Worksheet for class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
This page consists of MCQ-based questions with detailed solutions for Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants of class 7 science prepared by HT experts. Check out all the worksheets for class 7 science. Do solve NCERT textbook with the help of NCERT solutions for class 7 science.
1. Which one of the following is not an insectivorous?
(a) 
(b)
(c) 
(d)
Answer:
(b)
It shows different type of nutrition which is called symbiosis.
2. Select the correct option regarding the two figures :
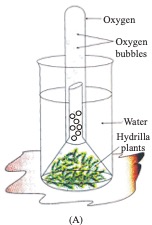
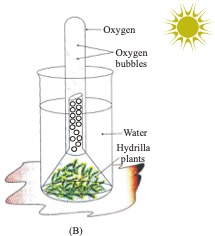
(a) more bubbles will be observed in A, in 10 min.
(b) more bubbles will be observed in B, in 10 min.
(c) no bubble will be observed in both A and B
(d) same no. of bubbles will be observed in A and B in 10 min.
Answer:
(b)
More bubbles will be observed in B in 10 min. because rate of photosynthesis increases in presence of sunlight and rate of photosynthesis amount of O2.
3. Which of the following raw material is not necessary for photosynthesis?
(a) CO2
(b) H2O
(c) Sunlight
(d) Nitrogen
Answer:
(d)
Plants are the autotrophs that can prepare food for themselves by using CO2, H2O and minerals in the presence of sunlight. Nitrogen is not required for photosynthesis.
4. Identify X in the following reaction :
CO2+ Water![]() X + Oxygen
X + Oxygen
(a) Vitamin
(b) Protein
(c) Carbohydrate
(d) Minerals
Answer:
(c)
During photosynthesis, chlorophyll containing cells of leaves in the presence of sunlight, use carbon dioxide and water to synthesis carbohydrates. The process can be represented as an equation:
Carbon dioxide + Water ![]() Carbohydrate + Oxygen.
Carbohydrate + Oxygen.
Presence of starch, a carbohydrate in the leaves is regarded as an evidence of photosynthesis.
5. Which of the following is the function of stomata?
(a) Carbon dioxide enters the leaf through stomata.
(b) Oxygen discharges into the atmosphere from the leaf through stomata.
(c) Food material synthesised in leaf is discharge into the atmosphere from the leaf through stomata.
(d) Water enter the leaf through stomata.
Answer:
(a)
Small pores are present on the lower surface of leaf. These pores performs the function of exchange of gases i.e. CO2enters the leaf and oxygen go out of the leaf. These pores are also control the rate of transpiration.
6. Pitcher plant is green in colour but it eats insects to complete the requirement of
(a) water
(b) carbon dioxide
(c) nitrogen
(d) oxygen
Answer:
(c)
Insectivorous plants, in fact, are green plants which prepare their own food from the raw material (carbon dioxide, water and sunlight) obtained from the soil and atmosphere, just like the autotrophs. The nitrogen requirement of these plants is provided by the insects which these plants capture.
7. Two different organisms living together and both benefiting from each other, are known as
(a) saprophytic
(b) symbiotic
(c) parasitic
(d) heterotrophs
Answer:
(b)
Some organisms live together and share shelter and nutrients. This is called symbiotic relationship. For example, certain fungi live in the roots of trees. The tree provides nutrients to the fungus and, in return, receives help from it to take up water and nutrients from the soil. This association is very important for the tree.
8. Saprophytic mode of nutrition is found in
(a) lichens
(b) bladderwort
(c) mushroom
(d) cuscuta
Answer:
(c)
Saprophytic mode of nutrition is found in mushrooms. In this mode of nutrition plant feeds on dead and decaying organic matter. The mode of nutrition of other three are given below.
Bladderwort Insectivorous mode of nutrition
Lichens Symbiotic mode of nutrition
Cuscuta Parasitic mode of nutrition
9. Which of the following is not true about saprophytic plants?
(a) These plants are green in colour.
(b) These plants are commonly seen during and after rain.
(c) Yeast shows saprophytic mode of nutrition.
(d) These plants secrete digestive juices from the dead and decaying organic matter..
Answer:
(a)
These plants lack green colour. They feed on digestive juices from the dead and decaying organic matter.
10. The green colour pigment in the leaves is
(a) chlorophyll
(b) anthocyanin
(c) protoplast
(d) chloroplast
Answer:
(a)
The leaves have a green pigments called chlorophyll. It helps leaves to capture the energy of the sunlight. This energy is used to synthesise food from carbon dioxide and water.
11. Which of the following part/s of a desert plant perform the function of photosynthesis?
(a) Leaves
(b) Stem
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c)
Besides leaves, photosynthesis also takes place in other green parts of the plant in green stems and green branches. The desert plants have scale- or spine-like leaves to reduce loss of water by transpiration. These plants have green stems which carry out photosynthesis.
12. Which of the following statements is false?
(a) Green plants are autotrophs.
(b) Photosynthesis takes place mostly in green leaves which contain green pigment, chlorophyll inside chloroplasts.
(c) Non-green plants and animals are heterotrophs.
(d) Photosynthesis does not takes place in deep red, violet or brown leaves.
Answer:
(d)
The leaves other than green also have chlorophyll. The large amount of red, brown and other pigments mask the green colour. Hence, photosynthesis also takes place in these leaves.
13. In a lichen which of the following is autotrophic?
(a) Algal partner
(b) Fungal partner
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a)
In a lichen, algal and fungal partners live together and both are mutually beneficial. Algal, a chlorophyll containing component of a lichen is autotropic. It provides food material to the fungal component in the lichen. In return, the fungus (heterotroph) provides shelter, water and minerals to the alga.
14. Which of the following is false statement?
(a) Rhizobium can take atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into a soluble form.
(b) Though nitrogen gas is available in plenty in the air, plants cannot use it in the manner they can use carbon dioxide.
(c) Plants need nitrogen in a soluble form.
(d) Rhizobium feed on atmospheric nitrogen.
Answer:
(d)
Rhizobium do not feed on atmospheric nitrogen. It cannot make its own food. So it lives in the roots of gram, peas, moong beans and other legumes and provide them nitrogen. In return, the plants provide food and shelter to the bacteria.
15. We will observe some green patches on a moist piece of bread if we leave it in moist warm place for 2-3 days. The green patches are
(a) green leafs
(b) atmospheric nitrogen
(c) water mixed with dust particles
(d) fungi
Answer:
(d)
These organisms are called fungi. They have a different mode of nutrition. They secrete digestive juices on the dead and decaying matter and convert it into a solution. Then they absorb the nutrients from it.
16. Farmers need to add nitrogen fertilizers to the soil in which.
(a) moong beans are grown
(b) peas are grown
(c) gram are grown
(d) wheat are grown
Answer:
(d)
Gram, peas and moong beans are leguminous plants. Rhizobium present in roots of these plants convert atmospheric nitrogen into the soluble form. That's why farmers do not need to add nitrogen fertilizers to the soil when moong beans, peas or gram to be grown in soil. Only wheat plant need nitrogen from soil to complete its requirement.
17. Heterotrophic plants are these which
(a) feed on dead and decaying organisms.
(b) draw nutrition from the living tissues of other organisms.
(c) depend on sources other than themselves for food.
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d)
Many plants (for example, fungi and bacteria) lack chlorophyll and cannot prepare their own food. Similarly, many plants derive their food by feeding on dead and decaying bodies, or by living in or on the bodies of other living organisms. Four such methods of heterotrophic nutrition are:
I. Saprophytic; II. Parasitic; III. Symbiotic; IV. Insectivorous.
18. Which one of the following organisms is a producer?
(a) Yeast
(b) Cow
(c) Grass
(d) Paramecium
Answer:
(c)
Producers can make their own food. Grass can produce its own food. It has chlorophyll to trap energy from sunlight for photosynthesis. The other organism can not produce their own food because they do not have chlorophyll.
19. What will happen on the earth in the absence of photosynthesis?
(a) Fruits are not available to eat.
(b) We can not get relief under the shadow of trees in hot summer days.
(c) All the flowers will be destroyed.
(d) Life would be impossible on earth.
Answer:
(d)
In the absence of photosynthesis there would not be any plants. The survival of almost all living organisms directly or indirectly depends upon the food made by the plants. Besides, oxygen which is essential for the survival of all living organisms is produced during photosynthesis. In the absence of photosynthesis, life would be impossible on the earth.
20. Amarbel is a
(a) host
(b) parasite
(c) authotroph
(d) saprotroph
Answer:
(b)
Amarbel does not have chlorophyll. It takes readymade food from the plant on which it is climbing. Since it deprives the host of valuable nutrients, it is called a parasite.
21. Which of the following is correct?
(a) Fungi like yeast and mushrooms are useful.
(b) Some fungi cause diseases in plants.
(c) Some fungi are also used in medicines.
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d)
We use mushroom as vegetable in our food. Some fungi are useful to men as these are used in medicines and some are harmful and causing disease (ringworm) to us.
22. Which of the following season provides ideal conditions for a fungi to grow are
(a) Cold weather
(b) Raining season
(c) Hot and humid weather
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d)
The fungal spores are generally present in the air. When they land on wet and warm things they germinated and grow.
23. Photosynthesis is a
(a) natural process
(b) chemical process
(c) natural chemical process
(d) physical process
Answer:
(c)
It is a natural chemical process in which plants makes their food with the help of CO2and H2O in the presence of sunlight.
24. Match the given in list I with the definition in list II :
| List I | List II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| I. | Nutrition | A. | Organism deriving its food from dead and decaying plants and animals |
| II. | Parasite | B. | Association of two different organisms in which both are benefited |
| III. | Saprophyte | C. | Process of obtaining and utilising food |
| IV. | Symbiosis | D. | Organism that derives its food from the living body of another organism |
(a) I-B, II-C, III-D, IV-A
(b) I-C, II-D, III-A, IV-B
(c) I-D, II-A, III-B, IV-C
(d) I-A, II-B, III-C, IV-D
Answer:
(b)
25. Variegated leaf means
(a) green leaf
(b) leaf having both green and white or yellow part
(c) Red leaf
(d) Black leaf
Answer:
(b)
Variegated leaves have both green and white or yellow parts in the same leaf. It shows that chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis.
Questions and answers for CBSE class 7 science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants Set-1
1. Living organisms are made up of tiny units called
(a) Nucleus.
(b) Cell.
(c) Cytoplasm.
(d) Cell membrane.
Answer:
(b)
Explanation: All living organisms are made up of a basic tiny unit called cell. Many cells join together to form a tissue, which in turn form organ, organ system and in the last a complete organism. Nucleus, cell membrane and cytoplasm are the components of a cell.
2. Stomata is surrounded by
(a) Guard cells.
(b) Chlorophyll.
(c) Carbohydrates.
(d) None of them.
Answer:
(a)
Guard cells.
Explanation: Guard cells are the chlorophyll containing cells that surround the stomatal opening and help in the opening and closing of stomata.
3. During photosynthesis, carbohydrates get converted to
(a) Proteins.
(b) Starch.
(c) Carbohydrates.
(d) All of them.
Answer:
(b)
Starch.
Explanation: During photosynthesis, carbohydrates get converted to starch which itself is a carbohydrate.
4. Slimy green patches are formed in ponds by
(a) Fungi.
(b) Algae.
(c) Bacteria.
(d) Lichens.
Answer:
(b)
Explanation: A slimy green layer of patches is formed on the surface of stagnant waters and ponds by the growth of certain organisms called algae.