Sexual reproduction occurs naturally in humans, animals, and most plants. It is a more complex and time-consuming process than asexual reproduction. However, it offers the advantage of genetic variation, resulting in unique offspring. This type of reproduction comprises three stages: Pre-fertilization, Fertilization, and Post-fertilization.
 Sexual Reproduction - Stages
Sexual Reproduction - Stages
Pre-Fertilization
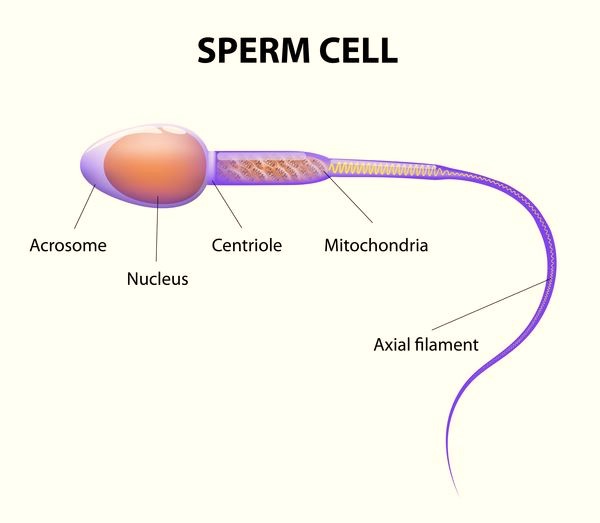
This stage encompasses the events preceding fertilization. Gamete formation (gametogenesis) and gamete transfer are the two processes that occur during this stage. Gametes, or sex cells, are haploid (23 chromosomes) and differ between males and females. The male gamete is sperm, while the female gamete is ovum or egg. These gametes are produced within specialized structures in all organisms. Since the female gamete is immobile, male gametes must be transferred for fertilization.
In plants, this is achieved through pollination. Unisexual animals transfer gametes through sexual intercourse.
Also Read: Asexual Reproduction
Fertilization
When the haploid male and female gametes combine to form a zygote, it is termed fertilization or syngamy. This process can happen externally, outside the body (external fertilization), or internally, inside the body (internal fertilization).
Post-Fertilization
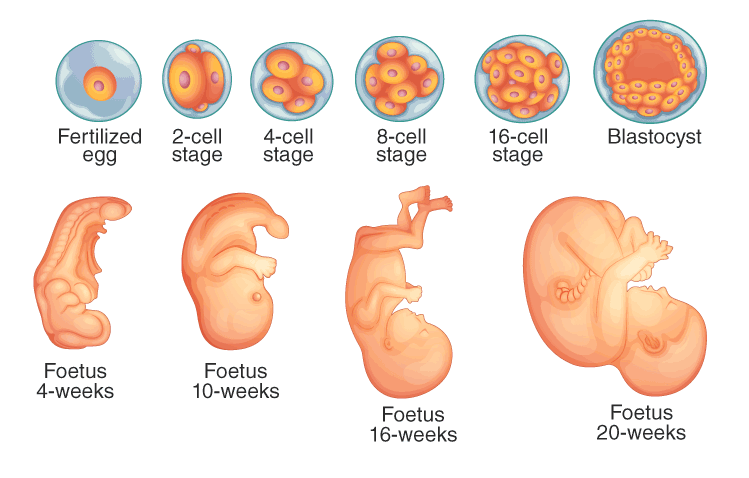
Fertilization leads to the formation of a diploid zygote, which then undergoes mitotic division to develop into an embryo, a process known as embryogenesis. During this process, cells differentiate and adapt accordingly. Zygote development varies based on the organism and its life cycle. Animals are categorized as oviparous or viviparous depending on whether the zygote develops outside or inside the body, respectively. In angiosperms, the zygote matures into the ovary, which transforms into the fruit, while the ovules develop into seeds.
Advantage of sexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction introduces new gene combinations in a population. Genetic variation allows for better adaptation which results in more offspring of a species to survive.
- With the exception of identical twins no two organisms resulting from sexual reproduction are exactly similar.
- It is important to note that no animal showing sexual reproduction is strictly male or female. Animals such as sea anemone, earthworm, etc. may have both male and female reproductive organs in the same individual. These organisms are called as hermaphrodites
- In some hermaphrodites self fertilization is possible but in most of the hermaphrodite animals cross fertilization takes place. This doubles the number of young ones produced.
Disadvantages of Sexual Reproduction
- Since meiosis is a lengthy process requiring a mate, it is both time and energy intensive. Consequently, the organism produces fewer offspring in its lifetime.
- Two parents are necessary for organisms to reproduce, requiring them to find a mate. This task can be challenging if the organism is isolated and must travel long distances.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans. In this type of reproduction fusion of two distinct gametes take place. Each parent contributes one gamete with only one set of chromosomes (haploid). The fusion of two gametes forms the zygote, having genes from both the parents.
Ans. One of the key benefits is the diversity in offspring. While variation may not appear significant at first, it becomes advantageous over time, especially when the environment changes. This can enhance an organism's survival chances, leading to advantages through natural selection. In crop production, selective breeding can be used to cultivate crops with desired traits.
Ans. Asexual reproduction is when a single individual produces offspring without genetic contribution from another individual. Sexual reproduction, on the other hand, involves two individuals of different sexes contributing genetic material to produce offspring.
Ans. There are two main forms: sexual and asexual reproduction.
Ans. It occurs in a variety of ways in animals. In some species, such as fish, the male releases sperm over the eggs after the female has laid them.