What is Vegetative Propagation?
Vegetative propagation is a method of asexual plant reproduction involving leaves, roots, and stems. It includes fragmentation and regeneration of specific plant parts. Let's delve into the types and examples of vegetative propagation.
Types of Vegetative Propagation
Different types of vegetative propagation are-
Natural Vegetative Propagation
This occurs without human interference, often enabled by adventitious roots. New plants can emerge from roots, stems, and leaves.
Vegetative propagation by root
In some plants like Dahlia, sweet potato etc., the adventitious roots become thick, swollen and tuberous due to storage of food. Adventitious buds are also present on them. When such roots, bearing these buds are planted in the soil, new plants are produced as a result of vegetative propagation.
Vegetative propagation by stem
Vegetative propagation by stems is of two types:
- By subaerial stems: Subaerial stems develop as lateral branches from the mother plant and give rise to a new individual after getting detached from the mother plant. Eg. Grasses.
- By underground stems: In some plants the underground stem gets modified for storage of food. e.g. Potato tuber has a number of eyes (buds) on its external surface. The buds develop into aerial shoots when such a tuber is planted in the soil. The bulb of onion is vertical in direction and its terminal bud gives rise to the aerial shoot. Axillary buds may also be produced in the axils of fleshy scales. These buds grow into aerial shoots under favourable conditions.
Vegetative propagation by leaves
The fleshy leaves of Bryophyllum bear adventitious buds in the notches along the leaf margin. When the leaves fall on the ground, the buds develop into small plants under favourable conditions. These plantlets can be easily separated to grow as independent plants e.g. Begonia, Kalanchoe, Streptocarpus bryophyllum (patharchatta).

Artificial Vegetative Propagation
This is a form of vegetative reproduction conducted by humans in fields and labs. Common types of artificially induced vegetative reproduction include:
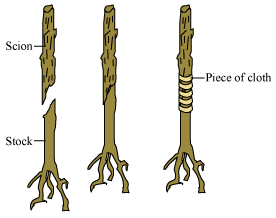
Grafting
- In this method, stems of two different plants (one with roots and the other without roots) are joined together, which then grows as a single plant.
- The cut stem with roots is called as stock, which makes the lower part of the plant.
- The other cut part of stem that is without roots is called as scion, which forms upper part of the plant.
- Cambium layer of scion should be in contact with cambium of stock, for the growth of plant to take place.
- Grafting method is mainly used for fruit trees like apple, peach, apricot, pear, mango etc.
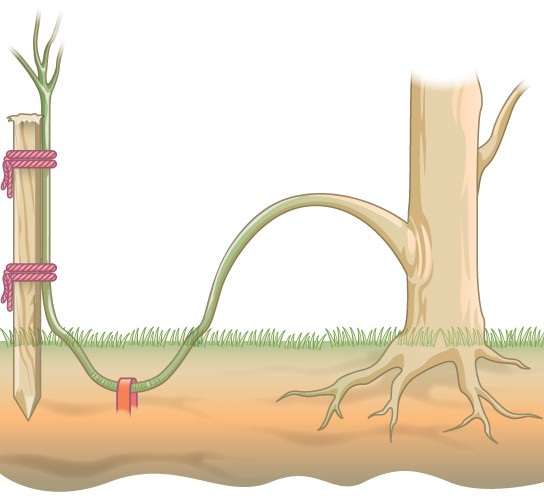
Layering
In this method, a branch of plant is bent downwards towards the ground and covered with moist soil. After some time new roots emerge from the part of the branch, buried into the soil.
When separated from the parent plant, it grows as a new individual plant. Plants like Jasmine, Hibiscus etc. can be propagated by this method.
Cutting
This is a very simple and common method of propagation in rose, sugar cane, Bougainvillea, etc. In this process, stem cuttings with some nodes and internodes are placed in moist soil, and they given rise to adventitious roots and a new plant subsequently.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Vegetative Reproduction
| Advantages of Vegetative Propagation | Disadvantages of Vegetative Propagation |
| It is quick and cheaper method of multiplying plants. | Neither good qualities are introduced nor bad characters are eliminated in plants which a multiplies through vegetative propagation. |
| It can overcome seed dormancy so it makes possible the propagation of plants such as banana, seedless grapes, orange, rose and jasmine. | Subsequent generations of plants show a general fall in vigour and vitality due to absence of variations. |
| It helps us to introduce plants in new area where the seed germination fails to produce a mature plants. | Vegetative organs like root, stem, leaves, bulbils used for propagation cannot be preserved for a long time. They get attacked by viral, fungal and bacterial diseases. |
| Grafting enables the physical and physiological joining of two separate individuals for the best quality of plants. | Plants produced by this method lack dispersal mechanism where as plants reproducing sexually are dispersed with the help of seeds. |
| Most of the ornamental plants are propagated by vegetative reproduction. e.g. carnations, roses, tulips. | Disease of parent plants generally spreads to all the daughter plants. |