What is Pollination?
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grains from a flower's male part (anther) to its female part (stigma). For successful pollination, the pollen grains must be transferred within the same flower species.

Pollination Definition
The transfer and deposition of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of a flower is called as pollination.
Process of Pollination
The process of pollination commences as pollen grains land on the stigma and form a pollen tube along the style, connecting the stigma to the ovary. Once the pollen tube is complete, sperm cells are transmitted from the pollen grain to the ovary. Subsequently, fertilization in plants occurs when the sperm cells reach the ovary and egg cells. The seed is then released from the parent plant, enabling it to germinate into a new plant, thus perpetuating the reproductive cycle through pollination.
Also Read: Asexual Reproduction
Types of Pollination
There are 2 types of pollination –
Self Pollination
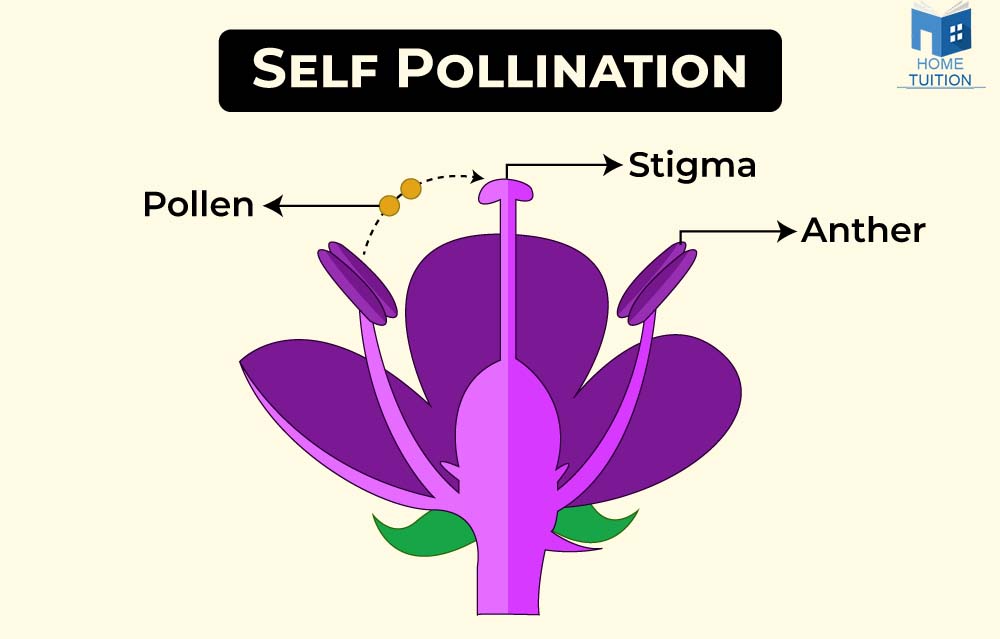
It is known as the primary form of pollination, involving a single flower. Self-pollination happens when pollen grains drop directly from the anther to the stigma. This process is simple and quick, reducing genetic diversity as the flower's sperm and egg cells share genetic information. It is further divided into two types :
- Autogamy: It is a type of self pollination in which the pollen grains are transferred from the anther to stigma of the same flower e.g. Wheat, rice pea etc.
- Geitonogamy: It is a type of self pollination in which the pollen grains are transferred from the anthers of one flower to the stigma of another flower borne either on the same plant or a genetically identical plant.
Also Read: Sexual Reproduction
Advantages and Disadvantages of Self-pollination
- Self-pollination helps in the elimination of recessive characters.
- The wastage of pollen grains is minimal in self-pollination compared to cross-pollination.
- Self-pollination maintains the purity of the race as there is no genetic diversity.
- Self-pollination does not rely on external factors like wind or water for pollination.
- Even a small quantity of pollen grains produced by plants in self-pollination has a high success rate.
Cross-Pollination
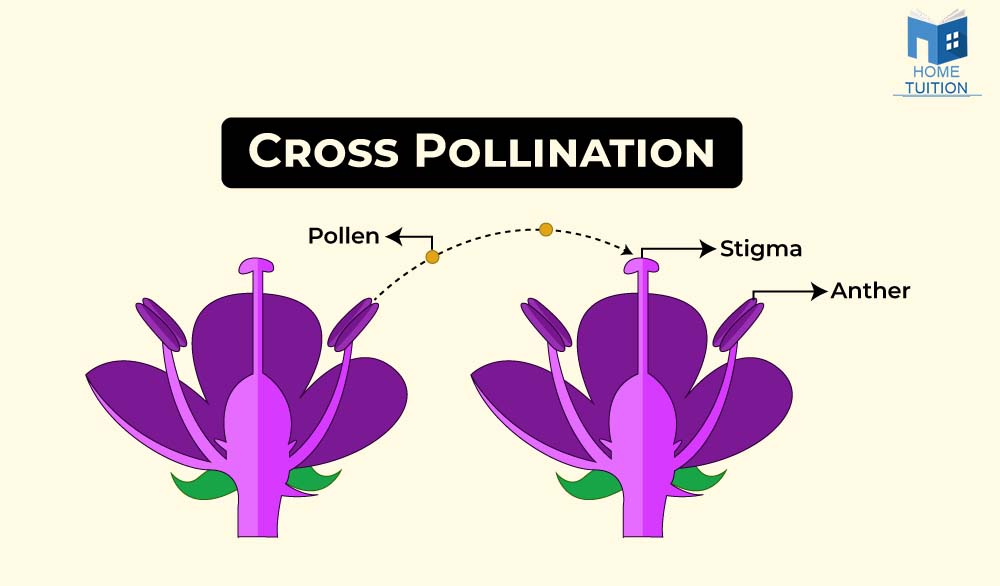
It is the process of transfer of the pollen grains from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower borne on a different plant of the same species.
Types of Cross-Pollination
The process of cross-pollination necessitates assistance from both biotic and abiotic agents such as animals, birds, wind, insects, water, and other pollinators.
Pollination by Wind- Anemophily
Only a few flowers utilize wind pollination, characterized by greenish, small, and odourless features. These flowers do not expend energy on colorful petals as they do not attract pollinators. This type of pollination occurs when plants lack nectar and other conspicuous features. Anemophilous flowers produce abundant pollen, and their stigmas are large, sticky, and feathery, extending outside the flower for better pollen capture.
Examples of wind-pollinated plants include coconut, palm, maize, grasses, and all gymnosperms. During spring, pollen is carried by the wind, coating surfaces like cars with a yellow film.
Also Read: Vegetative Propagation
Pollination by Animals – Zoophily
Animals play a crucial role in plant reproduction by aiding in seed dispersal. When animals consume fruits, they transport the seeds to new locations, facilitating the growth of new plants.
Artificial Pollination – Anthropophily
Human beings perform artificial pollination, also known as anthropophily. This method is used when natural pollination by abiotic or biotic agents is challenging. Pollen grains are manually spread over female flowers, and hybridization techniques are employed in this process.
Cross-pollination - Advantages
- The seeds produced exhibit strong vigour and vitality.
- Cross-pollination enables all unisexual plants to reproduce.
- Genetic recombination eliminates recessive traits in the lineage.
- This process enhances the offspring's immunity to diseases and environmental factors.
- Cross-pollination introduces new genes into species through fertilization between genetically distinct gametes.
Also Check: Nutrition In Plants
Cross-pollination - Disadvantages
- In this process, there is significant wastage of pollen grains.
- Due to genetic recombination during meiosis, there are possibilities of eliminating desirable traits and introducing undesirable characteristics in offspring.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans. Pollination involves transferring pollen from a plant's anther to its stigma, facilitating fertilization and seed production.
Ans. Pollination is crucial for plant reproduction. Pollen from a flower's anthers, the male part, is transferred to a pollinator. The pollinator then carries this pollen to another flower, where it adheres to the stigma, the female part. The fertilized flower ultimately produces fruit and seeds.
Ans. When birds, bees, bats, butterflies, moths, beetles, and other animals, as well as water or wind, transport pollen from one flower to another, or when it is transferred within flowers.
Ans. The two types of pollination are self-pollination and cross-pollination.