A force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a certain change, either concerning its movement, direction, or geometrical construction. To initiate any motion, force is required. Moving a cricket ball or opening a door, force is acting to put the objects into motion.

Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. We are able to walk or drive our car only because of friction.
Pressure is the ratio of force to the area over which that force is distributed. Pressure is force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Pressure difference is necessary for flying of airplane or drinking of cold drink through straw.
WHAT IS FORCE?
A force is a pull or push, which can at least do one of the following:
- Set a body at rest into motion. For example: A football set into motion by kick(force).
- Stop a moving body. For example: Moving car is stopped after hitting (force) from wall
- Change the speed of the moving body.
- Change the direction of the moving body. For example: A ball changes its direction after it get hit (force) by bat.
- Change the shape or size of the body. The direction in which the object is pushed or pulled is called as the direction of force.
TYPES OF FORCES
Forces are of two type, one that acts only when the body is in physical contact with another body and the other which does not need a physical contact, i.e., it can act from a distance. The first type is known as a contact force while the latter falls under non-contact forces.
CONTACT FORCE:
The forces which acts only when the body is in physical contact
- Muscular Force: This force is exerted by the muscle.
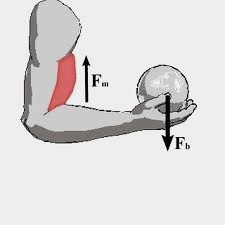
Muscular force holding a ball
- Frictional Force: It is the necessary evil which we will study in later part of the chapter. It acts tangential to the surface in contact.
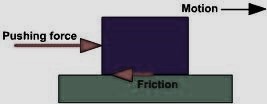
Friction force acts when we push a body
- Normal Force: This force acts when two objects come in contact with each other. This force acts perpendicular to the surfaces in contact.
- Elastic spring Force: force exerted by spring under compression or expansion on objects in contact
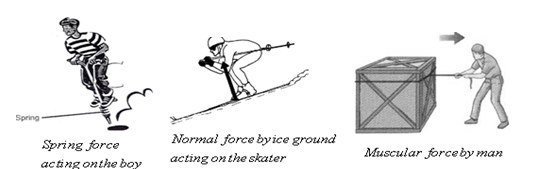
NON-CONTACT FORCE:
Physical contact is not necessary for this force to act. It acts from a distance.
- Magnetic force: A force which magnet exerts on other magnets or on magnetic substances like iron.

Under the influence of magnetic force of attraction, piece of irons and get attracted by magnet.
- Electrostatics force: The force which results due to the repulsion of similar charges or attraction of charges.

- Gravitational Force: The force by which two bodies attract each other by virtue of their masses.
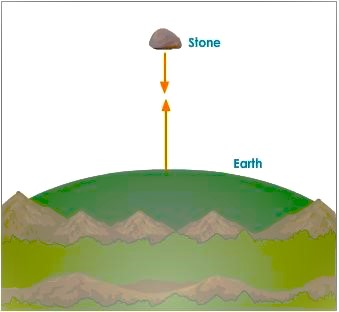
Under the influence of gravitational force, earth attracts stone.
UNITS OF FORCE:
- SI unit of force is newton (N)
- CGS unit of force is dyne
- Another unit commonly used is kilogram force (kgf).
- 1kgf = 9.8 N (It is the gravitational force acting on 1kg of mass)
MASS AND WEIGHT
Mass is the amount of matter in a body. For a particular body mass does not vary with conditions.
Unit of Mass
SI unit of mass is kilogram (Kg)
CGS unit of mass is gram (g).
Weight is the force with which Earth pulls a body towards itself.
Measurement of mass
Mass of a body is measured by a beam balance by comparing the mass with bodies of known mass. At one place, bodies of same mass have same pull of gravity on them.
Unit of weight
Units of weight are same as that of force. ‘kgf’ and ‘gf’ are generally used. If mass of a body is m, then its weight (W) is given by relation W = mg, where g is acceleration due to gravity (g = 9.8 m/s2)
Measurement of weight
Weight of a body is measured by a spring balance.
Illustration 1: Mass of an object is 10 kg. What is its weight on the earth? (acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2)
Solution: Mass,
Acceleration due to gravity,
Thus, the weight of the object is 98 N
Frequently Asked Questions
In physics, force is when you push or pull something with mass, making it change how fast it's moving. Force is something outside that can make things start moving, stop moving, or change direction. It has a size and a direction.
Force is what makes things move or change shape. The unit we use to measure force is called the Newton.
The strongest force is called the strong nuclear force, which is 100 times more powerful than the electromagnetic force.
There are two main types of forces:
- Forces that don't need to touch objects (non-contact forces)
- Forces that need to touch objects (contact forces)
Some examples of forces are:
- Gravity - the force that pulls things towards each other
- Electricity - the force that makes charged objects attract or repel
- Magnetism - the force that attracts or repels objects with magnetic properties
- Nuclear force - the force that holds atomic nuclei together
- Friction - the force that resists motion when two objects rub against each other
Related Links
| S.no | Formulas List |
|---|---|
| 1. | Force |
| 2. | Frictional Force |
| 3. | Thrust and Pressure |
| 4. | Buoyant Force |
| 5. | Waves |
| 6. | Sound |
| 7. | Some Natural Phenomena |
| 8. | Electroscope |
| 9. | Lightning |
| 10. | Earthquake |