List of Odd Numbers
Take a look at the following list of all odd numbers between 1 and 100. None of these numbers are multiples of two. You'll see that there are exactly 50 odd numbers in the first 100. Check out this list of odd numbers from 1 to 100.
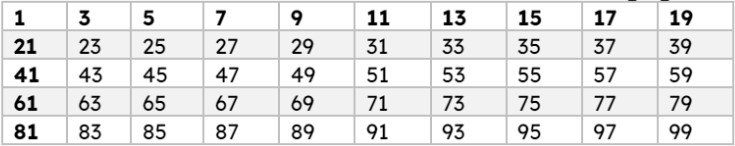
Odd Numbers
Odd numbers are those that cannot be grouped in pairs. In ancient Greece, numbers that couldn't be arranged in two rows were seen as unusual. Over time, this idea has changed. For instance, consider any number that is a multiple of 2. You'll notice that these numbers can be paired up. All whole numbers, except for multiples of 2, are odd numbers.
What are Odd Numbers?
Odd numbers are those that cannot be evenly divided into two equal parts. They include positive numbers like 1, 3, 5, 7, and so on. To illustrate, think of them like pairs of shoes and cherries. Imagine having 1, 3, 5, or 7 shoes, and pairs of cherries like 2, 4, 6, or 8. The graphic below helps visualize how these numbers pair up.
Also Check: Prime Numbers from 1 to 100
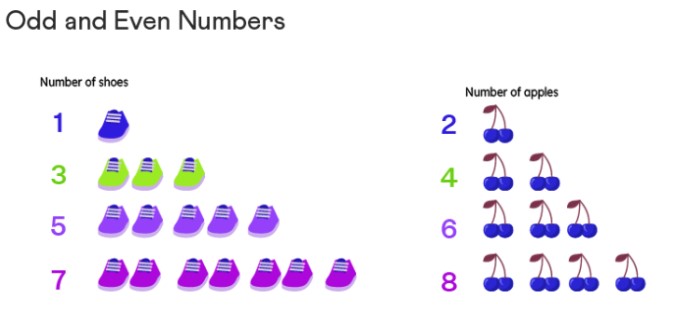
Odd Numbers and Pairs
When the quantity of items is odd, they may not always form complete pairs. One item could be left without a matching pair. This is because odd numbers, by definition, cannot be divided into two equal halves without leaving a remainder.
Also Check: Even Numbers
Even Numbers and Pairs
On the other hand, even numbers can be divided into two equal halves. This allows even numbers to be divided into pairs. For example, 4 can be split into 2 pairs of 2, and 8 can be divided into 4 pairs of 2.
Pattern in Odd Numbers
Yes, there is a clear pattern in the list of odd numbers:The rightmost digit (the ones place) in any odd number is always 1, 3, 5, 7, or 9. This is because odd numbers are those that leave a remainder of 1 when divided by 2.For instance:
- 1 divided by 2 leaves a remainder of 1
- 3 divided by 2 leaves a remainder of 1
- 5 divided by 2 leaves a remainder of 1
- 7 divided by 2 leaves a remainder of 1
- 9 divided by 2 leaves a remainder of 1
This pattern holds true for all odd numbers, as the ones digit must be one of these five numbers to ensure the number is odd.
Also Check: Co-Prime Numbers
Frequently Asked Questions
Odd numbers are those that cannot be divided into two equal parts without leaving a remainder. To find odd numbers, simply look for numbers that end in 1, 3, 5, 7, or 9.
The formula to identify odd numbers is: "2k + 1", where k is any integer. This means that any number that can be expressed in this form is an odd number.
Even numbers are those that can be divided into two equal parts without leaving a remainder, such as 2, 4, 6, 8, and so on. Odd numbers, on the other hand, cannot be divided into two equal parts without a remainder, such as 1, 3, 5, 7, and so on.
25 is an odd number. Odd numbers are those that end in 1, 3, 5, 7, or 9, and 25 ends in 5, so it is an odd number.
17 is an odd number. Odd numbers are those that cannot be divided into two equal parts without leaving a remainder, and 17 satisfies this condition.