Are you curious to know about the first organism that appeared on Earth? For a glimpse, it was none other than "BACTERIA," suggesting life probably began around 4 billion years ago. The oldest known fossils are bacteria-like organisms. Bacteria were the first life forms on Earth, appearing roughly 4 billion years ago. From these primordial microbes, life has diversified into an incredible variety of organisms over millions of years. This article provides an in-depth examination of bacteria, exploring their origins, structures, and their role as the foundation of all life on Earth.
Introduction
Bacteria belong to the prokaryotic group, one of the three domains of life, alongside archaea and eukaryotes. These microscopic organisms have a significant history of both infecting humans and supporting human health. Bacteria exhibit a remarkable variety and diversity, thriving in a wide range of habitats.
Definition:
"Bacteria are unicellular organisms lacking a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They possess distinct structural, physiological, and evolutionary characteristics."
Diagram of Bacteria
The diagram below illustrates the structure of a typical bacterial cell, highlighting key parts such as the cytoplasm, plasmid, cell wall, and flagella.
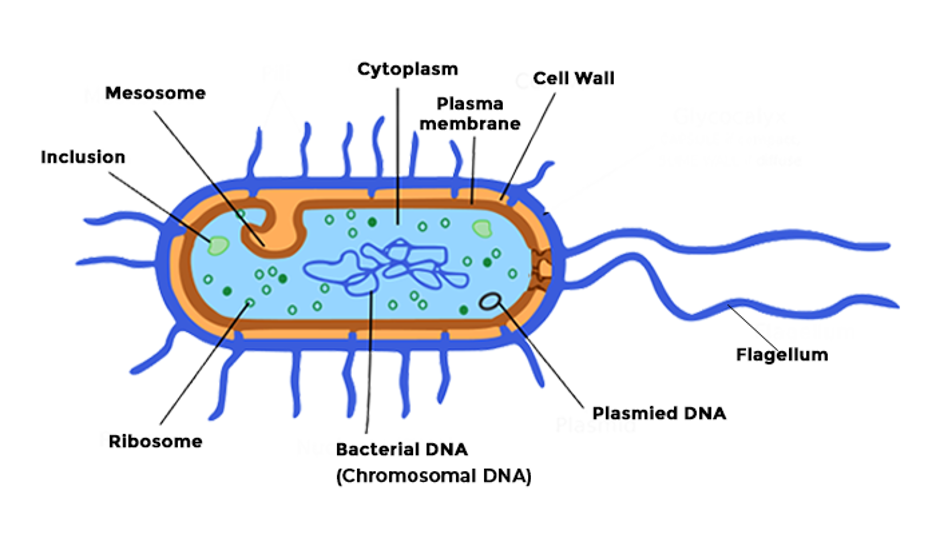
History
- Germ Theory: Louis Pasteur and Robert Koch proposed that diseases are caused by germs.
- Antibiotics: In 1910, Paul Ehrlich developed Salvarsan, the first antibiotic to treat syphilis.
- Gut Microbiome: In 2001, Joshua Lederberg introduced the term "gut microbiome," referring to all bacteria present in the intestine. Scientists are now extensively studying the gut microbiome to understand its structure, types, and benefits.
Scientists from around the world are actively exploring the “gut microbiome” to gain deeper insights into the various bacteria residing in the human intestines. Their ongoing research aims to reveal the intricate structures, classifications, and beneficial roles of these microorganisms, and they have made impressive progress in this field.
Characteristics of Bacteria
Bacteria have several fundamental characteristics:
- Unicellular and lack organelles such as chloroplasts and mitochondria.
- Possess continuous, circular DNA located in a nucleoid.
- Have a cell membrane and typically a cell wall made of peptidoglycan.
- Reproduce asexually through binary fission.
- Daughter cells resulting from binary fission have identical DNA to the parent cell.
Types of Bacteria
Bacteria can be categorized into different types based on several distinct criteria:
- Shape
- Composition of the cell wall
- Mode of respiration
- Mode of nutrition
- Temperature
Based on Shape
| TYPES | EXAMPLES |
| Bacillus (Rod-shaped) | Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Spirilla or spirochete (Spiral) | Spirillum volutans |
| Coccus (Sphere) | Streptococcus pneumoniae |
| Vibrio (Comma-shaped) | Vibrio cholerae |
Based on cell wall composition
| Type | Example |
| Peptidoglycan cell wall | Gram-positive bacteria |
| Lipopolysaccharide cell wall | Gram-negative bacteria |
Based on Respiration
| Type of Classification | Examples |
| Anaerobic Bacteria | Actinomyces |
| Aerobic Bacteria | Mycobacterium |
Based on mode of nutrition
Bacteria can be categorized according to their nutritional methods, as outlined below:
- Heterotrophic bacteria
Obtain energy by consuming organic carbon, either by absorbing dead organic material or through parasitism.
- Autotrophic bacteria
Bacteria utilize different methods for food production, including photosynthesis and chemosynthesis.
- Those that perform photosynthesis are known as photoautotrophs. Examples of these include Cyanobacteria, which are well-known for oxygen production, and heliobacteria.
- Conversely, bacteria that rely on chemosynthesis for energy are termed chemoautotrophs.
- These include organisms found in extreme environments such as ocean vents and also those associated with the roots of legumes like clover, beans, and peanuts.
Based on temperature
1. Psychrophiles:
- Grow between -20°C to 20°C
Examples: Vibrio marinus, Psychroflexus.
2. Psychrotrophs (facultative psychrophiles)
- Grow at 0°C but optimally at 20-30°C (e.g., Pseudomonas, Flavobacterium).
- For Example Pseudomonas, Flavobacterium, Alcaligenes, Acinetobacter, and Bacillus
3. Mesophiles
- Optimal growth at 37°C, common human pathogens (e.g., E. coli, Salmonella).
- Human pathogens are mesophilic.
- Examples: E. coli, Salmonella, Klebsiella, Staphylococci.
4. Thermophiles
- Bacteria which grow above 45 degrees celsius are called thermophiles.
- Examples: Streptococcus thermophilus, Bacillus stearothermophilus, Thermus aquaticus.
5. Hyperthermophiles
- Bacteria which have an optimum temperature of growth above 80 degrees celsius are called hyperthermophiles.
- Examples: Thermodesulfobacterium, Aquifex etc.
Reproduction in bacteria
Bacteria reproduce and modify themselves through:
- Binary fission
In this process single bacterium divides into two daughter cells which are identical to the parent cell as well as to each other. The beginning of fission is the replication of DNA within the parent bacterium.
- Transfer of genetic material
Through processes known as conjugation, transformation, or transduction cells acquire new genetic material.
- Spores
When some types of bacteria are low on resources, they form spores that hold the organism’s DNA material and contain the enzymes needed for germination.
Useful Bacteria
- Lactobacillus: Converts milk into curd and aids in digesting dairy products.
- Streptococcus and Bacillus: Used in food fermentation.
- Gut microbiome: Enhances the body's immune system.
- Antibiotics production: Streptomycin and tetracycline.
- E. coli: Aids digestion in animals.
- Bacillus thuringiensis: Eco-friendly pesticide alternative.
- Rhizobium: Facilitates nitrogen fixation for plants.
- Anaerobic bacteria: Aid in sewage treatment and cleaning oil spills.
- Research: Used in molecular biology, biochemistry, and genetics.
Harmful bacteria
These types of bacteria are referred to as pathogenic bacteria due to their role in causing a variety of diseases and health conditions.
- Strep throat: Streptococcus bacteria
- Staph infection: staphylococcus bacteria.
- Cholera:Vibrio cholerae
- Tuberculosis:Salmonella Typhi:
- Food poisoning:Clostridium botulinim
- Tetanus:Clostridium tetani.
Common Bacterial infection
Some other common infections are mentioned below:
- Ear infection
- Strep throat
- Sinusitis
- Whooping cough
- Bacterial meningitis
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Bacterial vaginosis (BV)
- Syphilis
- Gonorrhea
- chlamydia.
Prevention of Bacterial infection
- Proper wound care.
- Timely vaccinations.
- Use of surface disinfectants.
- Cooking food thoroughly.
- Maintaining hygiene.
- Sterilizing surgical equipment.
- Regular handwashing.
- Practicing safe sex.
- Avoiding sharing personal items.
- Staying clean and healthy.
- Avoiding unprotected sexual intercourse.
- Being mindful and avoiding public places visiting if infected.
- Avoid sharing personal items like toothbrushes, razors, soap, utensils, handkerchiefs etc.
- Staying neat and clean.
Frequently Asked Questions
Bacteria are tiny, single-celled microorganisms that lack a nucleus and can live in various environments. They are among the earliest forms of life on Earth and can be found in nearly every habitat.
The term “bacteria” comes from the Greek word “bakterion,” which means “small staff” or “rod,” referring to the rod-shaped appearance of many bacteria. It was first used in the 19th century to describe these microorganisms.
Bacteria are single-celled organisms that can be found in diverse environments. They play crucial roles in processes such as breaking down organic matter, producing food and medicine, and aiding digestion. For example, bacteria are used in making yogurt, cheese, and antibiotics.
Bacteria can be categorized into four main types based on their shapes and structural characteristics:
- Cocci: Spherical bacteria, such as Streptococcus.
- Bacilli: Rod-shaped bacteria, like Escherichia coli.
- Spirilla: Spiral-shaped bacteria, such as Spirillum.
- Vibrios: Comma-shaped bacteria, like Vibrio cholerae.