NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 Super Senses
Find pdf of NCERT Solutions for class 5 EVS Chapter 1 Super Senses prepared by expert teachers. All the questions asked in the exercise of Super Senses are solved with the required details.
A brief introduction to Chapter 1 Super Senses
Chapter 1 Super Senses- We humans have four main senses: sight, sound, smell, and taste. While humans have superior colour vision compared to most mammals, these four senses can be overloaded by sensory information. That's why we tend to tune out unpleasant stimuli and noise. We also have a tendency to lose track of what we see and experience by tuning out our senses to other, more important aspects of life. In the following section, we'll look at some examples of these senses, and how we can develop them to their full potential.
The human brain has three types of cone receptors. Three of these receptors detect different wavelengths of light. Humans have about one million colours. However, a rare mutation gives humans a fourth type of cone receptor. Tetrachromats are able to distinguish 100 times more colours! Some super senses include hearing in the form of echolocation. Echolocators make clicking noises and return information about objects based on the frequency and volume of the noises they hear. Brain scans reveal that the visual processing areas of the brain are active during echolocation.
Many animals have developed nifty senses that help them survive in the wild. In the daytime, their eyesight is good. However, their ultra-sound abilities are crucial for hunting at night. In addition, they use a series of high-pitched squeaks to bounce off objects and detect danger. Although some may consider bats to be the villains of the animal kingdom, they're not actually evil. So, when a bat pops out from a burrow, it can easily detect the presence of a shadow!
Find pdf of NCERT Solutions for class 5 EVS Chapter 1 Super Senses
Page No 2:
Question Tell:
· How did the ant know that the other ants were not from its group?
· How did the guard ant recognise this ant?
Answer:
· The ant had antennae to sense smell. With the help of the smell, it came to know that the other ants were not from its group.
· The guard ant recognised this ant by its smell.
Question Tell:
How did the ant know that the other ants were not from its group?
Answer:
The ant had antennae to sense smell. With the help of the smell, it came to know that the other ants were not from its group.
Question Try This and Write:
Drop some sugar, jaggery or anything sweet on the ground. Wait until the ants come there.
· How long did it take for the ants to come?
· Did one ant come first or a group of ants came together?
________________________________________
· What did the ants do with the food?
________________________________________
· Where do they go from there?
________________________________________
· Do they move in a line?
________________________________________
Now carefully, without harming the ants, block their path for a while with a pencil.
· Now observe, how do the ants move?
________________________________________
Answer:
Disclaimer: This section aims to boost the scientific ways of experimentation in students. Keeping the importance of this process in mind, the answers to the same have not been provided.
Page No 4:
Question Write: Do you and your friends have similar answers?
Answer:
This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping this in mind, it is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
Question Write: Write the names of five things you like and five things whose smell you do not like.
|
I like the smell of |
I do not like the smell of |
|
Rose |
Rotten Eggs |
|
Petrol |
Foul Breath |
|
Paint |
Cow Dung |
|
Wet Soil |
Crackers after they are burnt |
Answer:
Disclaimer: This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping the importance of this process in mind, sample pointers have been provided for the same.
Question Write: Name the animals that you would be able to recognise only by their smell, without seeing them?
Answer:
Disclaimer: This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping the importance of this process in mind, the answers to the same have not been provided.
Question Write: When do you find your sense of smell helpful to you? List some examples. Like – to know by its smell that food has gone bad or that something is burning.
Answer:
Our sense of smell can help us to avoid accidents in many ways. These include:
(i) Finding the leakage of cooking gas from cylinders;
(ii) Burning of wires or clothes.
Disclaimer: This is a sample answer. The answer of the students can vary from this.
Question Write:
· In what ways do human beings make use of this special sense of smell of dogs?
· When do you find your sense of smell helpful to you? List some examples. Like – to know by its smell that food has gone bad or that something is burning.
· Name the animals that you would be able to recognise only by their smell, without seeing them?
· Write the names of five things you like and five things whose smell you do not like.
|
I like the smell of |
I do not like the smell of |
|
Rose |
Rotten Eggs |
|
Petrol |
Foul Breath |
|
Paint |
Cow Dung |
|
Wet Soil |
Crackers after they are burnt |
· Do you and your friends have similar answers?
Answer:
· The special sense of smell of dogs is used by police to catch thieves, search for lost people and detect bombs. Dogs are also used to guard our houses from strangers.
· Our sense of smell can help us to avoid accidents in many ways. These include:
(i) Finding the leakage of cooking gas from cylinders;
(ii) Burning of wires or clothes.
Disclaimer: This is a sample answer. The answer of the students can vary from this.
Disclaimer: This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping the importance of this process in mind, the answers to the same have not been provided.
Disclaimer: This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping the importance of this process in mind, sample pointers have been provided for the same.
· This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping this in mind, it is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
Page No 5:
Question Do and Find Out:
From the smell of the clothes of your family members, can you say whom do they belong to? Try to recognise the clothes of any two members of your family in this way.
Answer:
Disclaimer: This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping this in mind, it is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
Question Think and Discuss:
· Sushila covered her nose when she cleaned Deepak’s nappy, but not when she cleaned her daughter. Why do you think she did this?
· How do you feel when you walk near a heap of garbage? Think of the children who spend the whole day picking things from such garbage.
· Is a smell ‘good’ or ‘bad’ for everyone in the same way? Or does it depend on how each one feels about it?
Answer:
Disclaimer: This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping this in mind, it is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
Page No 6:
Question Let’s See:
· Write the name of a bird which has eyes in front of its head (like in humans).
· Write the names of some birds which have eyes on either side of the head. What is the size of their eyes as compared to the size of their head?
Answer:
· An owl has eyes in front of its head (like in humans).
Disclaimer: This is a sample answer. The answer of the students can vary from this.
· Disclaimer: This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping this in mind, it is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
Question Let’s See:
Write the names of some birds which have eyes on either side of the head. What is the size of their eyes as compared to the size of their head?
Answer:
Disclaimer: This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping this in mind, it is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
Question Looking with One or:
Close your right eye or cover it with your hand. Tell your friend to stand to your right, at some distance, and ask him to do some action (wave hand, shake head, etc.)
· Could you see your friend’s action, without moving your neck?
· Now try to look at your friend’s action with both your eyes open but without moving your neck.
· What was the difference on looking with one or both eyes?
· Now toss a small ball or a coin and try to catch it. Try this with both your eyes open. Then close one eye and try to catch it. When was it easier to catch?
· Imagine how it would be to have your eyes in place of your ears? What would you be able to do then, which you cannot do now?
Some birds like kites, eagles, vultures can see four times as far as we can. These birds can see things from a distance of eight metres what we can see from a distance of two metres.
· Now can you guess from what distance can an eagle in the sky can see a roti on the ground?
Answer:
Disclaimer: This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping this in mind, it is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
Page No 8:
Question Write:
· The names of ten animals whose ears can be seen.
Answer:
· Animals whose ears can be seen are cat, rabbit, donkey, dog, lion, fox, tiger, bear, monkey and zebra.
Disclaimer: This is a sample answer. The answer of the students can vary from this.
Question Write: The names of some animals whose ears are bigger than our ears.
Answer:
Some animals whose ears are bigger than our ears are elephant, horse, goat and cow.
Disclaimer: This is a sample answer. The answer of the students can vary from this.
Question Think: Is there some link between the size of animals’ ears and their hearing?
Answer:
Disclaimer: This question aims to boost the skill of observation. Keeping this in mind, it is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
Question Try This:
For this activity find a quiet place in your school. Tell one of your friends to stand at a short distance and ask him to say something softly. The rest of you should listen carefully. Then all of you put your hands behind your ears, as
shown in the picture. Let the same child say something again as softly as before. In which case was the sound sharper? Ask your friends too.
· Put your hands over your ears and say something. Can you hear your own voice?
· Sit near a desk. Tap the desk once with your hand. Listen carefully. Now put your
· ear on the desk as shown in the picture. Tap on the desk once again with your hand. Listen again. Was there any difference in the sound of the tap?
This is how snakes hear. They do not have external ears (which you can see). They only feel the vibrations on the ground.
Answer:
Disclaimer: This section aims to enhance the thinking skills of students. Keeping this in mind, it is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
Page No 10: Question Sleeping and Waking:
When you see different animals, do you have any questions about them? Make a list of ten such questions.
Answer:
Yes, the questions which usually arise in my mind are: How do the animals talk to each other?
Why are some animals active at night?
How do they manage to catch their food (prey) at night?
Disclaimer: This is a sample answer. This question calls for the one’s own thinking. Keeping this in mind, only three questions have been provided. It is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
Question Sleeping and Waking:
Given here is the sleeping time of some animals. Below each picture write for how many hours a day that animal sleeps.
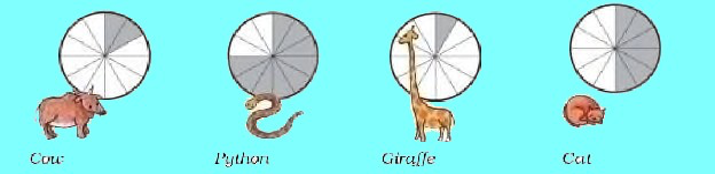
Answer:
Here each circle is equal to 24 hours. There are 12 sectors in the circle. So, each sector is equal to 2 hours.
According to the shaded portion, cow sleeps for 4 hours (1/6), python sleeps for 18 hours (3/4), giraffe sleeps for 2 hours (1/12) and cat sleeps for 12 hours (1/12).
Question Write: Do some animals understand your language? Which ones?
Answer:
Yes, on training or spending some time with certain animals they start understanding our language. These are animals like parrot, monkeys, dogs etc.
Question Write:
· Can you understand the sounds of some animals? Which animals?
· Do some animals understand your language? Which ones?
Answer:
· Yes, I can understand the sounds of some animals. Monkeys make a very strong chattering sound especially when they come in groups. Other than these, cats, dogs and parrots also have distinct voices.
Disclaimer: This is a sample answer. The answer of the students can vary from this.
· Yes, on training or spending some time with certain animals such as parrot, monkeys, dogs etc., they start understanding our language.
Question Sleeping and Waking:
· Have you noticed that during the cold season you cannot see any lizard in the house? Where do you think they have gone?
· Given here is the sleeping time of some animals. Below each picture write for how many hours a day that animal sleeps.
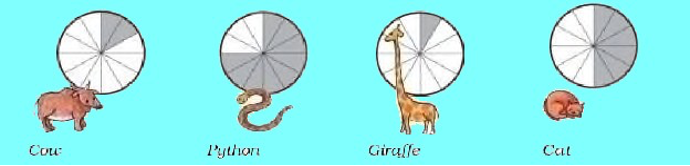
· When you see different animals, do you have any questions about them? Make a list of ten such questions.
Answer:
· Disclaimer: This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping this in mind, it is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
· Here each circle is equal to 24 hours. There are 12 sectors in the circle. So, each sector is equal to 2 hours.
According to the shaded portion, cow sleeps for 4 hours (1/6), python sleeps for 18 hours (3/4), giraffe sleeps for 2 hours (1/12) and cat sleeps for 12 hours (1/2)
· Yes, the questions which usually arise in my mind are: How do the animals talk to each other?
Why are some animals active at night?
How do they manage to catch their food (prey) at night?
Disclaimer: This question calls for the one’s own thinking. Keeping this in mind, only three questions have been provided. It is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
Page No 13: Question What we have learnt:
Give examples of animals that may have a strong sense of sight, hearing or smell.
Answer:
Animals with a strong sense of sight: Eagle, Vulture, Hawk Animals with a strong sense of hearing: Monkeys, Elephants, Tiger Animals having a strong sense of smell: Dogs, Tigers, Lions
Disclaimer: This is a sample answer. The answer of the student may vary from this answer.
Question Find Out:
· Where are other such National Parks in India?
· Collect information on these and write a report.
Answer:
Disclaimer: This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping this in mind, it is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
Question What we have learnt:
· Have you noticed that sometimes singers put their hand on their ear when they sing? Why do you think they may be doing this?
· Give examples of animals that may have a strong sense of sight, hearing or smell.
Answer:
· Disclaimer: This question calls for the process of one’s own observance. Keeping this in mind, it is strongly recommended that the students prepare the solutions on their own.
· Animals with a strong sense of sight: Eagle, Vulture, Hawk Animals with a strong sense of hearing” Monkeys, Elephants, Tiger Animals having a strong sense of smell: Dogs, Tigers, Lions
Disclaimer: This is a sample answer. The answer of the student may vary from this answer.