Metallurgy refers to the science and techniques involved in extracting metals in their purest form. Metals typically exist in nature combined with soil, limestone, sand, and rocks, forming compounds known as minerals. When these minerals can be economically and efficiently processed to extract metals, they are termed ores. In metallurgical processes, a substance called flux is introduced in the furnace to eliminate impurities, or gangue. Metallurgy encompasses the purification of metals and the development of alloys.
Also Check: Osmosis | Octane Number | Natural resourses |
Related Links: Fossils Fuels | Isomerism
Steps in Metallurgical Process
In metallurgy, the process involves several steps to extract and refine metals from ores. Here are the steps in a simplified and academic format:
-
Mining: Ore is extracted from the earth's crust, typically in large quantities.
-
Crushing and Grinding: The ore is crushed into smaller pieces and then ground into a fine powder. This increases the surface area for chemical reactions.
-
Ore Concentration: Through processes like flotation or magnetic separation, the desired mineral is separated from the gangue (unwanted material).
-
Smelting: The concentrated ore is heated in a furnace with a reducing agent (like carbon) to remove oxygen and other impurities, converting it into a metal oxide.
-
Refining: Further purification of the metal oxide is done to remove any remaining impurities, often through electrolysis or other chemical processes.
-
Alloying: Sometimes, metals are mixed with other metals to create alloys, which have improved properties for specific applications.
-
Shaping and Forming: The purified metal is then shaped into various forms through processes like casting, forging, or rolling.
-
Finishing: Finally, the metal may undergo finishing processes such as polishing or coating to enhance its appearance and protect against corrosion.
Each step in the metallurgical process plays a crucial role in obtaining metals that meet industrial and commercial standards.
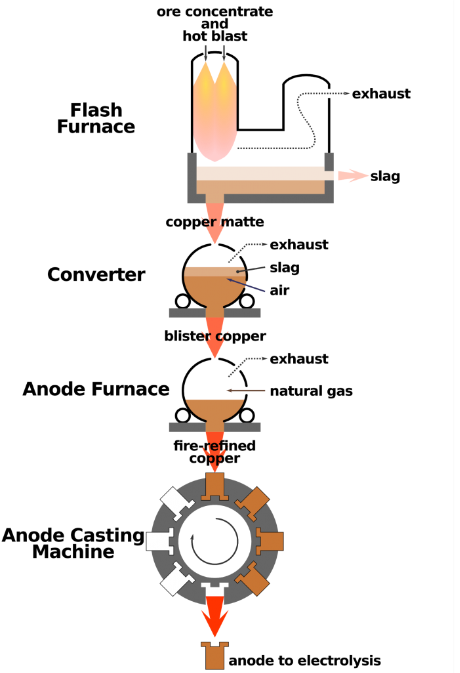
Principles of Metallurgy
"Principles of Metallurgy" refers to the fundamental concepts and theories that govern the behavior, properties, and processing of metals and alloys. Here's a simple and academic explanation:
Metallurgy is the study of metals and their properties. It involves understanding how metals are extracted from ores (rocks that contain metals), how they are purified, and how they can be modified to improve their strength, durability, and other properties.
Key principles of metallurgy include:
-
Extraction: Metals are often found in nature combined with other elements in ores. Metallurgists use various techniques such as smelting and leaching to extract pure metals from these ores.
-
Alloying: Most metals are rarely used in their pure form. Alloying involves mixing metals with other elements to create alloys that possess desired properties like strength, corrosion resistance, or conductivity.
-
Heat Treatment: Metals can be heated and cooled in specific ways to alter their physical and mechanical properties. Processes like annealing, quenching, and tempering are used to achieve desired hardness, toughness, and ductility.
-
Phase Diagrams: These diagrams depict the behavior of metals as they undergo changes in temperature and composition. They help metallurgists understand when different phases (such as solid, liquid, or gas) are present and how these phases affect a metal's properties.
-
Mechanical Properties: Metallurgists study how metals respond to forces and loads, including properties like strength, hardness, elasticity, and plasticity. Understanding these properties is crucial for designing and manufacturing metal components for various applications.
-
Corrosion and Protection: Metals can react with their environment, leading to corrosion (degradation). Metallurgists develop methods to protect metals from corrosion, such as coating them with paints or using corrosion-resistant alloys.
Frequently Asked Questions
Metallurgy is the study and practice of extracting metals from ores and refining them for use.
The three types of metallurgy are pyrometallurgy (using heat), hydrometallurgy (using liquids), and electrometallurgy (using electricity).
Metallurgy is important because it allows us to obtain metals needed for manufacturing goods, construction, and technology.
Metallurgy has been used historically to create tools, weapons, and materials for buildings and transportation, advancing human civilization.