Species Definition
A species is a group of similar organisms capable of interbreeding or exchanging genes among themselves.
What is species in biology?
Species refers to a group of organisms which resemble each other and are capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. It was a term coined by John ray. Each species is potentially interbreeding populations which are reproductively isolated from other such groups.
For instance Mangifera indica is the scientific name of Mango, and indica is the specific species of mango. Lion, Tiger, Leopard etc are closely related species categorized under genus Panthera.Each of these belong to different species and are named differently like Panthera leo(Lion), Panthera tigris(Tiger), Panthera pardus(Leopard) But for some organisms this definition does not work all the time. As in case of organisms that reproduce by asexual means, the term interbreeding do not fits into the criteria.
Also Read: What is symmetry in biology?
Accidental hybrids like Mule( Sterile hybrid of female horse and male donkey), Liger( Fertile hybrid of male lion and female tiger) etc. can be sterile or fertile but this does not fit into the earlier definition. Also sexual reproduction is not found in prokaryotes and some protists, therefore morphological differences and cytotaxonomy are taken into into consideration.
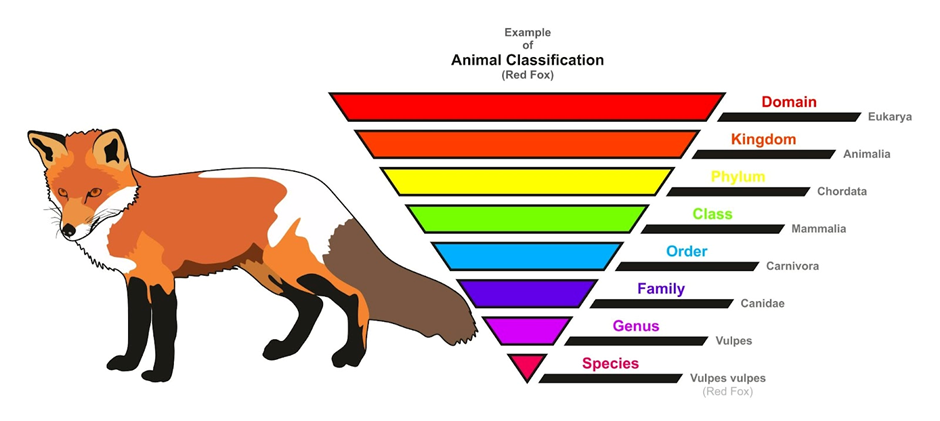
Types of species
In biology, species are categorized in several ways based on various criteria. Here are some of the main types:
- Biological Species: Defined by the ability to interbreed and produce fertile offspring. This is the most common definition used in biology.
- Morphological Species: Identified based on physical characteristics and structures. This approach is often used for fossil species and organisms where reproductive behavior is not well known.
- Ecological Species: Defined by their ecological niche, focusing on how a species interacts with its environment and other species.
- Genetic Species: Differentiated by their genetic makeup and DNA sequences. Advances in genetic technology have made this a prominent method for identifying species.
- Phylogenetic Species: Defined by their evolutionary history and ancestry, often determined by cladistic analysis which looks at shared derived characteristics.
Also Read: What is transpiration in biology?
Characteristics of Species
In biology, species are characterized by several key features:
- Reproductive Isolation: Members of a species can interbreed and produce fertile offspring, but they are reproductively isolated from other species. This means they do not normally breed with members of other species.
- Morphological Similarity: Individuals within a species share similar physical characteristics and genetic makeup, which distinguish them from members of other species.
- Genetic Cohesion: A species is a gene pool, meaning it consists of individuals that share a common genetic framework and can exchange genes within the group.
- Ecological Niche: Species occupy a specific ecological niche, which includes the role they play in their environment, their habitat, and their interactions with other organisms.
- Evolutionary Lineage: Species represent distinct evolutionary paths and are the smallest units in the classification system that reflect common ancestry and evolutionary history.
Read More: Assimilation