You have come to the right place if you are looking for information about flower inflorescence in an article format.
In this article, we will start with a brief introduction to inflorescence and then explore its different types. After that, we will discuss the various kinds of flowers.
The goal of this page is to provide a clear introduction to inflorescence and other relevant details. If you have limited time but still want to get all the important information, we suggest reading the introduction and the key points.
Also Check: Botanical Name of Coffee
Introduction
Inflorescence refers to the arrangement of flowers on the stalk of a plant. This arrangement can vary in complexity, size, shape, and pattern. Inflorescences can be classified into different types based on the arrangement and relationship of the flowers.
- Racemose Inflorescence
- Cymose Inflorescence
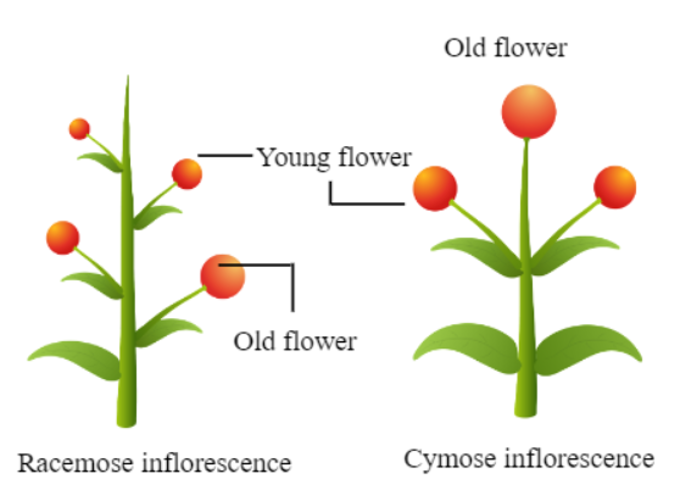
Racemose Inflorescence
A racemose inflorescence is a type of flower arrangement where flowers grow along an elongated main stem. This growth pattern can either continue indefinitely (indeterminate) or stop after a certain point (determinate). The flowers can be arranged in various ways. Here are some common types of racemose inflorescence:
Raceme
In a raceme, flowers grow on small stalks (pedicels) attached to the main stem (rachis). Typically, the flowers bloom from the bottom upwards, with the newest flowers appearing at the top.
Also Check: Botanical Name of Cauliflower
Examples:
- Lupine (Lupinus spp.)
- Snapdragons (Antirrhinum majus)
- Delphinium (Delphinium spp.)
- Goldenrod (Solidago spp.)
- Bottlebrush (Callistemon spp.)
- Crotalaria

Corymb
A corymb inflorescence is a type of flower arrangement where the flowers grow on stems (pedicels) of different lengths. These stems all start from one central point at the top of the main stem. In this arrangement, the flowers on the outer edges have the longest stems, while those in the center have shorter stems. This creates a flat or slightly rounded cluster of flowers.
Examples of Plants with Corymb Inflorescence:
| Common Name | Scientific Name |
|---|---|
| Yarrow | Achillea millefolium |
| Hawthorn | Crataegus spp. |
| Elderberry | Sambucus spp. |
| Mountain Ash | Sorbus spp. |
| Queen Anne's Lace | Daucus carota |

Umbel
An umbel is a type of flower arrangement that looks like an umbrella or parasol. In this arrangement, all the flower stalks (pedicels) start from the same point at the top of the stem. This makes the flowers appear to be at the same height, and their lengths are usually similar.
Also Check: Botanical Name of Banyan Tree
Examples of Umbel Inflorescence Plants
| Plant Name | Scientific Name |
|---|---|
| Dill | Anethum graveolens |
| Carrot | Daucus carota |
| Parsley | Petroselinum crispum |
| Queen Anne's lace | Daucus carota |
| Fennel | Foeniculum vulgare |


Capitulum
A capitulum is a type of flower arrangement where many small flowers are tightly packed together to create a round or flat structure. This arrangement is also called a head or a compound flower. Although the individual flowers in a capitulum are usually small and plain, they combine to form a beautiful and eye-catching display.
Also Check: Botanical Name of Pea
Examples of Capitulum Inflorescence
| Common Name | Scientific Name |
|---|---|
| Sunflower | Helianthus annuus |
| Dandelion | Taraxacum officinale |
| Globe Artichoke | Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus |
| Echinacea | Echinacea purpurea |
| Black-eyed Susan | Rudbeckia hirta |


Spike
A spike inflorescence is a type of flower arrangement where flowers grow directly on the main stem (spike) without significant spacing between them. The flowers are often neatly arranged and can either sit directly on the stem or have very short stems.
Examples of Spike Inflorescence Plants:
| Plant Name | Scientific Name |
|---|---|
| Wheat | Triticum aestivum |
| Liatris | Liatris spicata |
| Goldenrod | Solidago spp. |
| Catnip | Nepeta cataria |
| Veronica | Veronica spicata |
In spike inflorescences, the flowers are attached directly to the main axis (stem), giving a uniform appearance without branching or extended stem parts between the flowers. This arrangement is common in plants like wheat, liatris, goldenrod, catnip, and veronica.
Also Read: What is transpiration?

Spadix
A spadix inflorescence is a type of flower arrangement where flowers grow on a fleshy spike (spadix) surrounded by a modified leaf called a spathe. This arrangement is common in various plant species. The flowers on a spadix inflorescence are often small and inconspicuous, arranged irregularly or in clusters.
| Plant Species | Scientific Name |
|---|---|
| Jack-in-the-pulpit | Arisaema triphyllum |
| Skunk cabbage | Symplocarpus foetidus |
| Calla lily | Zantedeschia aethiopica |
| Philodendron | Philodendron bipinnatifidum |
| Peace lily | Spathiphyllum wallisii |
| Maize (corn) | Zea mays |


Catkin
A catkin, also known as an ament or amentum, is a type of flower arrangement found in many coniferous trees. Unlike typical flowers, catkins are borne on a drooping spike without individual stalks between them, giving them a distinct appearance. These inflorescences often feature tiny, sometimes barely visible, flowers that can be either male or female.
Read More: What is zygote?
| Examples of Trees with Catkin Inflorescences |
|---|
| Willow (Salix spp.) |
| Birch (Betula spp.) |
| Alder (Alnus spp.) |
| Hazelnut (Corylus avellana) |
| Oak (Quercus spp.) |
Catkins are adapted for efficient wind pollination due to their structure and placement, which aids in the reproduction of these tree species. They play a significant role in the lifecycle of many plants, particularly those in colder climates where insects for pollination may be less abundant.
This type of flowering arrangement is fascinating in its simplicity and effectiveness, showcasing nature's diverse strategies for plant reproduction.

Corymbose
A corymbose inflorescence is characterized by its flat-topped or slightly convex appearance due to the extended pedicels of lower flowers. This arrangement gives the inflorescence a uniform look with flowers placed regularly.
| Characteristic | Example |
|---|---|
| Flowers arranged in a flat-topped or convex manner | Mustard (Brassica juncea) |
In a corymbose inflorescence, the flowers are positioned in such a way that they create a balanced and organized floral display.

Panicle
A panicle inflorescence is a type of flowering arrangement characterized by a branched main axis that branches irregularly. The flowers are predominantly found on the lower branches towards the base of the inflorescence. This arrangement is also known as a pedunculate inflorescence. Typically, the upper branches of the panicle are shorter than the lower branches and bear flowers closer to the top of the inflorescence.
Also Check: Germination
Examples of Panicle Inflorescence Plants:
| Plant | Scientific Name |
|---|---|
| Oats | Avena sativa |
| Millet | Pennisetum glaucum |
| Wisteria | Wisteria sinensis |
| Cornflower | Centaurea cyanus |
| Delonix | - |
Panicle inflorescences are common in plants like oats, millet, wisteria, cornflower, and delonix. They are characterized by their branched structure, where flowers are distributed along the branches with those at the base typically appearing first.

Cymose Inflorescence
Cymose inflorescence describes a plant's flowering pattern where the main stem ends in a flower and lateral branches grow similarly to the main branch.
| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Solitary Cyme | A single flower develops at the end of the floral axis, which can be either axillary (arising from the leaf axil) or terminal (at the stem tip). | Datura, Hibiscus, Dianthus barbatus, Geranium sanguineum |



Monochasial Cyme
In this type of cymose inflorescence, the main stem produces lateral branches that grow alternately. Each branch terminates in a single flower.
Also Check: Indirect Development in Biology
| Plant Name | Common Name |
|---|---|
| Veronicastrum virginicum | Culver's root |
| Delphinium spp. | Larkspur |
| Lobelia cardinalis | Cardinal flower |
| Chrysanthemum spp. | Chrysanthemum |
| Aquilegia spp. | Columbine |


Dichasial Cyme
A dichasial cyme is a specific type of flowering arrangement seen in certain plants. In this type of inflorescence, the main stem produces two lateral branches. Each lateral branch then develops two more branches, growing in opposite directions.
Examples of Plants with Dichasial Cyme:
| Plant Name | Scientific Name |
|---|---|
| Guelder Rose | Viburnum opulus |
| Panicled Hydrangea | Hydrangea paniculata |
| Orpine | Sedum telephium |
| Pincushion Flower | Scabiosa columbaria |
| Blueblossom | Ceanothus thyrsiflorus |
Dichasial cymes are observed in these plants, where the branching pattern helps in understanding their growth and floral structure.
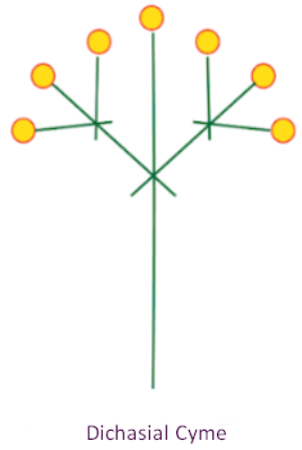

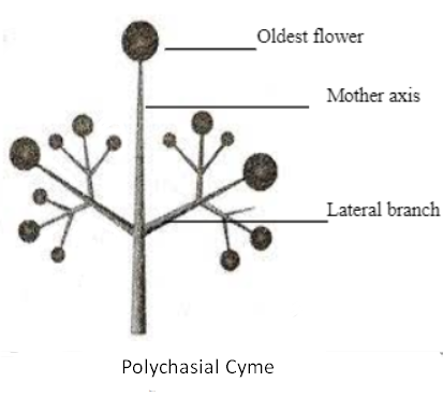
Polychasial Cyme
A polychasial cyme is a type of flowering arrangement where the main stem produces side branches. Each of these branches then develops multiple additional branches, creating a complex branching pattern.
Also Check: Fertilization in BIology
| Examples |
|---|
| Euphorbia milii |
| Yucca spp. |
| Hoya carnosa |
| Sambucus nigra |
| Syringa vulgaris |

Some Other Special Types of Inflorescence
Apart from racemose and cymose inflorescences discussed above, there are other special kinds such as those discussed below.
Compound Inflorescence
A compound inflorescence is a form of inflorescence in which the flowers are placed on branched or unbranched axes that originate from a central point. Compound inflorescences can also be unbranched.
Examples: Lupinus polyphyllus, Musa acuminata, Echinacea purpurea, Cymbidium spp., and Aloe vera.

Cyathium
In plants belonging to the Euphorbia genus, a specific kind of inflorescence known as a cyathium can be found. It is made up of a structure that resembles a cup and is referred to as an involucre. Within this structure are numerous distinct types of miniature flowers.
Examples: Euphorbia milii, Euphorbia pulcherrima, Euphorbia lactea, Euphorbia obesa, Euphorbia heterophylla.

Hypanthodium
In the plant family known as figs, an unusual kind of inflorescence known as hypanthium can be found. It is also known as a syconium and is a specialised, hollow receptacle enclosing many smaller flowers. This receptacle can go by a few different names.
Examples: Ficus carica, Ficus benghalensis, Ficus religiosa, Ficus microcarpa, and Ficus elastica.

Verticillaster
This type of inflorescence has the appearance of a whorled structure because the flowers are arranged in a cylindrical structure with two opposed cymes.
Examples: Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia), Mint (Mentha spp.), Thyme (Thymus vulgaris), Sage (Salvia officinalis), Oregano (Origanum vulgare).

Frequently Asked Questions
A head inflorescence is when flowers are grouped tightly together, often surrounded by bracts (leaf-like structures). This creates a dense cluster of flowers.
A peduncle is the stalk that supports a flower or a group of flowers.
An indeterminate inflorescence is where flowers bloom starting from the center and continue outward. The oldest flowers are at the bottom, and the youngest are at the top.
A determinate inflorescence is where flowers bloom from the outside inward. The youngest flowers are at the bottom, and the oldest are at the top, arranged in age order.
A pedicel is the small stalk that holds up an individual flower within an inflorescence.
An umbel is a type of inflorescence where flowers are clustered with a flat or rounded head, and all the flower stalks come from a single point. This is common in many flowering plants.