About Exponential Function
The exponential function is a type of mathematical function that can be used to calculate the growth or decay of a population, money, price, or any variable that grows or decays exponentially. Jonathan was reading a news piece about the most recent bacterial growth study. He learned that a single microbe was used in an experiment. The bacterium had doubled in size after the first hour and was now two in number. The number was four after the second hour. The number of microorganisms was increasing by the hour. If this pattern continued, he wondered how many bacteria there will be after 100 hours. When he asked his teacher about it, he was given the concept of an exponential function as a response. Get the list of Maths Formulas.
What is Exponential Function?
Exponents are used in exponential functions, as the name implies. It's worth noting, though, that an exponential function has a constant as its base and a variable as its exponent, not the other way around (if a function has a variable as the base and a constant as the exponent then it is a power function but not an exponential function). The following are the several types of exponential functions.
Exponential Function Definition
An exponential function in mathematics is one of the form f (x) = axe, where "x" is a variable and "a" is a constant that serves as the function's base and should be bigger than 0.
An exponential function can be in one of the following forms:
→ f(x) = bx
→ f(x) = abx
→ f(x) = abcx
→ f(x) = ex
→ f(x) = ekx
→ f(x) = pekx
Here b>0 and b ≠ 1
Exponential Function Examples
- f(x) = 2x
- f(x) = (1/2)x
- f(x) = 3e2x
- f(x) = 4(3)-0.5x
Exponential Function Formula
The definition of a basic exponential function is f(x) = bx, where 'b' is a constant and 'x' is a variable. f(x) = ex, where 'e' is "Euler's number" & e = 2.718, is a popular exponential function.... If we broaden the scope of distinct exponential functions, we can include a constant that is a multiple of the variable in its power. f(x) = ekx is another example of an exponential function. It can also have the shape of f(x) = p ekx, where 'p' is a constant. An exponential function can therefore take one of the following shapes.
- f(x) = bx
- f(x) = abx
- f(x) = abcx
- f(x) = ex
- f(x) = ekx
- f(x) = pekx
All letters except 'x' are constants, 'x' is a variable, and f(x) is an exponential function in terms of x. It's also worth noting that any exponential function's base must be a positive number. b > 0 and e > 0 in the above functions, for example. Also, b should not equal 1 (if b = 1, the function f(x) = bx becomes f(x) = 1, and the function is linear but NOT exponential in this case).
When the value of a quantity increases in exponential growth and drops in exponential decay, the exponential function appears. In the table below, we can observe further differences between exponential growth and decay, as well as their formulas.
| Exponential Growth | Exponential Decay |
| In exponential growth, a quantity increases slowly at first before rapidly increasing. | In exponential decay, a quantity drops fast at first, then gradually. |
| The exponential growth formulas are used to simulate population expansion, compound interest, doubling time, and other things. | The exponential decay can be used to represent population decay, calculate half-lives, and so on. |
| In exponential growth, the graph of the function is rising. | In exponential growth, the graph of the function is decreasing. |
In exponential growth, the function can be of the form:
|
In exponential decay, the function can be of the form:
|
In the above formulas,
- a (or) P00 = Initial value
- r = Rate of growth
- k = constant of proportionality
- x (or) t = time (time can be in years, days, (or) months. Whatever we are using should be consistent throughout the problem).
Exponential Series
ex=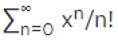 = (1/1) + (x/1) + (x2/2) + (x3/6) + ......
= (1/1) + (x/1) + (x2/2) + (x3/6) + ......
Expansion of some other exponential functions are given as shown below,
e =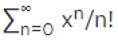 = (1/1) + (1/1) + (1/2) + (1/6) + ....
= (1/1) + (1/1) + (1/2) + (1/6) + ....
e-1 =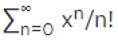 = (1/1) - (1/1) + (1/2) - (1/6) + ....
= (1/1) - (1/1) + (1/2) - (1/6) + ....
Exponential Function Rules
- Law of the Zero Exponent: a0 = 1
- Law of the Product: am x an = am+n
- Law of the Quotient: am/an = am-n
- Law of the Power of a Power: (am)n = amn
- Law of Power of a Product: abm = ambm
- Law of the Power of a Quotient: (a/b)m = am/bm
- Law of the Negative Exponent: a-m = 1/am
Apart from that, we may need to utilise the logarithmic to exponential form conversion formula, which is:
- bx = a ⇔ logb a = x
Equality Property of Exponential Function
If two exponential functions with the same bases are equal, their exponents are likewise equal, according to the equality property of exponential functions. i.e.,
Bx1 = Bx2 ⇔ x1 = x2
Exponential Function Graph
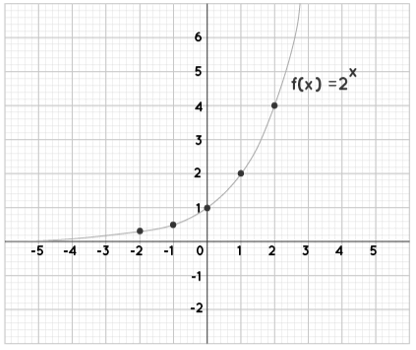
Using several examples, we may better comprehend the process of charting exponential functions. Consider the graphs of two functions, f(x) = 2x and g(x) = (1/2)x. We'll make a table of values with some random x values, plot the points on the graph, connect them with a curve, and extend the curve on both ends to graph each of these functions.
f(x) = 2x
| x | f(x) |
| -2 | 0.25 |
| -1 | 0.5 |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 |
2-2= 1/4 = 0.25
2-1= 1/2 = 0.5
20= 1
21= 2
22= 4
g(x) = (1/2)x.
| x | g(x) |
| -2 | 4 |
| -1 | 2 |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 0.25 |
(1/2)-2= 22 = 0.25
(1/2)-1= 21 = 2
(1/2)0= 1
(1/2)1= 1/2 = 0.5
(1/2)2= 1/4 = 0.25
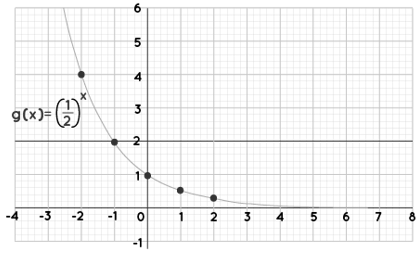
Note: We can see that f(x) = 2x is increasing while g(x) = (1/2)x is dropping in the two graphs above. As a result, the exponential function f(x) = bx graph.
increases when b > 1
decreases when 0 < b < 1
Domain and Range of Exponential Function
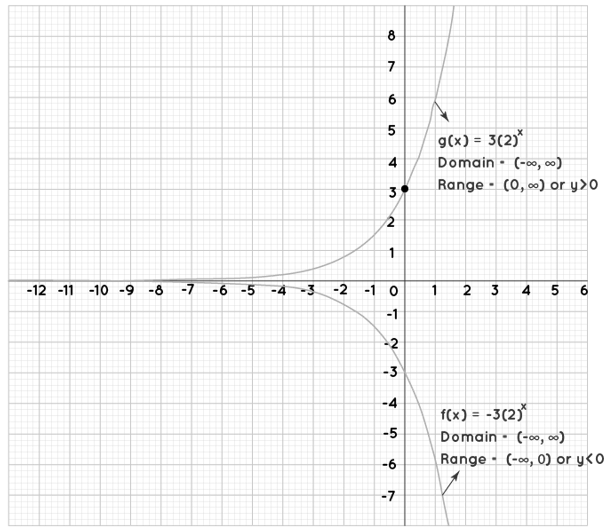
The domain of a function y = f(x) is set of all x-values (inputs) for which it can be computed, whereas the range is the set of all y-values (outputs). We can see that an exponential function may be constructed at any value of x from the graphs of f(x) = 2x and g(x) = (1/2)x in the preceding section. An exponential function's domain is thus the set of all real numbers (or) (-∞, ∞). The horizontal asymptote of graph, say y = d, and whether the graph is above or below y = d can be used to calculate the range of an exponential function. As a result, if f(x) = abx is an exponential function
- Domain is set of all the real numbers (or) (-∞, ∞).
- Range is f(x) > d if a > 0 & f(x) < d if a < 0.
Example:-
Exponential Function Derivative
- d/dx (ex) = ex
- d/dx (ax) = ax · ln a.
Integration of Exponential Function
- ∫ ex dx = ex + C
- ∫ ax dx = ax / (ln a) + C