What is Acid Rain?
Acid Rain it’s a chemistry reason to find the details harmful effects of Acid Rain, acid rain is more acidic in nature having acidic than normal with a pH ranging between (5.6 and 3.5).
What is ACID RAIN
Rain occurs when vapours condense in clouds & fall to earth. As it begins to fall, it is neutral (pH = 7). While it travels through the air, it dissolves floating chemicals & washes down the particles that are suspended in the air. These substances make the rain slightly acidic (pH = 6). This level of acidity is not dangerous.
However, when the rain falls through polluted air, it comes across chemicals such as gaseous oxides of sulphur (SOx), oxides of nitrogen (NOx), mist of hydrochloric acids & phosphoric acid etc. These substances dissolve in falling rain making them more acidic than normal with a pH ranging between (5.6 and 3.5).
Also Check: Baking Soda | Epsom salt | Glucose | Amino Acids
Related Links: Periodic Table Element | Metal | Electogravity
Chemistry of acid rain
Natural processes such as volcanic eruption, forest fires & biological decomposition of organic matter produce oxides of sulphur & nitrogen.
Man-made sources such as power plants, smelting plants, industrial plants, and the burning of coal & gasoline also release SO2, nitrogen oxides & acidic soots. Sulphur dioxide & nitrogen dioxide interact with water vapours in presence of sunlight to form sulphuric acid & nitric acid units.
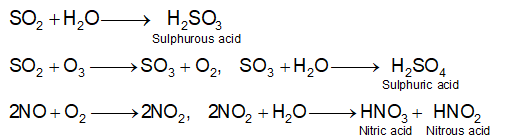
The harmful effect of acid rain
- Damage to animals: Most aquatic animals can not survive when the pH is less than 4. Certain fishes die even when the pH is less than 5.5.
- Damage to plants: Acidic water is dangerous for plants because leaf pigments are decolourised, and acid affects the green pigments of plants. Agricultural productivity is also decreased.
- Material Damage: Metallic surfaces exposed to acid rain are readily corroded. Textile fabrics, paper & leather products lose their material strength or disintegrate the acid rain.
Important points related to acid Rain
- Oxidation of sulphur in fossil fuels mainly produces SO2 and SO3 which are harmful. These gases react with water to form sulphuric acid. The acids, when precipitated as rain or snow, create acid rain.
- SO2 (oxidized) -> SO3 + H2O -> H2SO4
- NOX (oxidized) -> NO2 + H2O -> HNO3
- Acid rain damages buildings and statues of limestone.
- Acid rain is also harmful to some aquatic forms.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Why does rainwater have a pH of about 5 – 6?
Sol. Normally rain has a pH of about 5 – 6 due to the dissolution of the atmosphere into it.
Q2. When rain is considered to be acid rain?
Sol. When the pH of rain falls below 5 – 6, it becomes acid rain.
Q3. Why is acid rain considered a threat to the ‘Taj Mahal?
Sol. The Taj Mahal is made of marble. The acid rain contains which attacks the marble thereby pitting it, decolourising it and making it lustreless.
Q4. Which acids are present in acid rain?
Sol. H2SO4, HNO3 and HCl.
Q5. What is the harmful effect of acid rain?
Sol. Most aquatic animals can not survive when the pH is less than 4. Certain fishes die even when the pH is less than 5.5.
- Acidic water is dangerous for plants because leaf pigments are decolourised, and acid affects the green pigments of plants. Agricultural productivity is also decreased.
- Metallic surfaces exposed to acid rain are readily corroded. Textile fabrics, paper & leather products lose their material strength or disintexamplerate by acid rain.