1) and B(x2,y2,y3). Let 'd’ be the distance between A and B. By applying the same logic (as explained in the previous section) of finding the distance between two points in 2D, the distance between two points in 3D is,
d = √ [(x2 – x1)2 + (y2 – y1)2 + (z2 – z1)2]

