What is Velocity?
Velocity is defined as the speed of a body along a specific direction.
We know that speed is the amount of distance covered in a given amount of time. If a car travels at a speed of ‘50 meters per second’, for one minute, the total distance it covers turns out to be 3000 meters. But we do not know the direction in which the car traveled, nor its position.
In another case, a car travels at ‘50 meters per second’ for one minute in the north direction. From this we can say that the car traveled 3000 meters in the north direction. This way we can find the speed as well as the direction of that car. Hence, we can say that 50 m/s in the north direction is the Velocity of this car.
What is the Unit of velocity?
The established SI unit for Velocity is the same as that of speed. That is meters per second. The difference between Velocity and Speed is that speed has no direction while Velocity does.
How to calculate average velocity?
The average velocity depends on the start and endpoints, regardless of the path taken. Hence, the average velocity equals displacement over time.
𝐴𝑣𝑔./ 𝑉𝑒𝑙𝑜𝑐𝑖𝑡𝑦= 𝐷𝑖𝑠𝑝𝑙𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡/ =𝑇𝑖𝑚𝑒
Example 1. Suppose the displacement of a car is 20 kilometers due north in 2 hours. What is the average velocity of the car?
Ans. The average velocity will equal 20 kilometers divided by 2 hours. This equals 10 kilometers per hour due north.
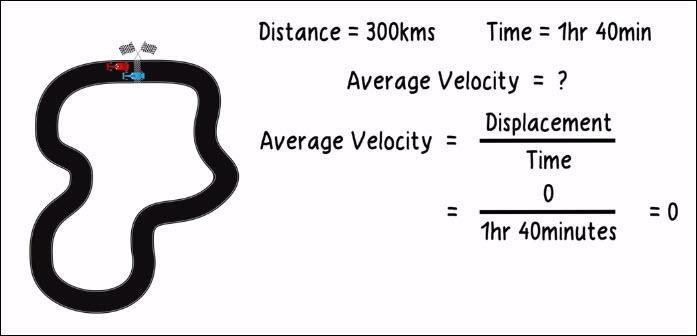
Example 2. Suppose a car driver finished a 300 km race in one hour and forty minutes on a racetrack having the start line and the finish line at the same point. What was the average velocity of that car?
Ans. The driver started the race and ended it at the same point. This means the displacement of the car is zero. And zero divided by the taken time, which is one hour forty minutes equals zero. That puts the average velocity for the race today at zero meters per second.
Average velocity example
