When we talk about even numbers, we refer to integers that can be evenly divided by 2. These numbers, such as 2, 4, 6, and 8, are fundamental in mathematics due to their distinct properties and applications. Discover what makes even numbers unique and explore their significance in various mathematical concepts.
What Are Even Numbers?
Even numbers are integers that can be exactly divided by 2. Examples of even numbers include 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10. These numbers always result in a whole number when divided by 2.
The Concept of Even Numbers
To illustrate the concept of even numbers, imagine John has six balls. He can pair up all six balls into three groups with no leftover balls. This scenario demonstrates that 6 is an even number.
When dividing 6 by 2, the result is 3, which represents the number of pairs. Since there is no remainder, John has successfully grouped all the balls without any remaining. This property is a defining characteristic of even numbers: dividing an even number by 2 always yields a remainder of 0.
Examples of Even Numbers
Patterns in Even Numbers
When examining even numbers, you’ll notice a consistent pattern: every even number is a multiple of 2. This pattern continues indefinitely, forming a sequence where each number is 2 more than the previous one.
Odd vs. Even Numbers: What’s the Difference?
Odd numbers are integers that cannot be evenly divided by 2. They always have a remainder of 1 when divided by 2. In contrast, even numbers are divisible by 2 with no remainder.
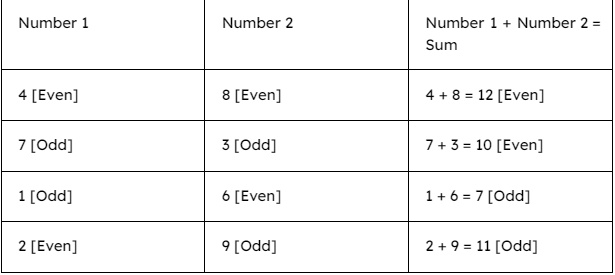
Addition of Even and Odd Numbers: What Happens?
Let’s explore what happens when we add different combinations of odd and even numbers. When odd and even numbers are combined together, we shall see how the numbers transform from odd to even.
Properties of Even Number
- Divisibility: Even numbers are divisible by 2 without leaving a remainder.
- Addition: The sum of two even numbers is always even.
- Subtraction: The difference between two even numbers is always even.
- Multiplication: The product of two even numbers is always even.
- Division: Dividing an even number by 2 yields a whole number with no remainder.
Real-Life Examples of Even Numbers
Even numbers are not just theoretical concepts; they appear in everyday life. Examples include:
- Pairs of shoes.
- Days of the month.
- Items on a shelf.
Conclusion
Even numbers are a fundamental concept in mathematics with clear patterns and properties. Understanding how they work helps in various mathematical operations and real-world applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
The even numbers between 1 and 10 are 2, 4, 6, and 8.
Odd Numbers are integers that are not divisible by 2. When divided by 2, they leave a remainder of 1. For example, numbers like 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 are odd numbers.
Even Numbers are integers that are divisible by 2 without leaving a remainder. These numbers can be divided by 2 evenly. Examples include 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8.
0 is classified as an even number. This is because 0 divided by 2 equals 0 with no remainder, which fits the definition of an even number.
1 is an odd number. When divided by 2, it leaves a remainder of 1, which is the characteristic of odd numbers.