What is Osmosis in Class 9 Biology?
The process by which water molecules move across a cell's semi-permeable membrane from an area with a high concentration of water molecules to an area with a lower concentration is called osmosis.
A semi-permeable membrane, also known as a selectively permeable membrane, allows only certain molecules or ions to pass through.
Given the higher concentration of water molecules on one side of the semi-permeable membrane, it is likely that many water molecules will collide with and pass through the membrane.
Conversely, on the side with a lower concentration of water molecules, fewer will collide with and pass through the membrane.
This results in a net movement of water molecules towards the lower concentration. However, it is important to explain to children that water molecules move in both directions.
Also Check: Indirect Development in Biology
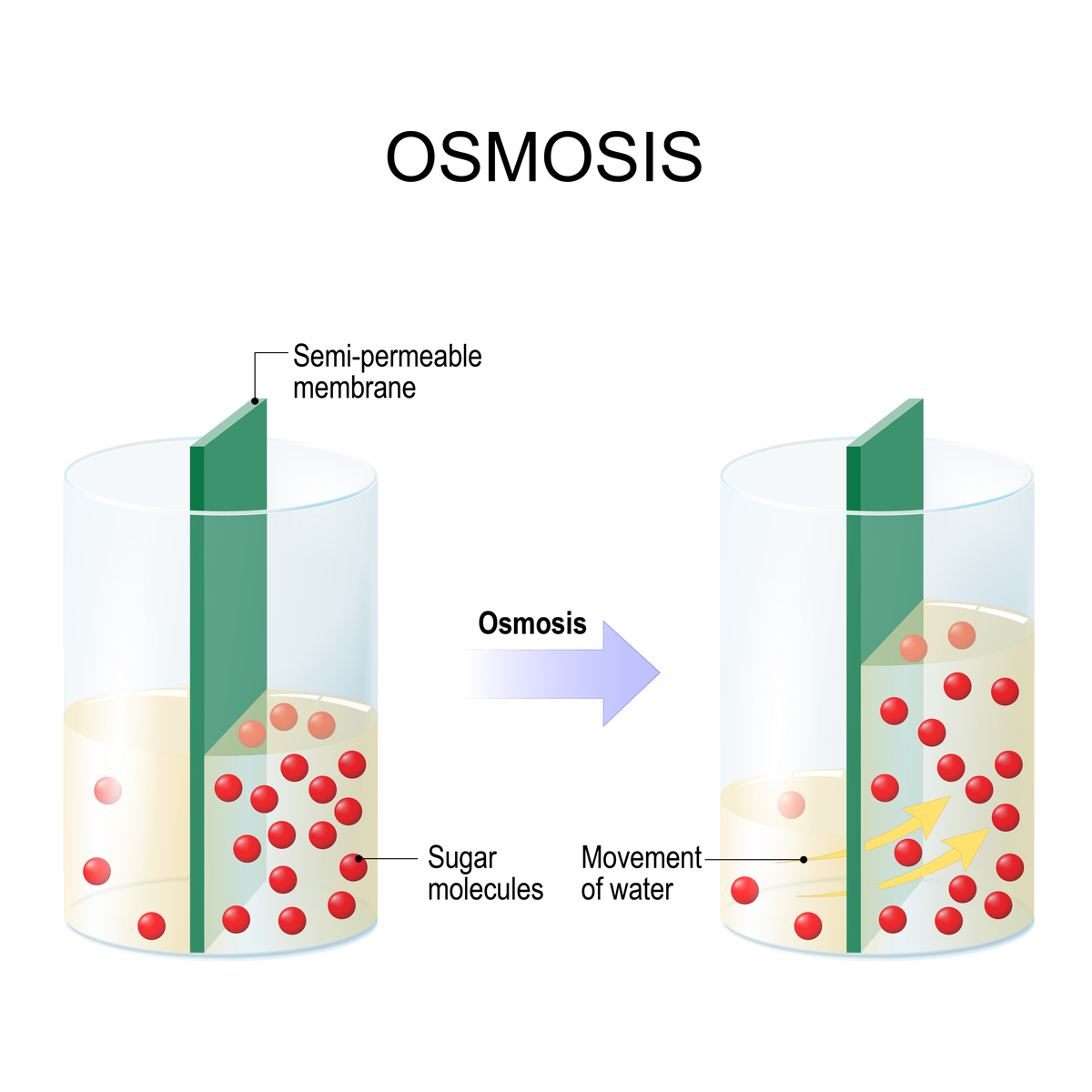
Osmosis in a Cell
The movement of water molecules through a cell's semi-permeable membrane from an area of higher water concentration to one of lower concentration is known as osmosis.
A selectively permeable membrane, or partially permeable membrane, allows only certain molecules or ions to pass through.
Due to the higher concentration of water molecules on the left side of the semi-permeable membrane, many water molecules are likely to collide with and pass through it.
Also Check: Respiration
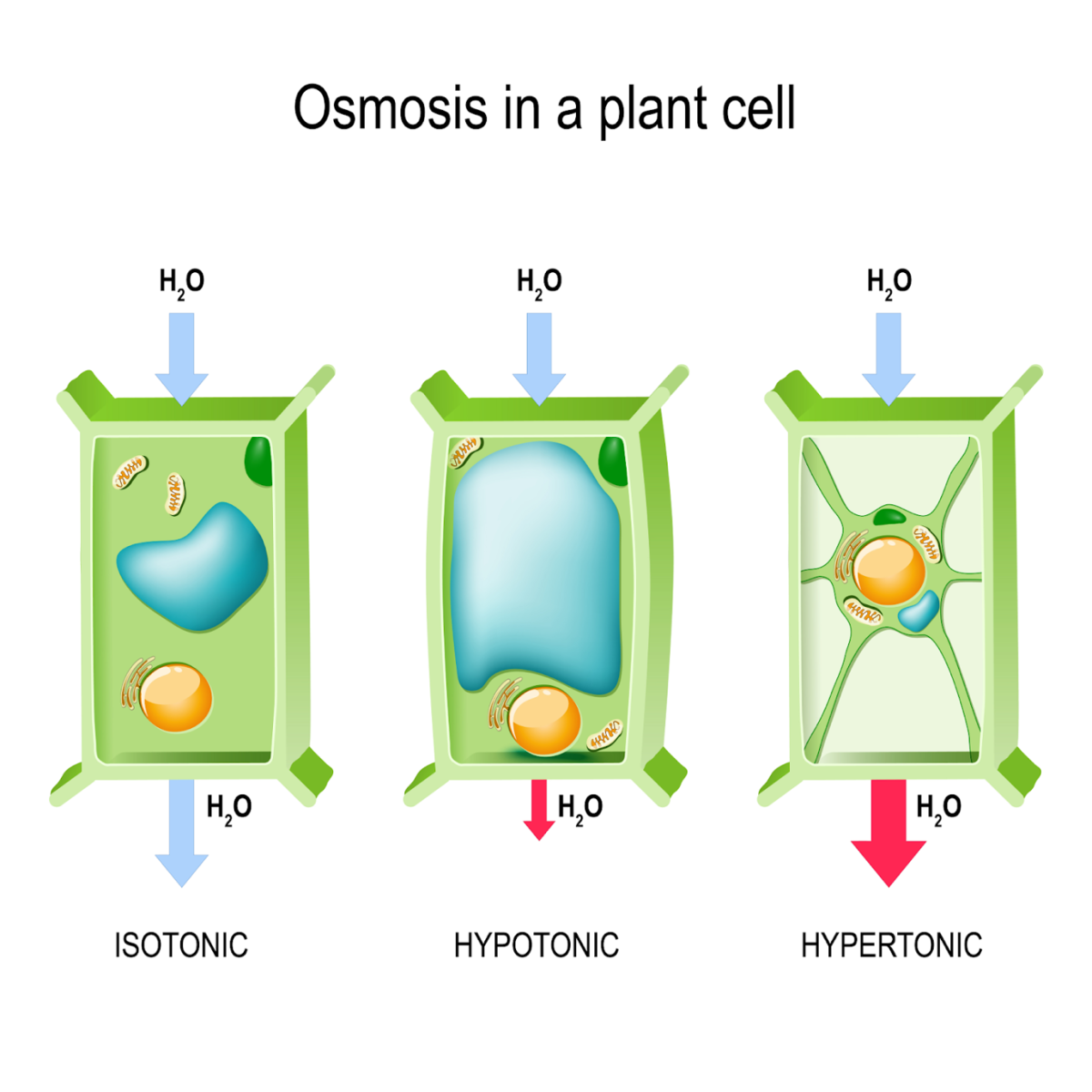
Types of Osmosis
-
Forward Osmosis: This is the process in which water molecules move across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. The goal is to balance solute concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
-
Reverse Osmosis: In this method, water is forced through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of high solute concentration to an area of low solute concentration using external pressure. This process is commonly used for water purification and desalination.
-
Chemiosmosis: This type involves the movement of ions across a membrane, typically within mitochondria or chloroplasts, during cellular respiration or photosynthesis. The energy from this ion movement is used to produce ATP, the energy currency of the cell.
Also Check: Fertilization in BIology
Effect of Osmosis on Cells
Osmosis is the movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane from a region of higher water concentration (lower solute concentration) to a region of lower water concentration (higher solute concentration). This process has different effects on plant and animal cells.
In plant cells, when placed in a hypotonic solution (higher water concentration), water enters the cell by osmosis, causing the cell to swell and the cell wall to become turgid. This provides structural support to the plant. In a hypertonic solution (lower water concentration), water leaves the plant cell by osmosis, causing the cell contents to shrink away from the cell wall (plasmolysis).
In animal cells, which lack a cell wall, the effects are different. In a hypotonic solution, water enters the animal cell, causing it to swell and potentially burst. In a hypertonic solution, water leaves the animal cell, causing it to shrink and become dehydrated.
Maintaining the right balance of solute concentrations on both sides of the cell membrane is crucial for proper cell function in both plants and animals. Osmosis plays a vital role in regulating the movement of water and solutes to keep cells healthy and functioning.
Significance of Osmosis
In Plant Cells:
- Helps absorb water from the soil through roots and root hairs
- Maintains water content and provides turgidity to plant cells
- Controls the opening and closing of stomata to regulate water loss
- Plays a crucial role in seed germination
In Animal Cells:
- Regulates the flow of water, dissolved solutes, and waste products across the cell membrane
- Assists in absorbing water from the intestines into the bloodstream
- Stabilizes the internal fluid levels and movement within the cell
- Facilitates the diffusion of nutrients and release of metabolic waste
Overall, osmosis is a vital passive transport process that helps maintain the proper balance of water and solutes on both sides of the cell membrane. This is essential for the healthy functioning and survival of both plant and animal cells.
Frequently Asked Questions
Osmosis is caused by the natural movement of water molecules from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration across a semi-permeable membrane. This movement occurs to equalize the concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
Yes, osmosis commonly occurs in water. Water is the most abundant solvent in living organisms and is essential for many biological processes. The movement of water across cell membranes through osmosis is crucial for maintaining the proper balance of water and solutes in cells and organisms.
One example of osmosis is the absorption of water by plant roots from the soil. The root cells have a higher solute concentration than the surrounding soil, causing water to move into the roots by osmosis. This process is essential for plant growth and survival.
Osmosis is defined as the spontaneous movement of solvent molecules, usually water, across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. This process continues until the concentrations on both sides of the membrane are equal.
Osmosis refers to the passive transport of water or other solvents through a semi-permeable membrane, driven by a difference in solute concentrations on either side of the membrane. It is a crucial process in living organisms, playing a vital role in maintaining the proper balance of water and solutes within cells and tissues.