The Sun, its planets and all the objects moving around it collectively form the solar system. Hence, the members of the solar system are:
- Sun
- Planets and Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids
- Meteors and Meteorites
- Comets
The Sun is the centre of a huge rotating system consisting of eight planets, dwarf planets, their satellites and numerous small bodies known as asteroids. The solar system is entirely dependent on the Sun, which is the most massive body and the only one which is self-luminous. The remaining members of the solar system shine by reflected sunlight and appear brilliant in our skies.
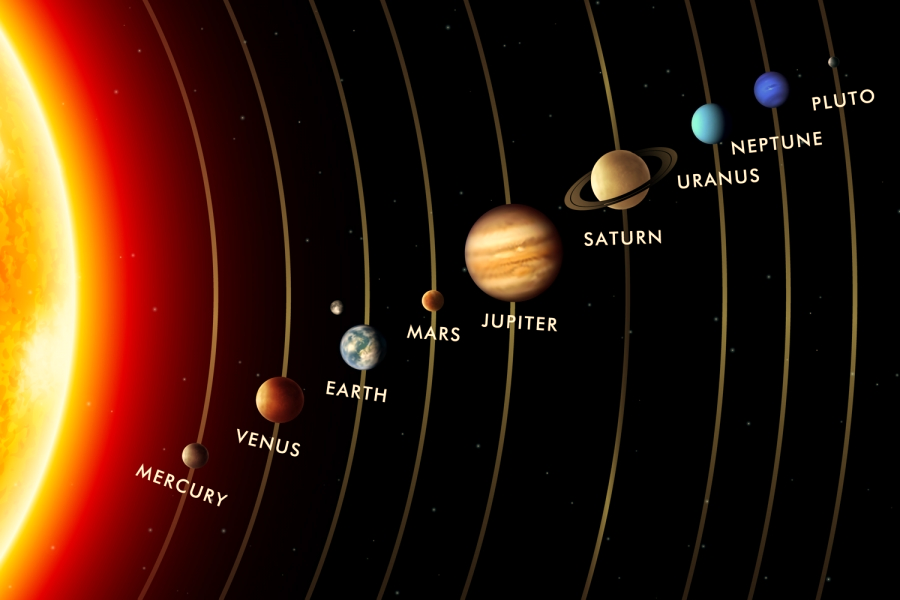
The Solar System
The radius of the Solar System is more than 5900 x 106 km which is the distance from the Sun to the farthest known planet, Pluto.Under the influence of the Sun’s gravitational force, each planet follows an elliptical orbit and travels in an anti-clockwise direction.
All planets rotate anti-clockwise (west to east) on their axis, with the exception of Venus and Uranus (Venus and Uranus rotate in the clockwise direction).
Also Check: Force
The Sun
The Sun is at centre of the Solar System and is believed to be at least 5000 million years old. It is the nearest star to the Earth. It is the provider of energy for life on Earth.
- Like all stars, the Sun is made of hot burning gases. Hydrogen and helium are the main gases that make up the Sun. It has a surface temperature of about 6000oC. The temperature at the centre is around 1,40,00,000oC.
- The Sun is about 150 x 106 km away from the Earth. Light, which travels at the speed of 3,00,000 km/s takes about 8 minutes to reach the Earth from the Sun.
The diameter of the sun is 109 times the diameter of the earth. In volume it is 1.3 million times bigger than the earth. Gravitational pull of the sun is 28 times the gravity of the earth. A body weighing 1 kg on the earth will weigh 28 kg on the sun.
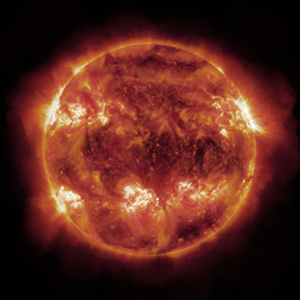
A photograph of the Sun showing solar flares
The sun rotates on its axis, as the earth does. The sun completes one rotation in about 25 days. It also revolves around the centre of the galaxy once in 225 million years.
Energy Source of the Sun
The core of the Sun is the powerhouse of the Sun and all the energy is generated here through a process called nuclear fussion.
There is enough hydrogen available to keep the Sun shining in its present form for at least another 5000 million years, or maybe longer.
Sunspots
The surface of the Sun has dark patches known as sunspots. These are patches of gas that look dark since they are cooler. They are caused by magnetic fields that slow down the heat from the Sun’s centre.Galileo first discovered them, and from their motion he deduced that the Sun rotates on its axis.
Also Check: Refraction
PLANETS AND DWARF PLANETS
Planets
Planets are solid heavenly bodies which revolve around the Sun in closed elliptical orbits. There are eight planets in the Solar System. Almost all the planets fall into two groups:
- Inner Planets: Mercury, Venus, Mars and Earth are called the Inner Planets. They are also known as terrestrial (Earth-like) planets.
- Outer Planets: These lie beyond the orbit of Mars. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are the Outer Planets.
There is another way of grouping the planets. Planets do not have light of their own but shine due to the reflected light of the sun. Important features of the planets are discussed below. These eight planets are in order of their distance from the Sun.
- Mercury (Budh) : The Innermost Planet

- It is the closest planet to the Sun.
- Large variations in day and night temperatures. Day temperature is 400oC; Night temperature is 180oC.
- Does not have any satellite.
- Does not support life as it has no atmosphere.
- Can be seen with the naked eye.
- Venus (Shukra): The Veiled Planet

- Brightest and hottest planet. Surface temperature is 450oC
- Does not have any satellite.
- Covered by dense yellow-white clouds of sulphuric acid gas which prevents the trapped heat to escape.
- Also known as the Morning star and Evening star.
- Can be seen with the naked eye.
- Earth (Prithvi): The Blue Planet
.png)
- Earth is the only planet that has an atmosphere that supports life. The atmosphere consists of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and water vapour
- Largest member of the group of inner planets.
- Has one natural satellite- the Moon.
- The Earth is called a watery planet because 70% of its surface is covered with water.
- The Earth reflects about one-third of the light that falls on it.
- The Earth’s atmosphere scatters the light and creates a predominantly blue planet
- Mars (Mangal): The Red Planet

- Closest planet to the Earth.
- It has two satellites.
- Does not support life as the atmosphere contains 95% carbon dioxide and only traces of oxygen.
- Absence of free water.
- Reddish planet and can be seen with naked eye.
- Jupiter(Brishaspati): The Giant Planet
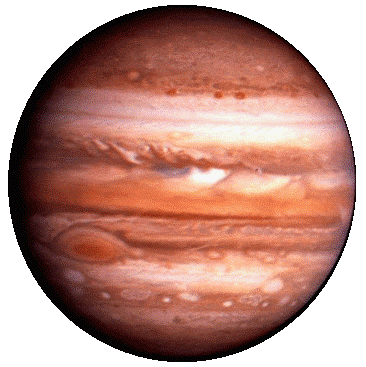
- Largest planet and has a mass 318 times more than that of Earth.
- Has gaseous surface of hydrogen and helium. The mixture is so compressed in the lower regions that it behaves more like a liquid than a gas. Deep within the core, the hydrogen is almost solid and shows metallic properties.
- Has at least 16 satellites.
- Can be seen with the naked eye.
- Jupiter is an “upright” planet, unlike the Earth, which tilts on its axis. The Earth is inclined at an angle of 23.5o from the perpendicular to the plane of the orbit. In the case of Jupiter, the tilt is only 3.1o.
- Saturn(Shani): The Jewel Planet
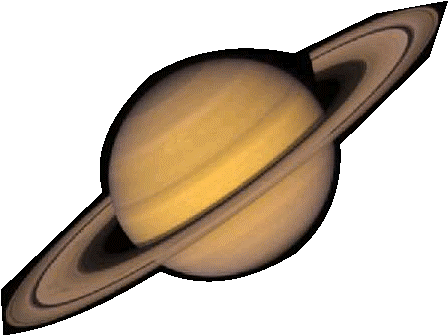
- Second largest planet and has a mass 95 times that of the Earth.
- Characterized by rings made up of millions and millions of tiny particles orbiting independently as ‘micro-moons’. Internal structure is very similar to that of Jupiter.
- Has twenty-two known satellites.
- Can be seen with the naked eye
- Uranus: A Planet on its Side
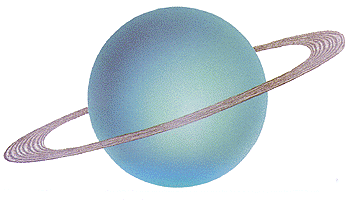
- Third largest planet.
- Rotates on its axis from east to west like Venus, All other planets rotate from west to east.
- Atmosphere consists mainly of hydrogen with traces of helium, ammonia and methane. The core is rocky.
- Has fifteen known satellites.
- Can be seen with the naked eye.
- Neptune: The Last Giant

- Most distant gas planet.
- Atmosphere consists of mainly hydrogen, about 10 % helium, and traces of methane. Methane, which is also present on Uranus, absorbs the red colour in the sun’s light before it is reflected from the cloud layers. This makes these planets appear blue and green.
- Has eight known satellites.
- Has at least three rings made up of dust.
- Cannot be seen with the naked eye.
- Pluto

- First member of the dwarf planets.
- Small in size. Nearly one-fifth the diameter of earth.
- It is a frozen world with a methane frost surface which probably covers a water-ice layer below.
- Has one satellite.
- Cannot be seen with the naked eye
| Name of Planet | Distance from sun (×106km) | Time period of revolution | Time period of rotation | Diameter of planet(km) | Mass of planet compared to earth | No. of satellites |
| Mercury | 58 | 88 days | 58days | 4880 | 0.055 | None |
| Venus | 108 | 225 days | 243days | 12100 | 0.8 | None |
| Earth | 150 | 365¼ days | 24hrs | 12760 | 1 | 1 |
| Mars | 228 | 687 days | 24hrs | 6780 | 0.1 | 2 |
| Jupiter | 778 | 11 ¾years | 9hrs 50mins | 142800 | 318 | 28 |
| Saturn | 1427 | 29 ½ years | 10hrs 14mins | 120000 | 95 | 30 |
| Uranus | 2870 | 84 years | 10hrs 49mins | 50800 | 15 | 21 |
| Neptune | 4504 | 165 years | 15hrs 48mins | 48600 | 17 | 8 |
Also Check: Sound
Dwarf Planets
Dwarf planetsare a new class of astronomical objects. In 2006 by the International Astronomical Union defined the word planet. As per definition to be a planet in our solar system, an object:
- must be in orbit around the Sun.
- must have enough mass so that it has become round in shape due to its own gravity.
- must have cleared out its orbital path around the Sun (so there are not similar objects to itself at roughly the same distance from the Sun).
Dwarf planets were declared to be the class of objects which met the first two requirements, but failed the third. It was then made clear that planets and dwarf planets are distinct classes of objects. Dwarf planets are not planets.
Pluto, Ceres, and Eris became the first three members of this dwarf planet classification, and many others are expected to follow. In fact, there are about 70 other known objects which may be moved into this classification in the near future. More than a hundred other such objects are thought to still be lurking undetected in the Kuiper Belt (The distant regionbeyond the orbit of Neptune).
Difference between a Star and a Planet
| Star | Planet |
| A star has its own light. | A planet has no light of its own. It shines because it reflects light received from the sun. |
| Stars twinkle at night. That is, their light increase and decrease continuously. | Planets do not twinkle at all. |
| Stars are countless in number. | There are only eight major planets. |
| Stars are very big in size. They appear small because they are very far off. | Planets are very small in size as compared to stars. |
| A star is a huge mass of extremely hot gases and its temperature is very high. | A planet is made of rocks and metal and its temperature depends on its distance from the sun. |
Also Check: Waves
COMETS
A comet is a collection of a large number of rocky and metallic particles forming a glowing tail and orbiting the sun, often in an elliptical, elongated orbit.
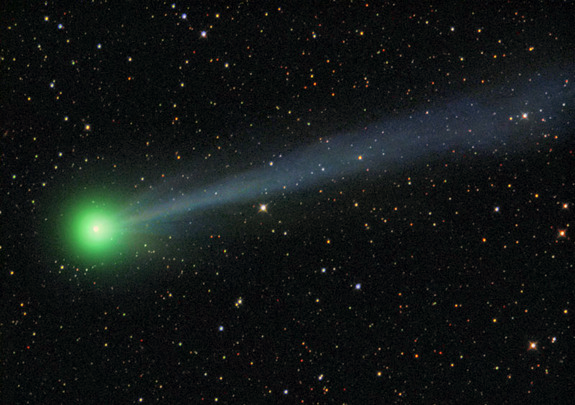

Comets are made up of frozen gases, for example water, ammonia, methane and carbon dioxide which hold, together rocky and metallic material. Comets have been compared to large dirty snowballs.
The comet becomes visible only when it travels close to the sun. Its ice melts and the gas and dust is swept back into a tail. The tail always points away from the sun.
A comet is characterized by a long, luminous tail. But this is visible only when the comet’s orbit passes close to the sun.
- When the comet travels close to the sun, the ice melts to a head of gas called a coma.
- The sun’s radiation sweeps this into a gas tail.
- Dust particles are also swept back to form a dust tail.
- Comets move around the sun in regular orbits but their orbits are such elongated ellipses that it takes those hundreds and sometimes even thousands of years to complete one revolution around the sun.
- Many comets are known to appear periodically. One such comet is Halley’s Comet, which appears after nearly every 76 years. It was last seen in 1986.
ASTEROIDS
There is a large gap in between the orbits of mars and jupiter. This gap is occupied by a large number of small irregular rocky objects that revolve around the Sun. These are called asteroids. Asteroids can only be seen through large telescopes.
The largest asteroid Pallas has a diameter of 500 km while smallest of them may be only one kilometer across. Thus, size of asteroid varies from barely a kilometer to a few hundred kilometers. Each asteroid has its own orbit and the orbits of all of them are spread over a large distance forming a band.

An Asteroid
Also Check: Thrust & Pressure
Meteors and Meteorites
When asteroids collide with one another, fragments of rocks may break off. These pieces may find their way towards the earth. Such objects are called meteors.
Meteors are usually small and burn up before they can reach the earth’s surface. They emit light due to heat produced by friction on entering the atmosphere with high velocity.
When meteors are large and do not burn completely, they land on the earth’s surface and are known as meteorites.

A meteor shower
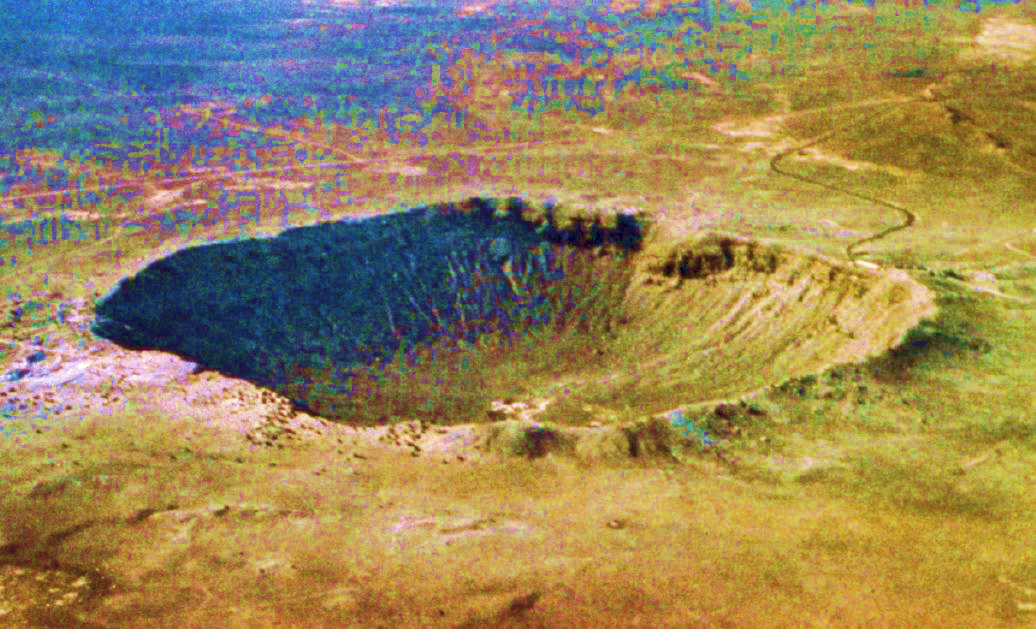

Impact: when a meteor hits earth
All meteorites are believed to originate in the asteroid belt, where a collision by chance may send them towards the earth and the earth’s gravity attracts them to its surface.
Also Check: Frictional Force
CONSTELLATIONS
A constellation is a group of stars in which the stars are arranged in some patterns resembling some recognizable figure.
To enable astronomers to roughly identify the position of the stars, the sky is divided into units just as state boundaries divide a country. These units are known as constellations.
These constellations were named in honour of mythological characters. They hardly bear resemblance to the names they are given.
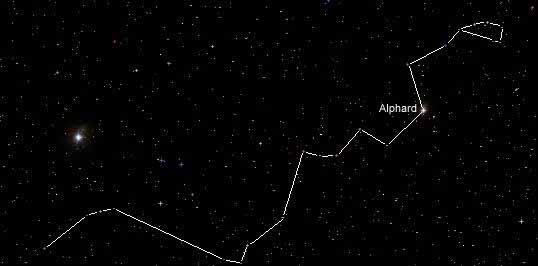
Hydra or Water snake- the largest constellation
Today, 88 constellations are recognized. Every star in the sky is not necessarily a part of one of these constellations.
Constellations of the Zodiac
As the earth moves around the sun, our perspective of the stars changes. In the earth’s journey around the sun, we see the stars only when we look away from the sun because the sun’s brightness blocks the view of the stars towards the sun.
As the earth with its moon moves around the sun, a different constellation is seen on each successive full moon. These twelve constellations are known as the Zodiac.
Some well-known constellations, with their Indian names are given below:
| 1. | Ursa Major (Great Bear) | Saptarishi |
| 2. | Ursa Minor (Little Bear) | DhruvaMatsya |
| 3. | Orion (Hunter) | Mirga |
| 4. | Draco (Dragon) | Kaleya |
| 5. | Scorpio | Vrishchika |
Related Links
| S.no | Formulas List |
|---|---|
| 1. | Force |
| 2. | Frictional Force |
| 3. | Thrust and Pressure |
| 4. | Buoyant Force |
| 5. | Waves |
| 6. | Sound |
| 7. | Some Natural Phenomena |
| 8. | Electroscope |
| 9. | Lightning |
| 10. | Earthquake |