Nutrition In Plants Definition
Nutrient in plants may be defined as a process of the synthesis of food, its breakdown, and utilization for various functions in the body.
Also Read: Neurons
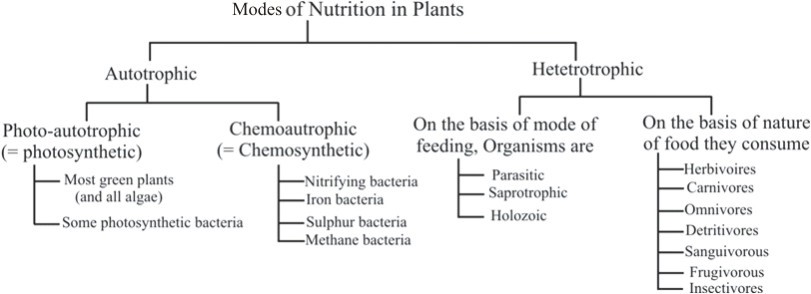
Modes of Nutrition
The process of acquiring and using food for growth, health, and repair is nutrition. Plants create food using raw materials like minerals, carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight. There are two types of nutrition:
- Autotrophic – Plants are autotrophs, producing food using light, carbon dioxide, and water.
- Heterotrophic – Animals and humans are heterotrophs, relying on plants for food.
Also Read: Asexual Reproduction
Autotrophs
The organisms which makes their own food from CO2 and H2O in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll are called autotrophs. e.g.: green plants and bacteria. All green plants are autotrophic and use light as a source of energy for the synthesis of materials.
- Photo-autotrophic: Those which utilize sunlight for preparing their food. e.g. plants, algae, purple red and green bacteria.
- Chemoautrophic: Those which utilize chemical energy for preparing their food. e.g.,Nitrifying bacteria, iron bacteria, sulphur bacteria, Methane bacteria.
Heterotrophs
The organisms which can not make their own food and depend directly or indirectly on autotrophs. E.g.; animals, fungi and most prokaryotic organisms.
Also Read: Sexual Reproduction
On the basis of mode of feeding, Organisms are categorized as:
Saprotrophic

- Organisms which get their food supply from dead or decaying organic matter are known as saprophytes.
- Common examples of saprophytes are bacteria, fungi like yeast and mushrooms, moulds etc.
- Saprophytes produce digestive enzymes which breaks down food into soluble form and it is then absorbed.
Also Check: Fibrous Joints
Parasitic
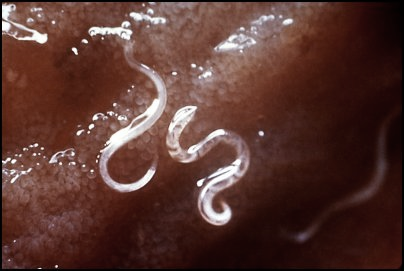
- The parasite is an organism which lives outside or inside the body of another organism called the host.
- Parasite derives its nutrition from the host and in turn cause harm to the host.
- Examples of parasites are disease causing Protozoans like Plasmodium, Trypanosoma, worms like round worms, flat worms and many fungi.
Holozoic
Complex organic matter is taken in by the body (ingestion), which is then digested and absorbed.
On the basis of food habits, holozoic animals are classified into three types:
- Herbivores – Cow, Sheep, Deer, Elephant
- Carnivores – Tiger, Leopard, Sharks, Snake
- Omnivores – Amoeba, Frog, Cockroach, Man
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans. The three types of nutrition in plants are: autotrophs, heterotrophs, and symbiotes.
Ans. Plants convert sunlight into chemical energy, making their food with carbon dioxide, water, and chlorophyll. This process, called photosynthesis, uses sunlight energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into food.
Ans. It is the mode of taking food by an organism and its utilisation by the body.
Ans. It create amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.