A cylinder is a three-dimensional shape with two parallel circular bases and a curved surface connecting them. It is one of the most basic shapes in geometry and is used in many real-world objects, such as containers, pipes, and engine cylinders.
Definition
In mathematics, a cylinder is a three-dimensional shape with two parallel circular bases and a curved surface connecting them. The height of the cylinder is perpendicular to the circular bases, and the curved surface is a rectangle with curved edges. A cylinder can be described by its radius and height.The distance between the bases is called the height or altitude (h), and the distance from the center to the outer surface is called the radius (r). The volume and surface area of a cylinder can be calculated using mathematical formulas.The volume of a cylinder is given by the formula V = πr²h, where r is the radius of the circular base and h is the height of the cylinder. The surface area of a cylinder is given by the formula A = 2πrh + 2πr².
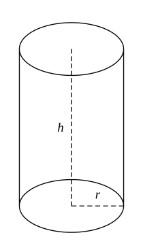
Properties of a Cylinder
A cylinder has some unique properties:
- It has a curved surface and two bases.
- The total surface area (TSA) is the sum of the area of the curved surface and the two bases.
- The bases are parallel and identical.
- It is similar to a prism because it has the same cross-section everywhere.
- A cylinder can have two types of bases: elliptical and circular.
Shape of a Cylinder
The shape of a cylinder is cylindrical, with two parallel circular bases and a curved surface connecting them. The height of the cylinder is perpendicular to the circular bases, and the curved surface is a rectangle with curved edges.The circular bases of a cylinder are similar to the bases of a cone, but unlike a cone, a cylinder has a curved surface that is continuous. The curved surface of a cylinder can be thought of as the surface of a rectangle that has been bent to form a circle.
Type of Cylinder
- Right Cylinder: This is the most basic type of cylinder and has its height perpendicular to the bases.
- Oblique Cylinder: This type of cylinder has a height that is not perpendicular to the bases and forms an angle with them.
- Truncated Cylinder: This type of cylinder has a portion of one or both of its circular bases removed.
- Elliptical Cylinder: This type of cylinder has elliptical rather than circular bases.
- Cone-Cylinder: This is a combination of a cone and a cylinder, where one of the circular bases has been replaced by a sloping surface.
- Double-Ended Cylinder: This is a cylinder with two circular bases that are of equal size and are at opposite ends of the cylinder.
- Hollow Cylinder: This is a cylinder with a hollow interior space.
Formulas
- Volume of Cylinder
V = πr^2h
where:
- V is the Volume of the cylinder
- π (pi) is the mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14
- r is the Radius of the circular base of the cylinder
- h is the Height of the cylinder
- Lateral (or Curved) Surface Area of a Cylinder
A = 2πrh
where:
- A is the Lateral Surface Area of the cylinder
- π (pi) is the mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14
- r is the Radius of the circular base of the cylinder
- h is the Height of the cylinder
- Total Surface Area of a Cylinder
A = 2πr^2 + 2πrh
where:
- A is the Total Surface Area of the cylinder
- π (pi) is the mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14
- r is the Radius of the circular base of the cylinder
- h is the Height of the cylinder
Also Read -
Frequently Asked Questions
A cylinder is a three-dimensional geometric shape with two parallel circular bases and a curved lateral surface connecting the bases. It is one of the most basic shapes in geometry and is used in a variety of real-world objects, such as containers, pipes, and engine cylinders.
The key formulas for cylinders are:Volume (V) = πr²h, where r is the radius of the circular base and h is the height of the cylinder.
Surface Area (A) = 2πrh + 2πr², where r is the radius and h is the height.These formulas allow you to calculate the volume and surface area of a cylinder given its dimensions.
A cylinder is a three-dimensional (3D) geometric shape because it has three dimensions: length, width, and height. The two circular bases of the cylinder represent the length and width, while the curved lateral surface represents the height. This three-dimensional nature distinguishes a cylinder from two-dimensional (2D) shapes like circles or rectangles.
In mathematics, a cylinder is a three-dimensional geometric shape with the following properties:
- It has two parallel circular bases.
- It has a curved lateral surface connecting the two bases.
- The height of the cylinder is perpendicular to the circular bases.
- The lateral surface is a rectangle with curved edges.