What is transportation in biology?
All living things require the transportation of water, food, minerals, and oxygen to various body parts. They support cellular development and respiration. The excretory organs receive the waste materials to be removed from the body. Animals use their circulatory and excretory systems in coordination to move them around.
Transportation in Animals
The substance that travels through blood vessels and carries digested food from the small intestine to various bodily regions is called blood. Veins and arteries are the two different types of blood vessels. Different sections of the body receive oxygen-rich blood from the heart through the arteries, while the veins return oxygen-deficient blood from every area of the body to the heart. The main organ responsible for moving blood throughout the body is the heart.
Excretion is the process through which waste is expelled from cells.The chemicals that must be expelled from the body include nitrogenous waste, too much blood sugar, too much salt, undigested wastes, and carbon dioxide. As lower organisms lack particular excretory organs, they expel nitrogenous waste by the process of diffusion across the cell membrane for example in amoeba, hydra, and paramecium.
The urinary bladder, urethra, ureter, and kidneys make up the human excretory system.The primary excretory organ that controls the body's mineral and water balance is the kidney. They take up minerals from the blood and pass urine to get rid of the blood's nitrogenous waste.
Transportation in plants
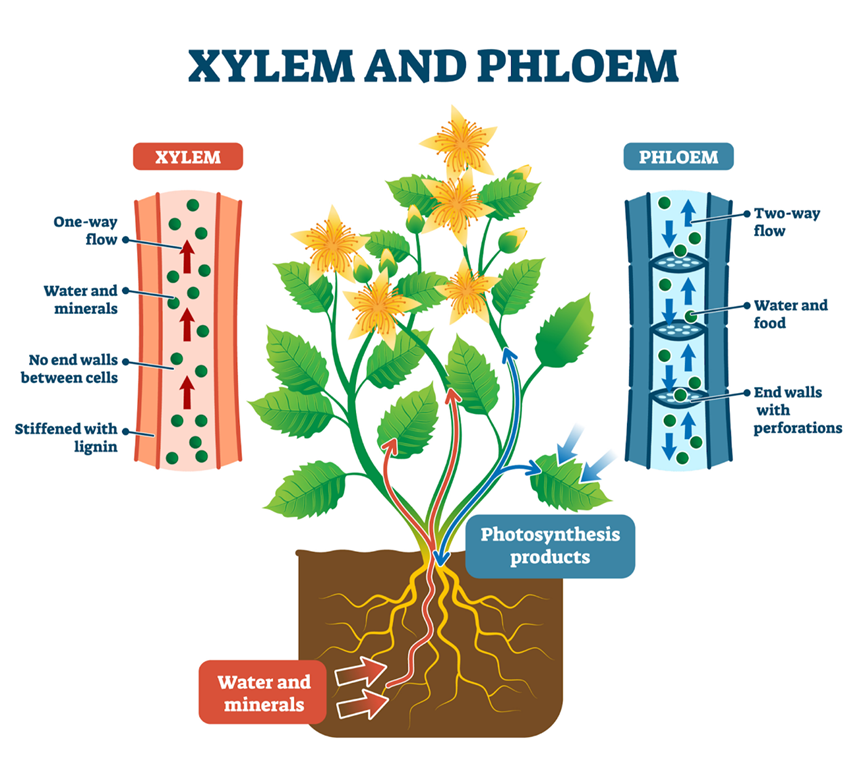
The process of moving water, vital nutrients, gases, and excretory products throughout the plant is crucial for a variety of functions. The vascular tissues in plants are in charge of movement. The suction force aids in the movement of minerals and water throughout the plant.
Water is carried from root hairs to the rest of the plant by a vascular tissue called xylem. The phloem has a two-way transport system. Phloem assists in moving the food molecules to the required locations.
Water and minerals are taken up by the root hairs from the soil and are stored there in vacuoles. The suction power of the plants draws this water inside them. The extra water in plants evaporates through the stomata in the leaves, where it is lost as water vapour.Through the phloem, the components necessary to create food are transported to various plant organs. In the plant's storage organs, the extra food is kept.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans. Transportation in the heart refers to the movement of blood through the heart's chambers and vessels, ensuring oxygen and nutrients are distributed throughout the body.
Ans. Transportation is necessary to distribute essential nutrients, oxygen, and hormones to cells and remove waste products like carbon dioxide, maintaining homeostasis in the body.
Ans. Transportation in plants involves the movement of water, nutrients, and food through xylem and phloem tissues, supporting growth and physiological processes.