What is fungi in biology?
Along with terrestrial plants and animals, fungi are eukaryotes with a huge range of body designs and are one of the main evolutionary lineages to occupy land. Although there are roughly 100,000 known species of fungi, there are about 1.5 million different types of fungi on Earth. Edible mushrooms, yeasts, black mold, and the producer of the antibiotic penicillin, Penicillium notatum, are all fungi. And currently the largest living organism on Earth’s surface is a fungus.
Although humans have used yeasts and mushrooms since prehistoric times, until recently, the biology of fungi was poorly understood.Fungi can be multicellular or unicellular, however they all share the following characteristics:
- Fungi are eukaryotic organisms, they have true nuclei that is protected by membranes.
- Vascular system is absent in them. There is no Xylem or Phloem.
- The cell walls of fungi is made of chitin (plants also have cell walls, but animals have no cell walls).
- Fungi do not have any embryonic stage.
- Typically, they are not mobile.
- The phenomena of altered generation is seen in fungi. Both haploid and diploid stages are present.
- Since fungi lack the chlorophyll pigments found in chloroplasts in plant cells—which are essential for photosynthesis—they are achlorophyllous.
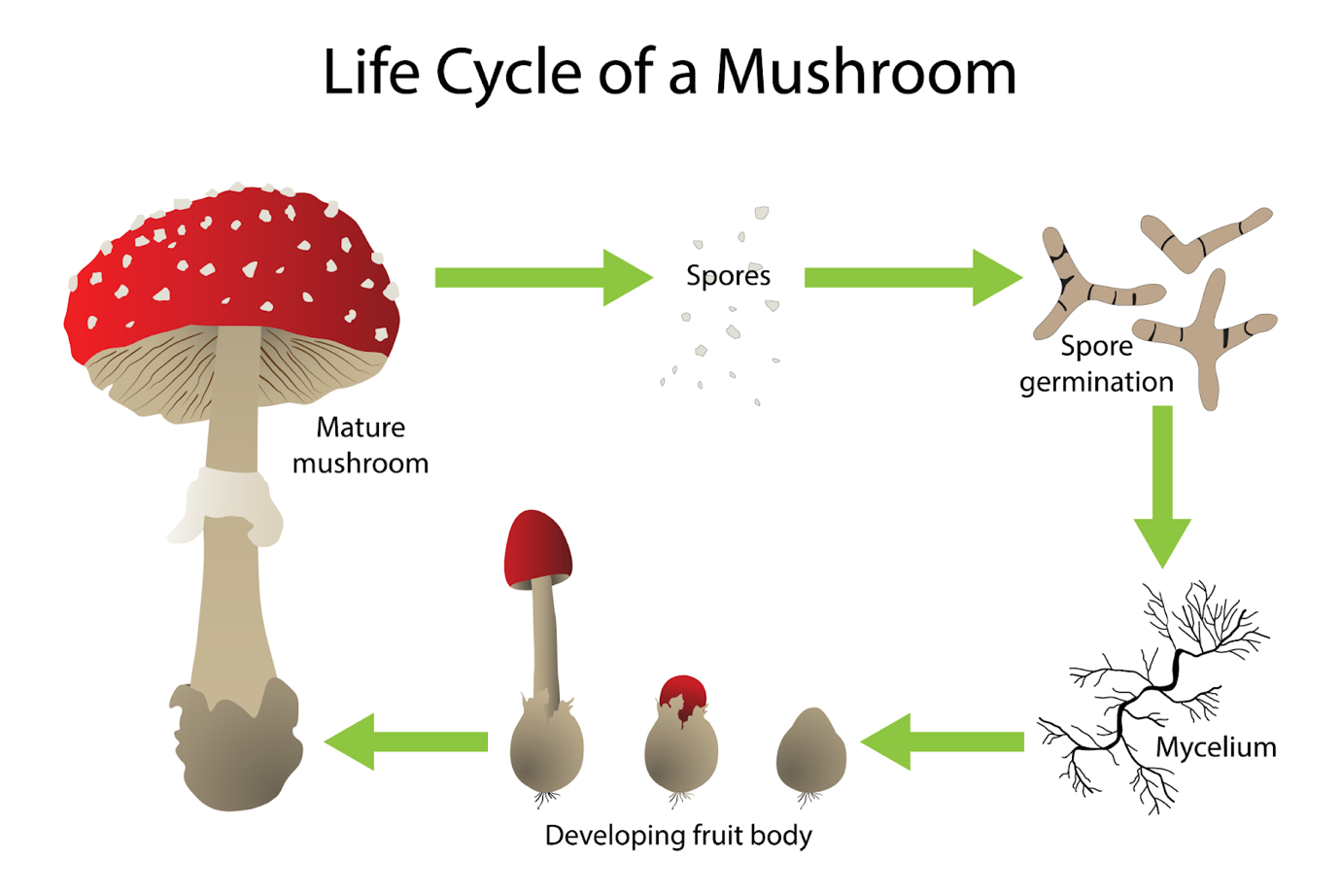
- The vegetative body of fungus might be made up of microscopic threads called hyphae or it can be unicellular.
- Hyphae can expand and develop into a network known as mycelium.
- As unicellular fungus, yeasts lack the ability to form hyphae.
 Along with terrestrial plants and animals, fungi are eukaryotes with a huge range of body designs and are one of the main evolutionary lineages to occupy land. Although there are roughly 100,000 known species of fungi, there are about 1.5 million different types of fungi on Earth. Edible mushrooms, yeasts, black mold, and the producer of the antibiotic penicillin, Penicillium notatum, are all fungi. And currently the largest living organism on Earth’s surface is a fungus.
Along with terrestrial plants and animals, fungi are eukaryotes with a huge range of body designs and are one of the main evolutionary lineages to occupy land. Although there are roughly 100,000 known species of fungi, there are about 1.5 million different types of fungi on Earth. Edible mushrooms, yeasts, black mold, and the producer of the antibiotic penicillin, Penicillium notatum, are all fungi. And currently the largest living organism on Earth’s surface is a fungus.
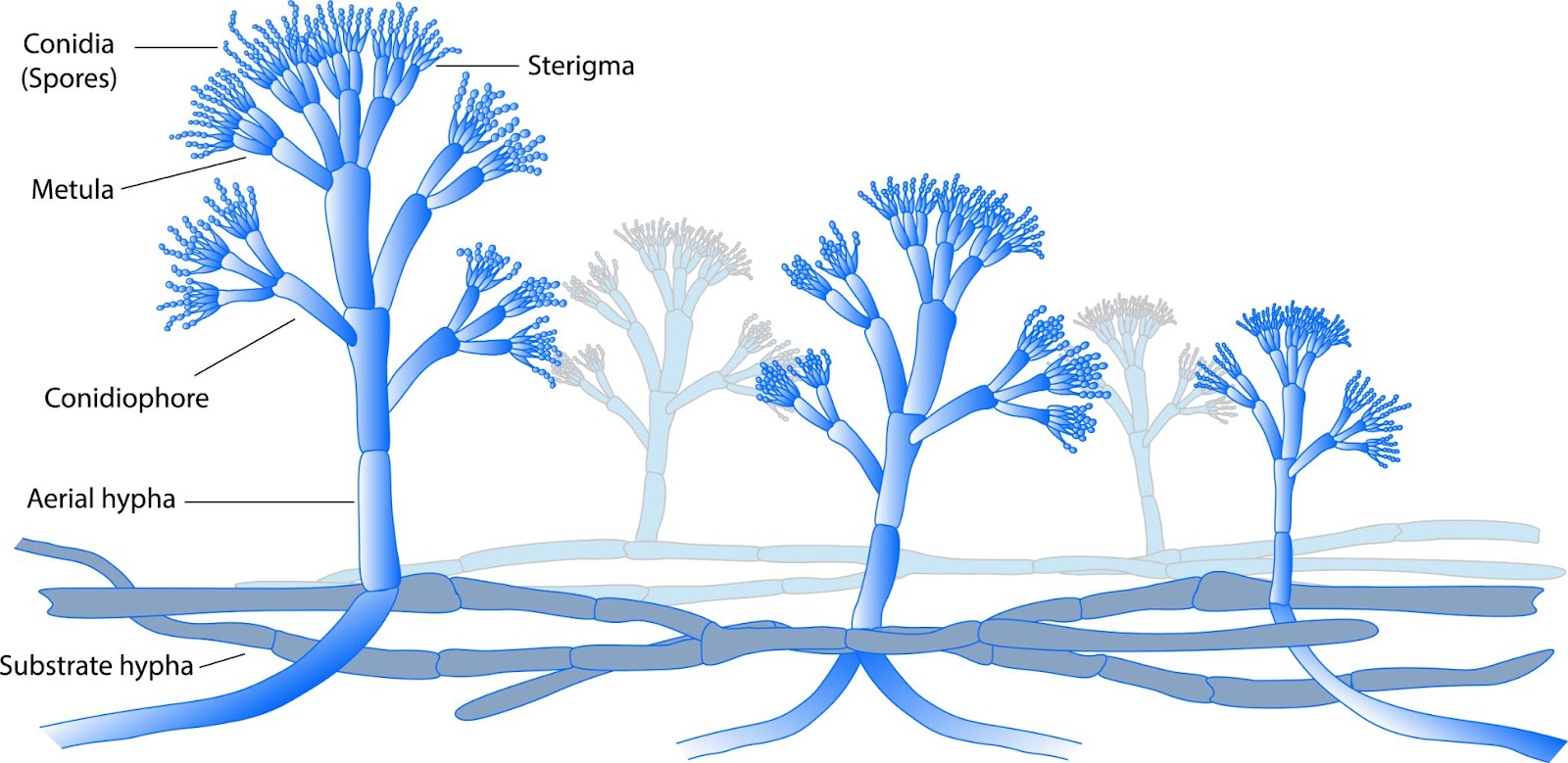
Penicillium an example of fungi:
Frequently Asked Questions
Fungi are a group of organisms that include microbes like yeasts, molds, and the more familiar mushrooms. They are classified as their own kingdom, separate from plants and animals.
- Fungi are eukaryotic, meaning they have a distinct nucleus and membrane-bound organelles in their cells.
- Fungi have cell walls made of chitin, unlike the cellulose in plant cell walls.
- Fungi are heterotrophs, meaning they obtain nutrients by absorbing organic matter rather than producing their own food through photosynthesis.
- Fungi reproduce using spores, which can spread through the air or water.
- Fungi play important roles in ecosystems as decomposers, recycling nutrients, and some form beneficial symbiotic relationships with plants.
Fungi are a diverse group of organisms that include microbes like yeasts and molds, as well as the more recognizable mushrooms. They are eukaryotic, meaning their cells have a distinct nucleus, and they have rigid cell walls made of chitin. Fungi obtain nutrients by absorbing organic matter, rather than producing their own food through photosynthesis like plants. They reproduce using spores that can spread through the air or water.
- Decomposition: Fungi break down dead organic matter, recycling nutrients in ecosystems.
- Symbiosis: Some fungi form beneficial relationships with plants, helping them absorb nutrients and water.
- Food production: Certain fungi are used to make foods like bread, cheese, and alcoholic beverages.
- Medicine: Some fungi produce medically useful compounds, like the antibiotic penicillin.
- Disease: Some fungi can infect and cause diseases in plants, animals, and humans.
- Mushrooms - The familiar fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting bodies of fungi.
- Molds - Fuzzy, often colored growths of fungal hyphae.
- Yeasts - Single-celled fungi used in baking and brewing.
- Rusts - Parasitic fungi that infect plants.
- Smuts - Parasitic fungi that infect grains and grasses.