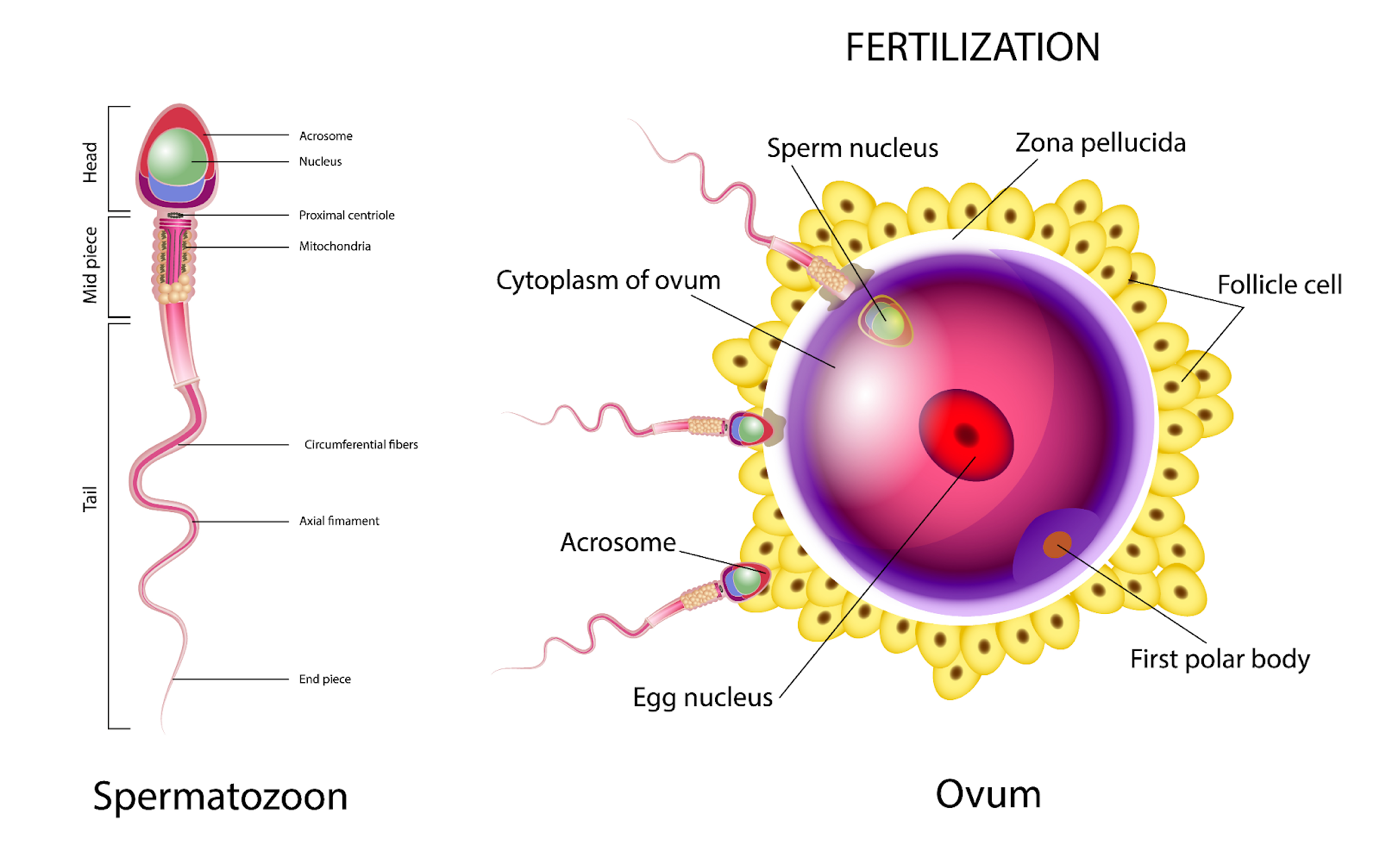
The process of fusing gametes to create a new individual organism or offspring and the development of that organism is known as fertilization, also known as generative fertilization, syngamy, and impregnation.
It is union of the male and female gametes which creates a zygote as a result, is the natural life process known as fertilization. In humans, the fallopian tube serves as the site of fertilization.
Also Check: Copulation in Biology
Thousands of sperms in semen are injected into the female vagina during coitus throughout this process. The sperm travel to the opening of the fallopian tube and then travel to the uterus. Few sperms will really make it to the fallopian tube's entrance.
The secondary oocyte emerges from the ovary's mature Grafian follicle and travels into the fallopian tube, where it is fertilized within 24 hours before getting discharged.
The oocyte is fertilized by a sperm(Only one) while being surrounded by numerous sperm. The sperm penetrates the secondary oocyte and completes the meiosis during meiosis-II. The egg is then known as the secondary oocyte.
Sperm and eggs can both only briefly display their vitality. In a female reproductive system, sperm can live for 48–72 hours, whereas, the egg can be fertilized for up to 24 hours before being released.
There are two types of fertilization observed : internal fertilization, in which the union of the egg and the sperm takes place inside the female reproductive tract, as in the case of humans; and external fertilization, in which the union of the male and female gametes takes place outside the body of the organism, as in the case of sea urchins, frogs, etc.
Figure- Fertilization in Human:
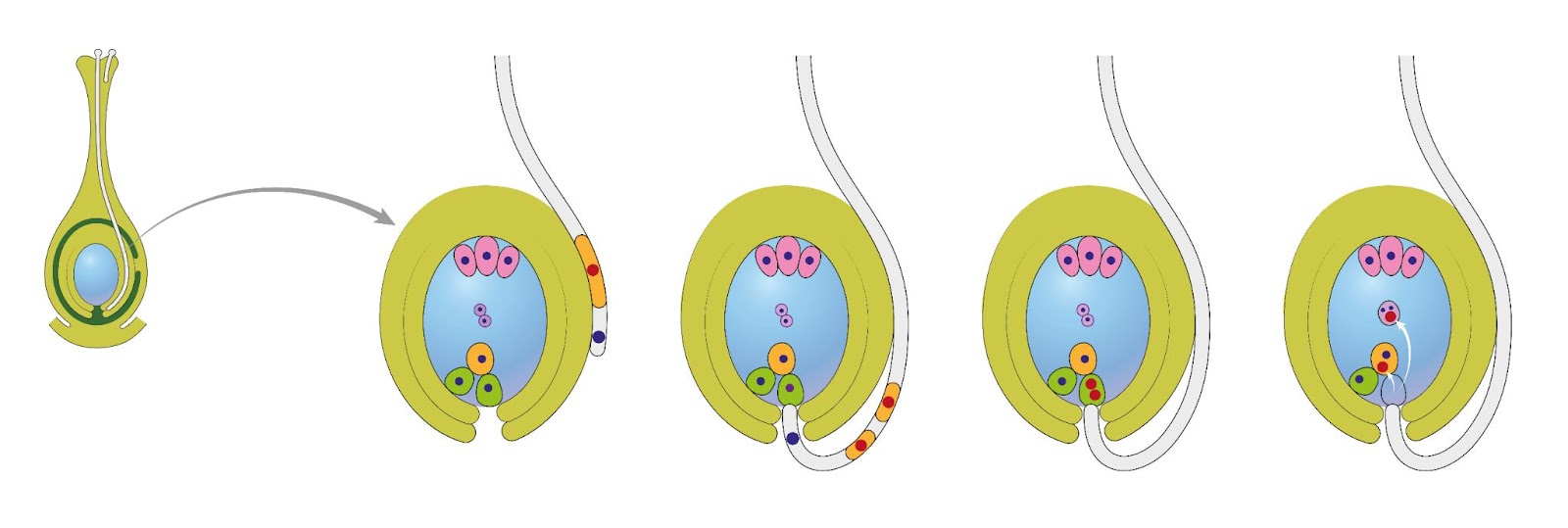
 The male sperm and female egg cells are the gametes involved in fertilization in plants. The processes by which the gametes produced by the male and female gametophytes combine and are fertilized vary among plant families. The archegonium is where sperm and eggs are fertilized in bryophyte land plants. The male gametophyte in seed plants is referred to as a pollen grain.A pollen tube grows and enters the ovule through a tiny orifice known as a micropyle after the pollen grain has germinated. The pollen tube transports the sperm from the pollen to the ovule, where they fertilize the egg. Two sperm cells are released from the pollen grain in flowering plants, and a second fertilization event occurs with the second sperm cell and the ovule's central cell, which is a second female gamete.
The male sperm and female egg cells are the gametes involved in fertilization in plants. The processes by which the gametes produced by the male and female gametophytes combine and are fertilized vary among plant families. The archegonium is where sperm and eggs are fertilized in bryophyte land plants. The male gametophyte in seed plants is referred to as a pollen grain.A pollen tube grows and enters the ovule through a tiny orifice known as a micropyle after the pollen grain has germinated. The pollen tube transports the sperm from the pollen to the ovule, where they fertilize the egg. Two sperm cells are released from the pollen grain in flowering plants, and a second fertilization event occurs with the second sperm cell and the ovule's central cell, which is a second female gamete.
Figure- Fertilization in ovary of plant:
Frequently Asked Questions
Fertilization is the process where a sperm cell fuses with an egg cell to form a new cell called a zygote, which develops into a new organism
The four main steps of fertilization are:
- Sperm binds to receptors on the egg surface
- Sperm releases enzymes to break down egg coating
- Sperm nucleus enters egg and fuses with egg nucleus
- Egg completes meiosis and restores chromosome number
In biology, fertilization is the fusion of male and female gametes (sperm and egg) to form a zygote. This restores the normal chromosome number and initiates embryonic development
Sperm fertilize the egg by first binding to receptors on the egg surface. The sperm then releases enzymes to break down the egg's outer coating. Finally, the sperm nucleus enters the egg and fuses with the egg nucleus.
The zygote is the name given to the new cell formed by the fusion of the sperm and egg during fertilization. It contains the full set of chromosomes and begins dividing to form an embryo.