During rainy season, many times we see a flash of light in the clouds in the sky which is followed by a loud sound called thunder. The bright flash of light which we see in the clouds is called lightning. Lightning is an electric discharge in the atmosphere between oppositely charged clouds (or between charged cloud and the earth). The electric nature of lightning was established by a scientist named Benjamin Franklin.

When a storm cloud develops in the sky, strong winds move upwards through the cloud and make the water drops present in the cloud to rub against one another. This rubbing together of water drops produces extremely large electric charges in the cloud due to friction.
Also Check: Force
The small water drops acquire a positive charge and, being lighter, move to the upper part of the cloud with rising wind. On the other hand, the larger water drops acquire a negative charge and, being heavier, come down in the lower part of the cloud. In this way, the top of the cloud becomes positively charged whereas the bottom of the cloud becomes negatively charged.
When the amount of opposite electric charges on the top and bottom of a storm cloud becomes extremely large, then electric charges start flowing with high speed through the air between them. When the positive and negative charges of a cloud meet, they produce an intense spark .
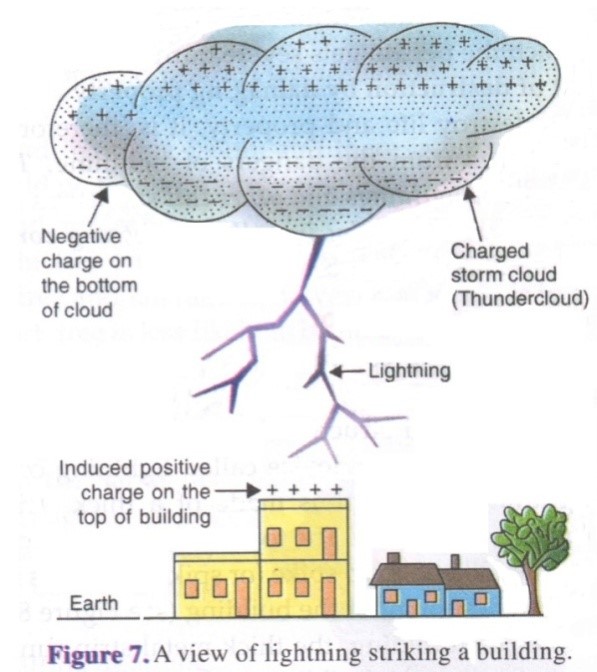
A view of lightning striking a building.
Lightning strikes are more frequent in the hilly areas because in such areas clouds are comparatively closer to the ground than in the planes. In the planes, lightning usually strikes tall structures like tall buildings, factory chimneys, radio and TV transmission towers or big trees. This is because all these tall objects are closer to the charged clouds than the ground.
When we take off woollen or synthetic clothes (like polyester or nylon clothes), sometimes we hear a crackling sound. And if it is dark (as during night), we can even see tiny sparks. This happens as follows: When we lake off a woollen (or synthetic) sweater, it rubs against our shirt. The rubbing together of sweater and shirt produces opposite electric charges on them. The discharge of these electric charges produces tiny sparks of light as well as crackling sound. Sometimes we also see electric sparks in our home when a plug is loose in its socket and a current is switched on.
Also Check: Frictional Force
Dangers of Lightning
A flash of lightning carries a lot of electric energy. When lightning strikes a building, its tremendous electric energy can set the building on fire or cause serious damage to its structure. When lightning strikes a tree, it can burn up the tree and damage it by its enormous electric energy. And when a person is hit by lightning during a thunderstorm, then the electric energy passes through the body of the person due to which the person gets severe burns and gets killed. Thus when lightning strikes the earth, it can cause a lot of destruction by damaging property (buildings etc.), trees and killing people.
Also Check: Sound
Lightning Conductor
Lightning conductor is a device used to protect a building from the effects of lightning. The tall buildings(and other tall structures) are protected from lightning strikes by using a device called lightning conductor. A lightning conductor is made of a thick strip of metal (usually of copper). The top end of lightning conductor is pointed like a sharp spike (or spikes) and it is fixed above the highest point of the building. From the top of the building, the thick metal strip runs along the outer wall of the building to the ground. If lightning strikes, it will hit the top of the lightning conductor rather than the building. The electric energy of lightning passes through the metal strip and gets discharged safely into the ground through the buried metal plate.

Diagram to show the use of a lightning conductor to protect a tall building from lightning.
We can see the lightning conductors fixed on many tall buildings, chimneys, qutub minar etc. Lightning conductor was invented by Benjamin Franklin.
Also Check: Waves
Measures to Protect Ourselves from Lightning
We can take the following measures (or steps) to protect ourselves from lightning strikes during thunderstorm:
- No open space is safe during lightning and thunderstorm. A house (or any other building) is a safe place during lightning.
- Open vehicles like motorbikes, scooters, tractors, and construction machinery (like earth movers etc.) are not safe during lightning and thunderstorm. However we are safe inside the car (or bus) with windows and doors of the vehicle closed.
- A person should squat low on the ground during lightning. When he is open space. The persons should place his hands on his knees with his head between the hands. This position will make the person the shortest object around which is unlikely to be hit by lightning. The person should also stay away from electric poles, telephone poles and tree during lighting.
- We should avoid raising an umbrella over our head during lightning. This is because lightning may strike the top end of the metal rod of umbrella (held high over the head) and harm us.
- The TV antennas and dish antennas fixed on tall buildings are especially prone to lightning strikes. We should, therefore, switch off our TV sets during frequent lightning otherwise TV sets may get burnt.
- Lightning can strike metal pipes (such as water pipes) fixed in buildings. So, during a thunderstorm when lightning is taking place, we should avoid touching the metal pipes fixed in a house or building.

The safe position during lightning (when a person is in open space with no shelter nearby).
Frequently Asked Questions
Lightning is a bright flash in the sky, happening when electricity flows between clouds or from a cloud to the ground. This electric burst heats the air and often produces thunder. Lightning might look like a jagged line, a wide flash, or sometimes even a red glowing sphere.
Lightning starts with static charges building up in a storm cloud. The cloud's internal winds, which are very strong, carry water droplets upward. These droplets then freeze in the colder upper parts of the cloud.
Thunder is the sound that follows a lightning flash, audible up to about 10 miles away from where the lightning strikes. Hearing thunder means you are close enough to be at risk from the lightning and should seek shelter immediately.
Cloud-to-ground lightning typically starts with a process called a stepped leader. This involves a quick succession of negative charges moving down from a cloud to the ground, creating a pathway for electricity at speeds around 200,000 mph (300,000 kph). Each segment of this path is about 150 feet (46 meters) long.
Related Links
| S.no | Formulas List |
|---|---|
| 1. | Force |
| 2. | Frictional Force |
| 3. | Thrust and Pressure |
| 4. | Buoyant Force |
| 5. | Waves |
| 6. | Sound |
| 7. | Some Natural Phenomena |
| 8. | Electroscope |
| 9. | Lightning |
| 10. | Earthquake |