What is Respiration in Biology?
Respiration goes beyond mere breathing; it involves the exchange of gases within our bodies. This process occurs at two levels: internal and external.
Internal respiration, known as cellular respiration, takes place within mitochondria where oxygen is utilized to produce ATP (energy) and carbon dioxide as a byproduct.
External respiration involves the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body's tissues and the surrounding environment.
It is a chemical process through which organic compounds, such as glucose, release energy to fuel various bodily functions. Some organisms rely on oxygen to efficiently extract energy from organic compounds, a process known as aerobic respiration. Conversely, there are organisms and cells that can generate energy from organic compounds without requiring oxygen, termed anaerobes, and their respiration is referred to as anaerobic respiration.
Also Check: Germination
Figure- Respiration in Human
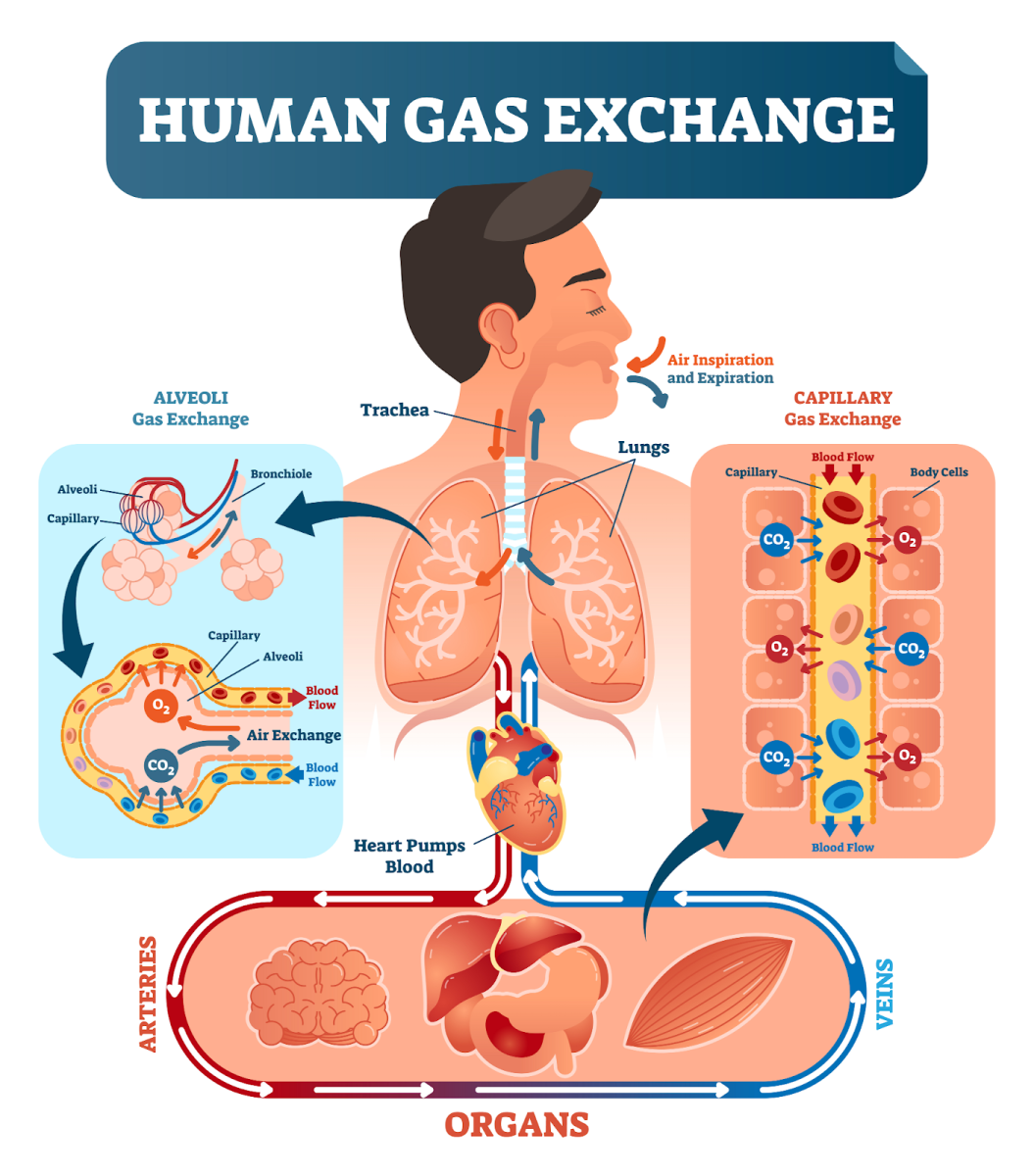
Example:
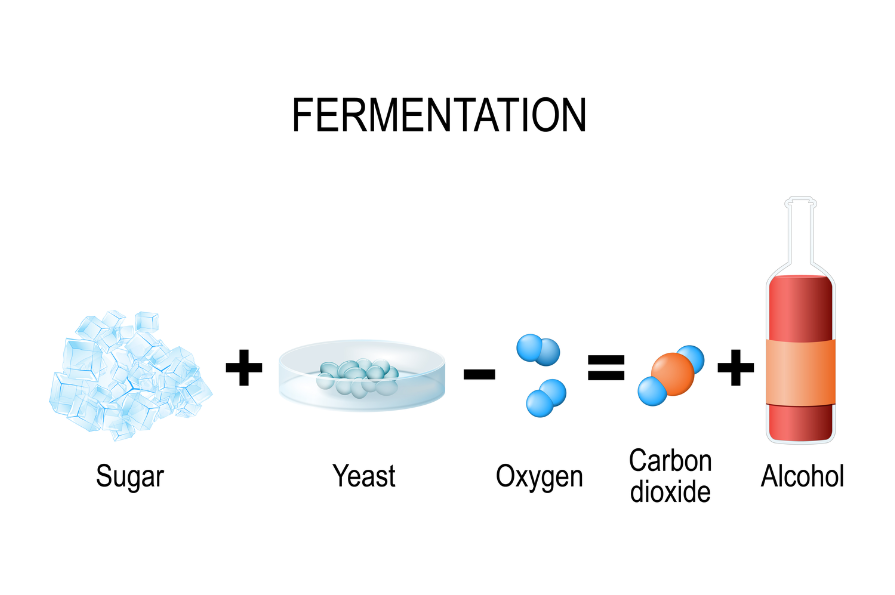
Yeast follows anaerobic respiration i.e respiration in absence of oxygen. The yeast utilise the glucose present in dough or any other substance and convert glucose into ethanol(Alcohol ) , carbon dioxide and little energy. This process is also called fermentation.
Also Check: Indirect Development in Biology
Figure- Fermentation in yeast
Types of Respiration
There are two main types of respiration:
Aerobic Respiration
- Occurs in the presence of oxygen.
- Involves the complete breakdown of glucose to carbon dioxide and water.
- Produces a large amount of ATP (38 ATP molecules).
- Takes place in the mitochondria of cells.
The overall equation is:
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + ATP
Anaerobic Respiration
- Occurs in the absence of oxygen.
- Involves the partial breakdown of glucose.
- Produces a smaller amount of ATP (2 ATP molecules).
- Takes place in the cytoplasm of cells.
- The end products can be either:
- Lactic acid (in animals)
- Ethanol and carbon dioxide (in yeast and some bacteria)
The overall equation is:
Glucose → Lactic acid/Ethanol + Carbon dioxide + ATP
The key differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration are the presence/absence of oxygen, the completeness of glucose breakdown, the amount of ATP produced, and the end products formed.
Also Check: Fertilization in BIology
Phases of Respiration in Organisms
Glycolysis
- Occurs in the cytoplasm of cells.
- Glucose is broken down into pyruvic acid.
- 2 ATP and 2 NADH molecules are produced.
- Pyruvate enters the mitochondria for further processing.
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
- Takes place in the mitochondrial matrix.
- Pyruvate is oxidized to CO2.
- 2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 FADH2 molecules are produced.
Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation
- Occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- NADH and FADH2 from glycolysis and Krebs cycle donate electrons.
- Electrons are passed through a series of carriers.
- As electrons move, they release energy used to pump H+ ions into the intermembrane space.
- H+ ions flow back through ATP synthase, driving the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP.
- Most ATP is produced in this phase (32-34 ATP per glucose).