Important Questions for Chapter-4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- BoardCBSE
- TextbookNCERT
- ClassClass 8
- SubjectScience
- ChapterImportant Questions for Chapter-4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Chapter NameChapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- CategoryImportant Questions
Important questions for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter-4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
This page is prepared by the HT experts and consists of all the important questions chapter-wise; you can find important questions for CBSE class 8 science Chapter -4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals. Chapter -4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals required a good understanding of the theory so before solving the given questions read the theory given in the NCERT textbook for Chapter -4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals. Check out the list of chapter-wise Important questions for class 8 science prepared by experts do follow NCERT Solutions for class 8.
Important Questions for Class 8 Science consists of Subjective Questions of the following Types
Section-1 It consists of the Most Important Questions from Chapter -4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals having 5 Marks with solutions
Section-2. It consists of the Most Important Questions from Chapter -4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals having 3 Marks with solutions
Section-3. It consists of the Most Important Questions from Chapter -4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals having 2 & 1 Marks with solutions
Questions based on Chapter-4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
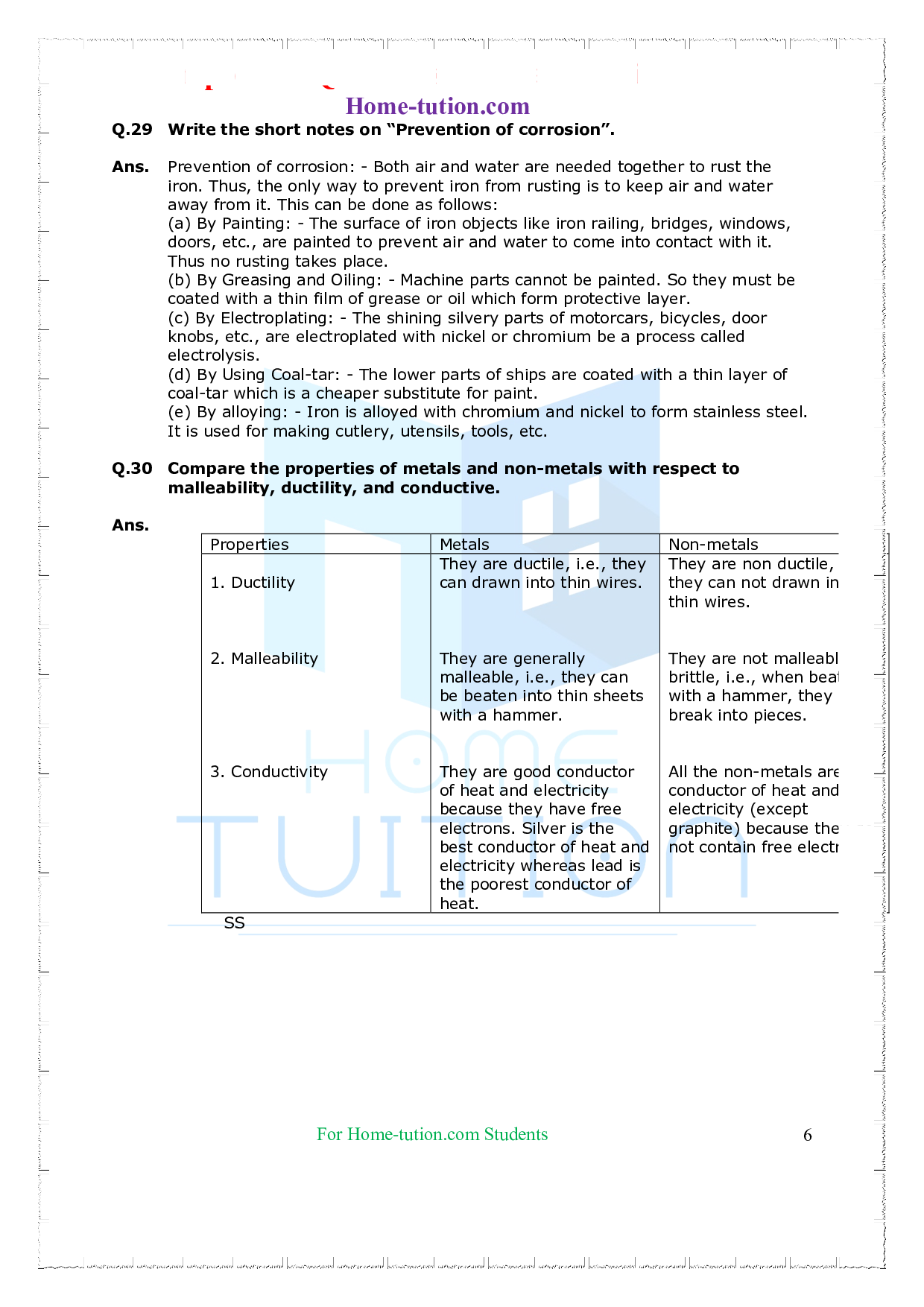
Q.1. What do you understand by the ductility of metals?
Ans. Metals can be drawn into very thin wires. This property of metals is known as ductility eg. Gold, and silver.
Q.2. What happens when the iron railings on the outside are not painted?
Ans. They will be rusted due to the formation of hydrated ferric oxide (Fe2O3. XH2O)
Q.3. Which chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?
Ans. Reduction
Q.4. Name a non-metal which is a good conductor of heat.
Ans. Graphite
Q.5. Name 2 metalloids
Ans. Silicon and germanium
Q.6. Why do gold and silver often occur in a free state?
Ans. Gold and silver are less reactive. They remain unaffected by air, water or acidic substances. Hence, they often occur in the free state.
Q.7. Write the main constituent of brass.
Ans. Copper and Zinc
Q.8. Write the most abundant metal in the earth’s crust.
Ans. Aluminium
Q.9. Silver articles on exposure to air acquire a blackish tinge. What is the name of the black substance?
Ans. Silver Sulphide (Ag2S)
Q.10. What important properties of Al are responsible for its great demand in the industry?
Ans. Low density and resistance to corrosion.
Q.1 Define Ore.
Ans. An ore is a naturally occurring mineral from which one or more metals can be profitably extracted.
Q.2 What is the Metallurgy?
Ans. Metallurgy is a science.
Q.3 Name the metals that occur in a free state.
Ans. Gold, Silver and Platinum
Q.4 Name the metal which is liquid at room temperature.
Ans. Mercury
Q.5 Name the non-metals that occur in a free state.
Ans. Helium, Neon, Argon, Krypton and Xenon
Q.6 Define metals
Ans. The elements which lose the electron and form cations are called metals.
Q.7 Define non-metals
Ans. The elements which gain the electron and form anions are called non-metals.
Q.8 Define minerals.
Ans. The naturally occurring compounds of metals which are generally mixed with other matter such as soil, sand, limestone and rocks are called minerals.
Q.9 What is the activity series?
Ans. When common metals are arranged in order of decreasing reactivity, a series is formed which is known as activity series.
Q.10 What is the mean of malleability?
Ans. The property of beating metal into sheets is called malleability.
Q.11 Define corrosion.
Ans. Eating away of metal by air, water or any other substances around it is called corrosion.
Q.12 Define the term alloy.
Ans. The homogenous mixture of two or more two metals or non-metals is known as an alloy.
Q.13 What do you understand by the term refining of metals?
Ans. The process of purification of impure metals obtained during extraction is known as the refining of metals.
Q.14 What are the constituents of bronze?
Ans. Copper and Tin are the constituents of bronze.
Q.15 Name the components of stainless steel.
Ans. Iron, chromium and nickel are components of stainless steel.
Two Marks Q-Ans
Q.16 Name the general steps involved in the metallurgy of a metal.
Ans. (i) Crushing of ore (ii) Concentration of ore
(iii) Reduction (iv) Refining of metal.
Q.17 What would you observe when a strip of zinc is dipped in the solution of copper sulphate?
Ans. Zinc replaces copper with copper sulphate because the reactivity of zinc is higher than copper.
Zn(s) + CuSO4 (aq) ---------- ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu(s)
Q.18 Name the various processes used for refining metals.
Ans. The various processes used for refining metals are:
(i) Liquation (ii) Distillation (iii) Electrolytic refining
Q.19 How does electroplating prevent metals from rusting?
Ans. Metals are protected from rusting by coating them with a layer of tin or chromium metals which are resistant to rusting.
Q.20 Why is tincture iodine applied to wounds?
Ans. Tincture iodine is a solution of iodine in alcohol and it has antiseptic properties.
Find pdf for Important questions for CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter -4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals






Related Links
- Important Questions for Chapter -1 Crop Production and Management
- Important Questions for Chapter-2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- Important Questions for Chapter -3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- Important Questions for Chapter-4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- Important Questions for Chapter-5 Coal and Petroleum
- Important Questions for Chapter -6 Combustion and Flame
- Important Questions for Chapter -7 Conservation of Plants and Animals
- Important Questions for Chapter-8 Cell -Structure and Functions
- Important Questions for Chapter -9 Reproduction in Animals
- Important Questions for Chapter -10 Reaching The Age of Adolescence
- Important Questions for Chapter -11 Force and Pressure
- Important Questions for Chapter -12 Friction
- Important Questions for Chapter -13 Sound
- Important Questions for Chapter -14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- Important Questions for Chapter -15 Some Natural Phenomena