What is Chemical Reaction
Chemical changes involve the breaking of bonds between the atoms of the reactants and the formation of bonds between the atoms of the products.
A few common examples of chemical changes are: rusting of iron, souring of milk, fermentation of grapes, cooking of food and its digestion inside our body, respiration, burning of L.P.G in a burner etc.
The chemical changes are represented by chemical equations.
In a chemical reaction, reactants are transformed into products. The products thus formed have properties which are entirely different from those of the reactants. Thus Chemical reactions represent changes of reactants into products.
Also Check: Baking Soda | Epsom salt | Glucose | Amino Acids
Related Links: Periodic Table Element | Metal | Electogravity
Characteristics of Chemical Reactions
- There is generally a change in color of the reacting species taking part in the change.
- Some chemical reactions are characterized by change in state.
- In some cases, a gas may be evolved. For example, Hydrogen gas is evolved when granules of zinc react either with dilute hydrochloric acid or with dilute sulphuric acid.
![]()
- In most of the chemical changes, the temperature also undergoes a change.
- The chemical change is of permanent nature and cannot be easily reversed.
- Some chemical reactions are characterized by the formation of a precipitate. For example:
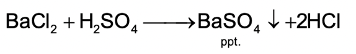
- There are some chemical reactions which can show more than one characteristic.For example, the chemical reaction between zinc granules and dilute sulphuric acid shows two characteristics: the evolution of a gas (hydrogen gas) and a change in temperature (rise in temperature).
Exothermic and endothermic reactions
- There are two types of reactions on the basis of heat changes involved: exothermic reactions and endothermic reactions.
Exothermic Reactions: Those reactions in which heat is evolved are known as exothermic reactions. For example, The burning of carbon in oxygen is an exothermic reaction because heat is evolved in this reaction.
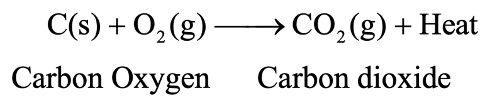
An exothermic reaction is indicated by writing “+ Heat” or “+ Heat energy” or just “+ Energy” on the products’ side of an equation. (as shown in the above equation).
Note:All the combustion reactions are exothermic reactions.
- If energy needed in the bond breaking in the reactants is less than the energy released when new bonds are formed resulting in products, the chemical reaction is of exothermic nature.
Endothermic Reactions: Those reactions in which heat is absorbed are known as endothermic reactions.
For example
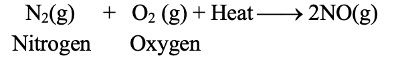
The reaction between nitrogen and oxygen to form nitrogen monoxide is an endothermic reaction because heat is absorbed in this reaction. An endothermic reaction is usually indicated by writing “+ Heat” or “+ Heat energy” or just “+ Energy” on the reactant side of an equation (as shown in the above equation).
Important Points about Chemical Reactions
The different types of reactions are: combination reactions, decomposition reactions, displacement reactions and redox reactions.
- Reaction in which two or more substances combine to form another compound are combination reactions.
- Reactions in which a compound breaks up into simple substances are decomposition reactions.
- Reactions in which an atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms are displacement reactions.
- Reactions in which two compounds react to form two other compounds by mutual exchange of their ions are double displacement reactions.
- Oxidation is a process which involves addition of oxygen or removal of hydrogen. According to electronic concept, oxidation is a process which involves loss of electrons.
- Reduction is a process which involves addition of hydrogen or removal of oxygen. According to electronic concept, reduction is a process which involves gain of electrons.
- Oxidising agent is a substance which gives oxygen or removes hydrogen and causes oxidation of other substances. It gets itself reduced.
- Reducing agent is a substance which gives hydrogen or removes oxygen and causes reduction of other substance. It gets itself oxidised.
- Irreversible reaction is that which reaches to completion.
- Reversible reaction is that which do not reaches upto completion and occur in both directions.
- At equilibrium state both opposing process takes place with equal rates.
- Rate of reaction depends upon the active masses of reactants.
- Any change in the state of equilibrium leading with equilibrium.
Frequently Asked Questions
Chemical reactions are processes where substances change to form new substances with different properties.
Chemical reactions are when substances combine or break apart to form new substances.
A chemical reaction is when two or more substances react to form different substances. For example, burning wood is a chemical reaction where wood and oxygen react to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Chemical reactions involve the transformation of substances into new substances through chemical bonds breaking and forming.
A simple chemical reaction is when two substances mix and a new substance is formed, like when vinegar and baking soda mix to produce carbon dioxide gas
The four main types of chemical reactions are synthesis (combination), decomposition, single displacement, and double displacement reactions.