Share
Report
Question
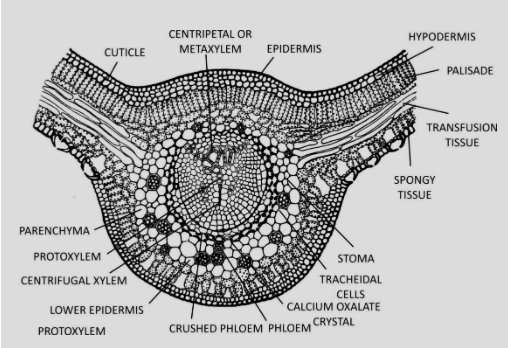
Pinnule refers to the leaflets of the Cycas plant. The upper and lower epidermis, which contain compactly packed cells, are separated by the hypodermis layer.
Stomata can be seen on both the top and lower epidermis. Palisade and spongy tissue are the two tissues that make up the mesophyll.
The palisade tissue is made up of long cells that are tightly packed together. The loosely organised cells are found in spongy tissue.
There are conjoint and collateral vascular bundles.
Protoxylem points to the lower epidermis, while metaxylem points to the top epidermis. In the layout, the xylem is central and centrifugal. Phloem tissue can be seen in the lower epidermis.
These plants have several adaptations in common with xerophytic plants. A thick cuticle protects the plant from excessive transpiration.
There are sunken stomata, which help to decrease water loss.
Certain hypodermis thick-walled cells restrict water loss by preventing water passage.
The spines are formed from the final leaflets, reducing the surface area available for transpiration.
Pinnule refers to the leaflets of the cycas plant. The upper and lower epidermis, which contain compactly packed cells, are separated by the hypodermis layer. Stomata can be seen on both the top and lower epidermis. Palisade and spongy tissue are the two tissues that make up the mesophyll. There are conjoint and collateral vascular bundles. Protoxylem points to the lower epidermis, while metaxylem points to the top epidermis.
The following are some of the Xerophytic adaptations of the cycas leaf:
Excess transpiration is prevented by a thick cuticle.
The presence of sunken stomata in leaves minimises water loss.
solved
5
wordpress
4 mins ago
5 Answer
70 views
+22

Leave a reply