Share
(i) x + y = 5, 2x – 3y = 4
(ii) 3x + 4y = 10, 2x – 2y = 2
(iii) 3x − 5y – 4 = 0, 9x = 2y + 7
(iv) x/2 + 2y/3 = -1, x - y/3 = 3
Report
Question
(i) x + y = 5 … (1)
2x – 3y = 4 … (2)
Elimination method:
Multiplying equation (1) by 2, we get equation (3)
2x + 2y = 10 … (3)
2x − 3y = 4 … (2)
Subtracting equation (2) from (3), we get
5y = 6⇒ y = 6/5
Putting value of y in (1), we get
x + 6/5= 5
⇒ x = 5 − 6/5= 19/5
Therefore, x = 19/5 and y = 6/5
Substitution method:
x + y = 5 … (1)
2x − 3y = 4 … (2)
From equation (1), we get,
x = 5 − y
Putting this in equation (2), we get
2 (5 − y) − 3y = 4
⇒ 10 − 2y − 3y = 4
⇒ 5y = 6 ⇒ y = 6/5
Putting value of y in (1), we get
x = 5 − 6/5= 19/5
Therefore, x = 19/5 and y = 6/5
(ii) 3x + 4y = 10… (1)
2x – 2y = 2… (2)
Elimination method:
Multiplying equation (2) by 2, we get (3)
4x − 4y = 4 … (3)
3x + 4y = 10 … (1)
Adding (3) and (1), we get
7x = 14⇒ x = 2
Putting value of x in (1), we get
3 (2) + 4y = 10
⇒ 4y = 10 – 6 = 4
⇒ y = 1
Therefore, x = 2 and y = 1
Substitution method:
3x + 4y = 10… (1)
2x − 2y = 2… (2)
From equation (2), we get
2x = 2 + 2y
⇒ x = 1 + y … (3)
Putting this in equation (1), we get
3 (1 + y) + 4y = 10
⇒ 3 + 3y + 4y = 10
⇒ 7y = 7⇒ y = 1
Putting value of y in (3), we get x = 1 + 1 = 2
Therefore, x = 2 and y = 1
(iii) 3x − 5y – 4 = 0 … (1)
9x = 2y + 7… (2)
Elimination method:
Multiplying (1) by 3, we get (3)
9x − 15y – 12 = 0… (3)
9x − 2y – 7 = 0… (2)
Subtracting (2) from (3), we get
−13y – 5 = 0
⇒ −13y = 5
⇒ y = −5/13
Putting value of y in (1), we get
3x – 5 (−5/13)− 4 = 0
⇒ 3x = 4 − 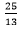
⇒ x = 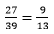
Therefore, x = 9/13and y = -5/13
Substitution Method:
3x − 5y – 4 = 0 … (1)
9x = 2y + 7… (2)
From equation (1), we can say that
3x = 4 + 5y⇒ x = 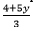
Putting this in equation (2), we get
9 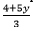 − 2y = 7
− 2y = 7
⇒ 12 + 15y − 2y = 7
⇒ 13y = −5 ⇒ y = -5/13
Putting value of y in (1), we get
3x – 5 (-5/13)= 4
⇒ 3x = 4 − 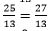
⇒ x = 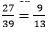
Therefore, x = 9/13 and y = -5/13
(iv) x/2 + 2y/3 = -1 ....(1)
x - y/3 = 3… (2)
Elimination method:
Multiplying equation (1) by 2, we get
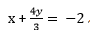 … (3)
… (3)
substracting equation (2)from (3) we get
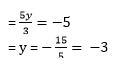
Putting value of x in (2), we get
x + 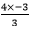 = -2
= -2
=x-4=-2
=x=2
Substitution method:
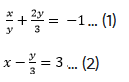
From equation (2), we can say that 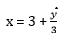
Putting this in equation (1), we get
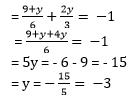
solved
5
wordpress
4 mins ago
5 Answer
70 views
+22

Leave a reply