Assimilation in Biology
The word Assimilation in biology is used in many contexts , some of which are mentioned below.
Within the Human Digestive System ,the process of digestion involves major five steps, namely Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption , Assimilation and Egestion.
- Ingestion is uptake of food , mastication and swallowing or deglutition of food.
- Digestion involves breaking down complex food nutrients into simple absorbable forms.
- Absorption is the reaching of simple absorbable compounds formed during digestion into blood vessels.
- Assimilation is the step when the food so absorbed by blood vessels reaches the target area and is used by body cells for the purpose of growth and development.
- Egestion is the final step when undigested or non-absorbed food is removed from the body via anus.
Also Read: Fertilization in Biology
The following food substrates breaks as given below-
- Carbohydrates break down into Glucose, fructose and galactose
- Proteins break into amino acids
- Lipids break into Fatty acids and Glycerol
- Nucleic acid breaks into Nitrogenous base and pentose sugars.
The above broken down compounds are then utilized for various purposes.
Example- Glucose is utilized during the process of respiration to obtain energy Amino acids build new proteins .
Assimilation of glucose and proteins occur in Liver as it converts the glucose into glycogen for the purpose of storage and amino acids into proteins .
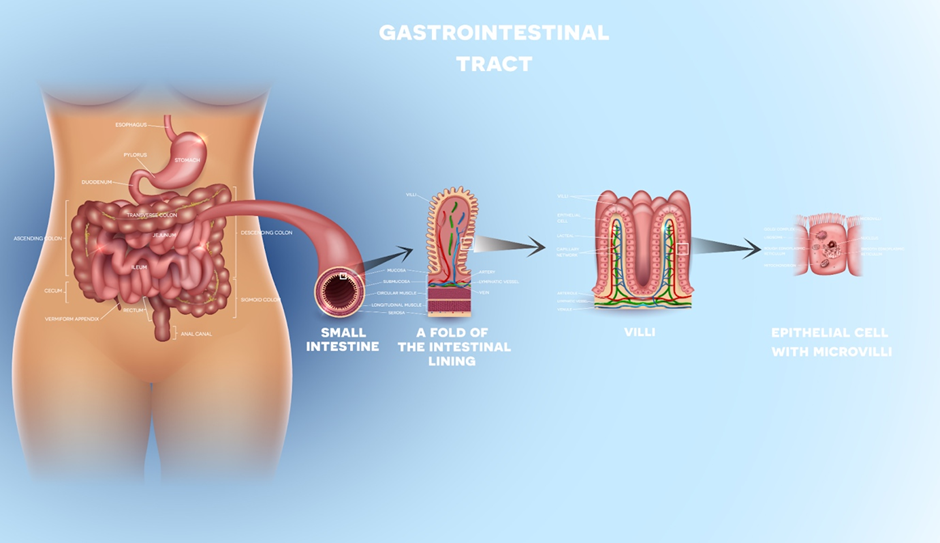
Figure 1 : Site for absorption and assimilation of nutrients
Also Read: Asexual Reproduction
Nitrogen assimilation
Nitrogen is abundant in our surroundings . Present in Proteins, Nucleic acids , Biomolecules in living organisms and as Gaseous Nitrogen in atmospheric air. But none of the compounds mentioned above is of use for the plants directly. For growth, plants require nitrogen in simpler forms like nitrate or nitrite.
Plant roots absorb the nitrogen in the form of Ammonium ion ( NH4+) or Nitrite( NO3-) present in soil due to ammonification and nitrification respectively. These forms of nitrogen are further converted into organic molecules ( Amino acids or proteins) which are utilized by plants for growth and development.
Conversion of ammonium ion into amino acids involves sequential action of two enzymes-Glutamine synthetase and Glutamate synthase which forms Glutamate and Glutamine(Both are amino acids). Ammonia after getting assimilated into Glutamate and glutamine further incorporate into amino acids and finally into proteins. This protein in turn is used for various purposes by plant cells.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans. Assimilation is the process of integrating new information or experiences into existing frameworks, while absorption involves the uptake of substances or nutrients into cells or tissues, as seen in digestion.
Ans. Assimilation involves adopting new cultural traits or information; for example, immigrants learning and incorporating the language and customs of their new country.
Ans. The process of assimilation includes integrating new information, experiences, or cultural traits into one's existing knowledge base or identity, often resulting in changes or adaptation.
Ans. In biology, assimilation refers to the process by which organisms convert absorbed nutrients into usable forms, incorporating them into their body tissues and cellular structures.
Ans. The two types of assimilation are cultural assimilation, where individuals adopt the cultural traits of another group, and biological assimilation, where absorbed nutrients are converted into bodily tissues.