About Unit Circle
A unit circle is defined as a circle with a radius of one unit. A circle is a closed geometric form that has no angles or sides. The unit circle has all of the features of a circle, and its equation is derived from a circle's equation. A unit circle can also be used to calculate the standard angle values of all trigonometric ratios.With the use of trigonometric ratios of cos and sin, we will learn the equation of the unit circle and how to represent each point on the circumference of the unit circle. Get the List of all Maths formulas in one place.
What is Unit Circle?
A unit circle is defined as a circle with a radius of one unit. The cartesian coordinate plane is commonly used to depict the unit circle. The second-degree equation with two variables x and y is used to represent the unit circle algebraically. The unit circle is used in trigonometry to obtain the values of trigonometric ratios such as sine, cosine, and tangent.
Unit Circle Definition
A unit circle is defined as the locus of a point that is one unit away from a fixed point.
Equation of a Unit Circle
A circle's general equation is (x - a)2 + (y - b)2 = r2, which depicts a circle with the centre (a, b) and radius r. This circle equation is simplified to illustrate a unit circle equation. With its centre at (0, 0), the origin of the coordinate axes, and a radius of 1 unit, a unit circle is constructed. As a result, the unit circle's equation is (x - 0)2 + (y - 0)2 =1 2. The equation of a unit circle is obtained by simplifying this.
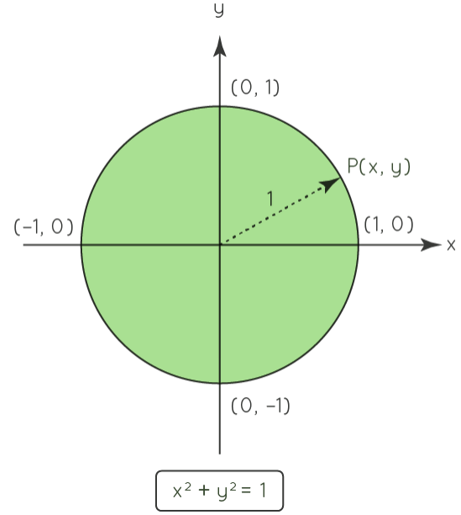
Equation of the Unit Circle: x2 + y2 = 1
The centre of the unit circle is (0,0), and the radius is 1 unit. All of the locations on the circle in the four quadrants satisfy the above equation.
Finding Trigonometric Functions Using a Unit Circle
A unit circle can be used to calculate the trigonometric functions of sine, cosine, and tangent. To comprehend trigonometric functions, use the Pythagoras theorem in a unit circle. Consider a right triangle in the cartesian coordinate plane, which is centred on a unit circle. The hypotenuse of a right triangle is represented by the circle's radius. The radius vector forms an angle with the positive x-axis, and the radius vector's endpoint coordinates are (x, y). The lengths of the base and altitude of the right triangle are represented by the values of x and y. With the sides 1, x, and y, we now have a right angle triangle. We may obtain the values of the trigonometric ratio by using this in trigonometry.
- sinθ = y/1 = Altitude / Hypoteuse
- cosθ = x/1 = Base / Hypotenuse
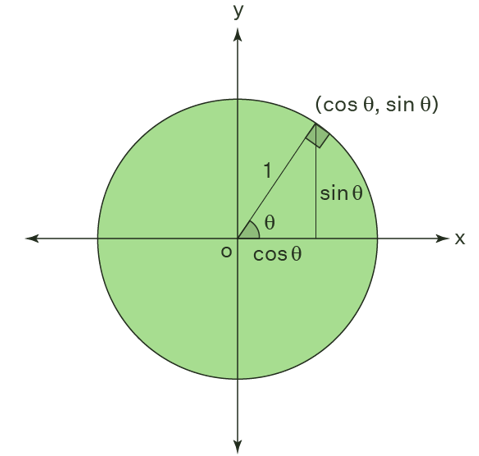
We now have sin = y and cos = x, and we can use this to get tan = y/x. Similarly, the right-angled triangle within the unit circle can be used to find the values of the other trigonometric ratios. We can also get the principal values of these trigonometric ratios by modifying the values.
Unit Circle with Sin Cos and Tan
The coordinates(x, y) of any point on the unit circle are equivalent to the trigonometric identities (cos, sin). The cosine and sine of any values made by the radius line with the positive x-axis are represented by the coordinates of the endpoint of the radius. We have cos = x and sin = y, which are useful in calculating the other trigonometric ratio values. By extending this, we get tan = sin/cos or tan = y/x.
Another key element to remember is that the sin and cos values are always between 1 and -1, and the radius value is 1, with a negative x-axis value of -1. The full circle symbolises a 360o angle, while the circle's four quadrant lines indicate 90°, 180°, 270°, and 360° (0). Because the cos value is 0 for 90 and 270, the tan values at these angles are indeterminate.
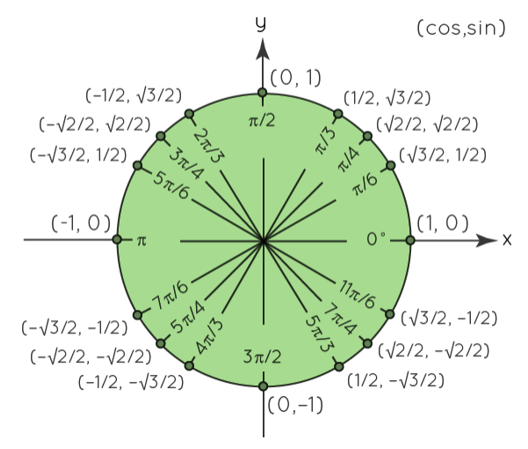
Unit Circle Chart in Radians
A complete angle of 2π radians is represented by the unit circle. And the unit circle is divided into four quadrants by angles of π/2, 3π/2, and 2π. The standard values, which are appropriate to trigonometric ratios, are further within the first quadrant at the angles of 0, π/6,π/4,π/3,π/2. The standard angle values of the cosine and sine ratios are represented by the points on the unit circle for these angles. The values are repeated across the four quadrants, but with a change in sign, as seen in the diagram below. The reference x-axis and y-axis, which are positive on one side and negative on the other, account for the change in sign.
Unit Circle and Trigonometric Identities
Other trigonometric identities such as cotangent, secant, and cosecant can be obtained using the unit circle identities of sine, cosecant, and tangent. The reciprocal of the sine, cosine, and tangent are the unit circle identities cosecant, secant, and cotangent. Furthermore, we may calculate the value of tanθ by dividing sinθ by cosθ, and the value of cotθ by dividing cosθ by sinθ.
The unit circle identities for a right triangle set in a unit circle in the cartesian coordinate plane with hypotenuse, base, and altitude measuring 1, x, and y units respectively can be written as,
- sinθ = y/1
- cosθ = x/1
- tanθ = sinθ/cosθ = y/x
- sec(θ = 1/x)
- csc(θ) = 1/y
- cot(θ) = cosθ/sinθ = x/y
cot(θ) = cosθ/sinθ = x/y
- 1=sin2θ + cos2θ
- sec2θ =1 + tan2θ
- cosec2θ=1 + cot2θ
Unit Circle and Trigonometric Values
A unit circle can be used to compute the various trigonometric identities and their principal angle values. The x-coordinate of the unit circle is cosine, while the y-coordinate is sine. Let us now calculate their respective values for θ = 0° and θ = 90°.
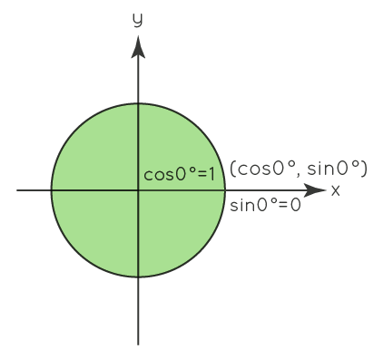
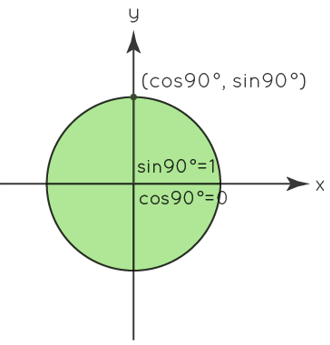
For θ = 0°, 1 is the x-coordinate, while 0 is the y-coordinate. As a result, cos0 equals 1 and sin0 equals 0. Let's take a look at another 90 angle. Here, cos90 equals 0 and sin90 equals 1. Let us now use this unit circle to calculate key trigonometric function values such as 30, 45, and 60. These values can also be expressed in radians. We know that 360 degrees equals 2 radians. We can now transform angular measurements to radian measurements and express them in radians.
Unit Circle Table???????
| Angle θ | Radians | Sinθ | Cosθ | Tanθ = Sinθ/Cosθ | Coordinates |
| 0° | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | (1,0) |
| 30° | π/6 | 1/2 | √3/2 | 1/√3 | (√3/2, 1/2) |
| 45° | π/4 | 1/√2 | 1/√2 | 1 | (1/√2, 1/√2) |
| 60° | π/3 | 1/2 | 1/√2 | √3 | (1/2, √3/2) |
| 90° | π/2 | 1 | 0 | Undefined | (0,1) |
- secθ = 1/cosθ
- cosecθ = 1/sinθ
- cotθ = 1/tanθ
Unit Circle in Complex Plane
A unit circle consists all complex numbers of absolute value as 1. Therefore, it has the equation of |z| = 1. Complex number z = x + iy will lie on unit circle with equation given as x2 + y2 = 1.
In a complex plane, the unit circle can be thought of as a set of unit complex numbers z provided by the form,
z = e^it = cos t + i sin t = cis (t)
Euler's formula is represented by the above relationship.





