The Étard reaction is a chemical process where an aromatic or heterocyclic methyl group is changed directly into an aldehyde using chromyl chloride. For instance, toluene can be turned into benzaldehyde this way. The reaction is named after the French chemist Alexandre Léon Étard (5 January 1852, Alençon – 1 May 1910).
What is Etard Reaction Mechanism
The Etard reaction is a chemical process used to selectively oxidize an aromatic methyl group (attached to a benzene ring) to an aldehyde. This reaction is particularly useful in organic chemistry for synthesizing benzaldehyde derivatives.
The Etard reaction involves the oxidation of a methyl group (-CH3) on an aromatic ring to a formyl group (-CHO). This is done using chromium trioxide (CrO3) in the presence of hydrochloric acid (HCl), typically within a solvent like carbon tetrachloride (CCl4).
Also Check: Osmosis | Octane Number | Natural resourses |
Related Links: Fossils Fuels | Isomerism | Metallurgy
Mechanism Steps
-
Formation of Chromyl Chloride Complex:
- The first step involves the formation of a complex between the methyl group on the benzene ring and the chromyl chloride (CrO2Cl2) generated in situ from CrO3 and HCl.
-
Oxidation of the Methyl Group:
- The chromyl chloride complex facilitates the oxidation of the methyl group (-CH3) to a formyl group (-CHO).
-
Hydrolysis:
- The final step is the hydrolysis of the intermediate complex to yield the desired aldehyde.
Let's break it down further with an example.
Example: Oxidation of Toluene to Benzaldehyde
Step-by-Step Mechanism
-
Formation of Chromyl Chloride:
- CrO3 reacts with HCl to form chromyl chloride (CrO2Cl2).
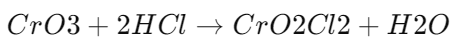
-
Complex Formation:
- Toluene (methylbenzene) reacts with chromyl chloride to form a complex.
-
Oxidation:
- The methyl group of toluene is oxidized to a formyl group.
-
Hydrolysis:
- The complex is hydrolyzed to produce benzaldehyde.
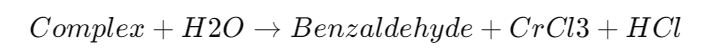
Summary
The Etard reaction is a valuable method for converting a methyl group on an aromatic ring to an aldehyde. It involves forming a complex with chromyl chloride, oxidizing the methyl group, and then hydrolyzing the complex to yield the aldehyde.
Key Points
- Reagents: Chromium trioxide (CrO3), Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- Solvent: Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)
- Product: Aldehyde from the oxidation of an aromatic methyl group
Frequently Asked Questions
The Etard complex is a chromium(VI) complex used to oxidize toluene to benzaldehyde
The reagent is chromyl chloride (CrO2Cl2).
The Etard reaction oxidizes toluene (a benzene derivative) to benzaldehyde using chromyl chloride.
The process involves oxidizing toluene to benzaldehyde using chromyl chloride (CrO2Cl2).
Etard reagent is chromyl chloride (CrO2Cl2), used in the Etard reaction.