What is an Ecosystem?
The term Ecosystem was coined by Tansley. According to him Ecosystem is a symbol of structure and function of nature. The term Ecology was coined by Reiter. The term Ecology was first of all described y E.Haeckel.
Father of India Ecology - Prof. Ramdas Mishra. The boundaries of ecosystem are indistinct and have an overlapping character with each other. It means any structural and functional unit of the environment that can be identified and studied is called as ecosystem. Ecosystem may be natural or artificial, permanent or temporary. Large ecosystem is called as biome such as desert, forest etc.
Ecosystem Definition
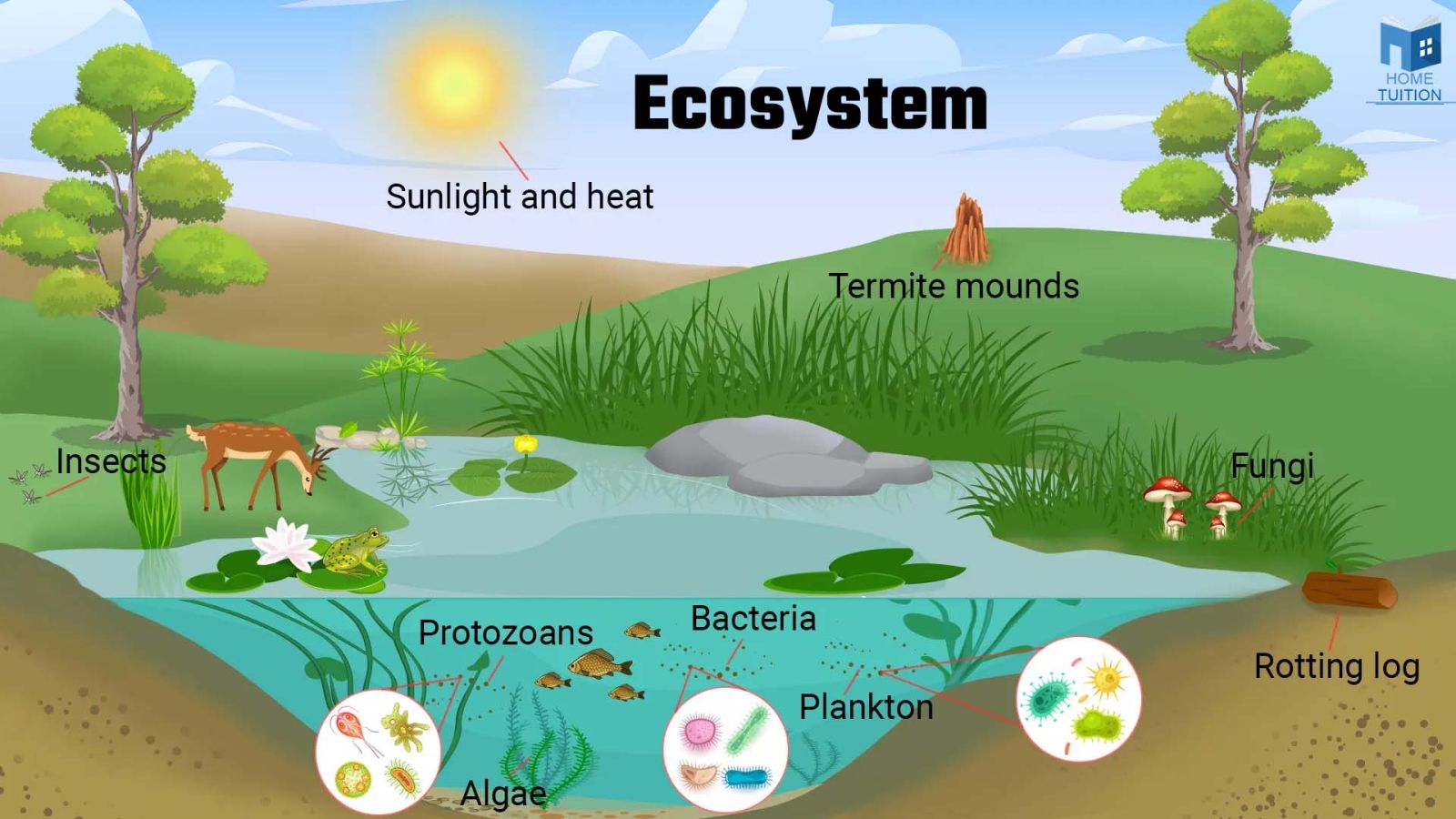
The total group of living things and environment of factors present in a particular place is called as ecosystem.
Also Read: Asexual Reproduction
Structure of the Ecosystem
The structure of an ecosystem is characterized by the physical organization of biotic & abiotic components. The major structural features of an ecosystem are species composition, stratification, trophic organization and nutrients.
- Species composition : Each ecosystem has its own type of species composition. Different ecosystems have different species composition. A great variety of species is found in forest ecosystem, whereas a few species occur in a desert ecosystem.
- Stratification : The organisms in each ecosystem from one or more layers or strata, each comprising the population of particular kind of a species.
- Trophic organization : Food relationship of producers and consumers is another way to predict ecosystem structure. In an ecosystem there an be only 4 - 5 successive trophic levels because
- All the food available in one tropic level is not being eaten by another animal in the next trophic level.
- All the food eaten by an animal is not useful, thus a part of energy containing food is passed out as waste products.
- A large amount of energy is lost in respiration to drive organisms metabolism and thus, there is not much energy left to support higher trophic levels.
Also Read: Sexual Reproduction
Components of Ecosystem
Ecosystem consists of two components :
- Biotic component
- Abiotic component
Biotic Components
Biotic components encompass all living elements within an ecosystem. They can be classified into autotrophs, heterotrophs, and saprotrophs (or decomposers) based on their nutrition.
Producers
All the autotrophs of ecosystem are called as producers. The green plants are the main producers. Green plants absorb solar energy and convert it into chemical energy. It means energy enters into the ecosystem through the produces. The solar energy is the only ultimate source of energy in ecosystem. This energy is available to the remaining living organisms through the medium of food.
Also Read: Pollination
Consumers
All the heterotrophy of the ecosystem are known as consumers. Animals are the main consumers. They directly (herbivorous) or indirectly (carnivorous) depend upon the producers. There are various types of consumer which are as follows :
- Primary consumers : They are also known as secondary producers because they synthesize complex materials in the cells by the digestion of food which they obtain from the plants. Such living organisms which obtain food form the producers are known as primary consumers. Such as all the herbivores of ecosystem.
- Secondary consumers : Animals which feed upon primary consumers and obtain their food. It means those carnivorous which kill and eat the herbivorous. So that they are called as predators e.g. Dog, Cat, Snake etc. In aquatic system whale fish is a secondary consumer.
- Top consumers : Those animals which kill other animals and earth them by they are not eaten by other animals in the nature .e.g Lion, Vulture, Peacock and Man (human) in our ecosystem. Man and peacock may be omnivorous.
Decomposers or Microconsumer
Those living organisms which decompose the dead bodies of producers and consumers and release mineral substances again into the soil which are present in the dead bodies. So that decomposers help in mineral into the soil which are present in the dead bodies. So that decomposers help in mineral cycle. Only because of this land is the main source of minerals. The main decomposers in ecosystem are - bacteria and fungi which decompose continuously dead animals and dead plants.
Scavengers
Vulture never kills any animal so that vulture is a scavenger, not a decomposer. The process of decomposition takes place outside the body of bacteria. The break down of the food materials takes place in the body of vulture and minerals are released into the soil in the form faecal material. They are also called as reducers because they decomposes and remove the dead bodies of the organism.
Functions of an Ecosystem
- Productivity : Ecosystem helps of maintain the productivity, of the system. The rate of organic matter or biomass production is called as productivity. The study of biomass production in the ecosystem is called as production ecology.
- Energy flow : Energy flow in an ecosystem is a key function of an ecosystem.
- Nutrient cycles : All living organisms get matter from the biosphere component i.e. lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere. Essential elements or inorganic substances are provided by earth and are required by organisms for their body building and metabolism, they are known as biogeochemical or biogenetic nutrients.
- Development and stabilization : This function is necessary for the development and giving stability to various life form’s by undergoing certain modifications.
Also Check: Nutrition In Plants
Types of Ecosystem
There are two types of ecosystem:-
Terrestrial Ecosystems
Terrestrial ecosystems consist solely of land-based ecosystems, which are found in various geological zones. Various types of terrestrial ecosystems are distributed across these zones, including:
- Forest Ecosystem
- Grassland Ecosystem
- Tundra Ecosystem
- Desert Ecosystem
Aquatic Ecosystem
Aquatic ecosystems refer to ecosystems found in a water body. These can be categorized into two types, namely:
- Freshwater Ecosystem
- Marine Ecosystem
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans. A community or group of organisms that coexist and interact with each other within a defined environment.
Ans. The four types of ecosystem are - artificial, terrestrial, lentic and lotic.
Ans. Sir Arthur G. Tansley
Ans. The seven main ecosystems are - forest ecosystem, grassland ecosystem, tundra ecosystem, desert ecosystem, freshwater ecosystem, and marine ecosystem.
Ans. There are five main types of ecosystems: aquatic, grassland, forest, desert, and tundra.