Definition of Metals
Though there are millions of substances in this world, they are all made up of a limited number of basic substances, which are called elements.
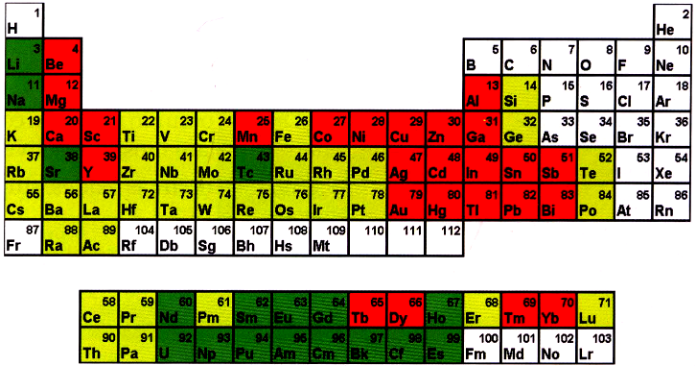
You have already studied elements as being pure substances that each are made up of one kind of atom only. For the convenience of study, these elements are divided into two broad classes: Metals and non-metals. This division of elements is based on the fact that there are certain properties that are found only in metals and certain others that are found only in non-metals. But, there are also some elements that show the properties of both metals and non-metals. They are known as metalloids. Some common metalloids are arsenic, antimony and silicon. The noble (inert) gases from the fourth category of elements. The majority of the elements known to us are metals. For example gold, silver, platinum, copper, iron aluminium, tin, nickel chromium, mercury, calcium, magnesium, lithium, sodium, potassium, zinc, and many more.
Also Check: Baking Soda | Epsom salt | Glucose | Amino Acids
Related Links: Periodic Table Element
Electropositive or electronegative nature of Metal
From the electronic viewpoint, metals are defined as elements which form positive ions by losing electrons. They contain 1, 2 or 3 valence electrons. For example, a sodium atom loses 1 electron, a calcium atom loses 2 electrons and an aluminium atom loses 3 electrons, to form the respective positively charged ions (Na+1, Ca+2, Al+3).
Non-metals-They is defined as elements which form negative ions by gaining electrons. They contain 5, 6 or 7 valence electrons. For example, chlorine contains 7 valence electrons and gains 1 electron to form a negatively charged chloride ion (Cl–1). Oxygen contains 6 valence electrons and gains 2 electrons to form the negatively charged oxide ion (O–2).
Occurrence of metals
Minerals: In nature, most metals occur in the combined state as minerals. Nearly all rocks contain some metallic minerals.
Ore: The amount of metal present in the rock is so little that it is too expensive to mine these rocks and extract the metals from them. If the amount of metal is more, it is profitable to mine the rocks and extract the metal. Such rocks are called ores.
Gangue: In ores, the useful metallic mineral is mixed with other minerals which are not of much use. These minerals, present as impurities, are called gangue (pronounced as 'gang').
Noble Metals: Some metals, such as silver, platinum and gold, are not very reactive. They occur in the free state in nature. Their ores contain particles of metals mixed with large quantities of impurities. They are known as noble metals.
Ores of Reactive Metals: The ores of very reactive metals, such as sodium or calcium, contain chlorides or carbonates of the metals, for example, rock salt (NaCl), dolomite (CaCO3 · MgCO3).
Ores of Less Reactive Metals: The ores of other metals, such as aluminium, iron, copper or zinc, contain mostly oxides or sulphides, for example, bauxite (Al2O3), iron pyrite (FeS2), hematite (Fe2O3), copper glance (CuS), and zinc blende (Zns).
Metallurgy: The series of processes carried out to extract pure metals from their ores is called metallurgy.

Some metals
Physical properties of metals
The important physical properties of metals are discussed below :
(i) Physical State: All metals (except mercury and gallium) are solids at room temperature. Mercury, gallium (at 300C), caesium and francium occur in liquid state in nature.

Liquid Metal: Mercury
(ii) Metals are malleable: Metals are generally malleable. This means that the metals can be beaten with a hammer into very thin sheets without breaking. This property of metals is called malleability. Gold and silver are among the best malleable metals. Aluminium and copper are also highly malleable metals. All metals are not malleable. e.g. sodium, potassium & calcium are not malleable.

Sodium can be easily cut with a knife
(iii) Metals are ductile : It means that metals can be drawn (stretched) into thin wires. This property of metals is called ductility. Gold and silver are the most ductile metals. Copper, aluminium and tungsten are also very ductile, and therefore, these can be drawn into thin wires which are used in electrical wiring. Metals like Na, K, Ca etc. are not ductile, while metals like Sn. Pb etc. are less ductile.
(iv)Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity : All metals are good conductors of heat and electricity. The ability of metals due to which they allow electric current and heat to pass through them is called electrical and thermal conductivity respectively. Silver is the best conductor of heat. Copper and aluminium are also good conductors of heat and therefore, they are used for making household utensils. Lead is the poorest conductor of heat. Mercury metal is also a poor conductor of heat.
The electrical and thermal conductivities of metals are due to the presence of free electrons in them. Among all the metals, silver is the best conductor of electricity. Copper and aluminium are the next best conductors of electricity. Since silver is expensive, therefore, copper and aluminium are commonly used for making electric wires.
(v) Metals are lustrous and can be polished : Most of the metals have metallic lustre (shine) and they can be polished. The shining appearance of metals is also known as metallic lustre. For example, gold, silver and copper metals have metallic lustre.
(vi) Metals have high densities : Most of the metals are heavy and have high densities. 'For example, the density of mercury metal is very high (13.6 g cm-3). However, there are some exception. Sodium, potassium, magnesium and aluminium have low densities. Densities of metals are generally proportional to their atomic masses.
The smaller the metal atom, the lesser is its density.OSMIUM has maximum density (22 g cm-3) among all elements.
(vii) Metals are hard : Most of the metals are hard, but all metals are not equally hard.Metals like iron, copper, aluminium etc. are quite hard. They cannot be cut with a knife. Sodium and potassium are common exceptions which are soft and can be easily cut with a knife.
(viii) Metals have high melting and boiling points: Of metals Most of the metals (except sodium and potassium) have high melting and boiling points.
(ix) Metals are rigid: Most of metals are rigid and they have high tensile strength.
(x) Metals are sonorous: Most of the metals are sonorous i.e., they make sound when hit with an object.
(xi) Colour: Most metals are white or silvery-grey in colour. Exceptionally, gold is yellow (yellow metal) and copper is reddish-brown.
Chemical properties or characteristics of metals
The chemical properties of the metals are determined by their:
Electronic configuration
(ii) valency
(ii) reducing nature.
(i) Electronic configuration of metals: The distribution of electrons in the orbits (energy shells) of the atom of an element is known as the electronic configuration of that atom/element.
A metal has 1 or 2 or 3 electrons in its valence shell. These valence electrons are easily lost during chemical combination.
(ii)Valency: Valency refers to the number of electrons that are lost or gained by an atom during chemical combination. Metals have valencies +1 or + 2 or +3. They lose their valence electron during chemical combination to form cations (Positive ions).
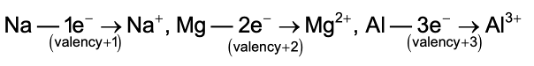
(iii) Reducing nature: Since metals lose their valence electrons, so they are good reducing agents.
Reaction of metals with oxygen
(i) In the presence of heat, most metals react with oxygen (or air) to form their respective oxides. These metallic oxides are of a basic nature. Therefore they are known as basic oxides. Basic oxides form salt and water when they react with acids.
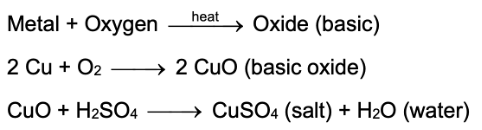
(ii) On the other hand, metals like sodium and potassium react vigorously with oxygen (even in the absence of heat) to form their respective oxides.
Calcium too forms its oxide without being heated. The metallic oxides so formed being soluble in water, they form their respective metallic hydroxides, which are called alkalis. They turn red litmus (an indicator) blue.
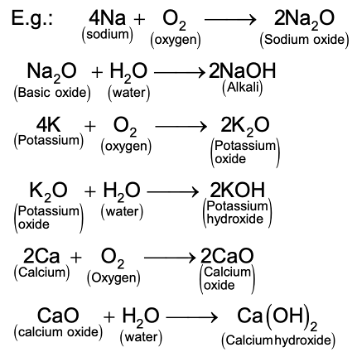
Note: Alkalis are soluble bases. All alkalis are bases but all bases are not alkalis. This is because all bases are not soluble in water.
(iii) Metals like magnesium, aluminium, zinc, iron, lead, copper and mercury react with oxygen on heating to from oxides that are basic in nature but insoluble in water, i.e., they are not alkaline [but magnesium hydroxide is alkaline in nature].
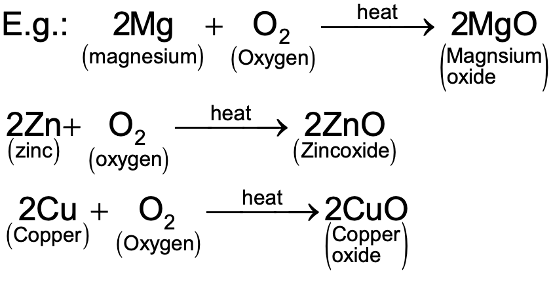
Metals like silver, gold and platinum do not react with oxygen even on strong heating. Therefore they are called noble metals.
Reaction of metals with water
Depending upon their level of reactivity, metals react with water or steam to form their corresponding metallic hydroxides or oxides, along with hydrogen gas.
(i) Metals like sodium and potassium react violently with cold water to form their hydroxides as well as hydrogen gas.
The reaction is so vigorous that a fire or an explosion can occur. Calcium too reacts with cold water to from its hydroxide and hydrogen, but the reaction is a moderate one
Reactivity series of metals :
(a) The more reactive metals always displace less reactive metals in chemical reactions. If a metal loses electrons easily to form positive ions, it will readily react with other substances. On the other hand if a metal loses electrons less rapidly to form a positive ion, it will react slowly with the other substances. Such a metal will be less reactive.
The arrangement of metals in the order of decreasing reactivities is called thereactivity series or activity series of metals.
It may be noted that hydrogen is not a metal, but even then it has been placed in the reactivity series. This is due to the fact that :
(i) Hydrogen can also lose electron and form positive ion, H+.
(ii) Hydrogen has also been included in the series to compare the reactivities of metals with respect to it.The more reactive nature of iron as compared to copper can be easily shown by dipping some iron nails in the solution of copper suphate. The iron nails get covered with copper layer and the blue colour of copper sulphate solution change to greenish colour of ferrous sulphate